Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Uploaded by
api-297071461Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- DNA EssayDocument1 pageDNA EssaymartaNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONDocument56 pagesDNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONAmari JeonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument1 pageDNA StructureparaxNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument20 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1ngubobomikaziNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument25 pagesDna Code of Liferaym6270No ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument2 pagesStructure of DNAGuilbert ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Dna 120505163257 Phpapp02Document12 pagesDna 120505163257 Phpapp02Toni Tabi SeunghyunNo ratings yet
- GenBio EssayDocument2 pagesGenBio EssayPrincess Gracel CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA NOTESDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DNA Structure...Document8 pagesIntroduction To DNA Structure...Bhuvan S RamaniNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1survey1hloboNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument1 pageStructure of DNAvuminhtut66No ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Document16 pagesScience-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Azhell VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument2 pagesWhat Is DNAElweelee ElainNo ratings yet
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesStructure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsVignesh Reddy100% (1)
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- Dna SystemDocument2 pagesDna Systemmuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18Document18 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18ADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNADocument20 pagesBiotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNAKimberly Esmelo100% (1)
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Digi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishDocument1 pageDigi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishasdfNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsayesheedattaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocument63 pagesTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeNo ratings yet
- DNA MetalcomplexDocument25 pagesDNA MetalcomplexclrichemNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material - Dna and RnaDocument32 pagesGenetic Material - Dna and Rnaapi-217439283No ratings yet
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Document5 pagesWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Histology - REspiratory SystemDocument5 pagesHistology - REspiratory SystemNusrat HafeezNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument1 pageDNA and RNABea Angela CabajarNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenGan Kah KhengNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument6 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNo ratings yet
- L2 CytoDocument16 pagesL2 CytoDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- What Do You Need To KnowDocument6 pagesWhat Do You Need To Knowrecquelle danoNo ratings yet
- BIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019Document119 pagesBIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019JOHN MVULA IINo ratings yet
- What Is DNA?: Learn MoreDocument2 pagesWhat Is DNA?: Learn Morenikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de ElyDocument8 pagesTrabajo de ElyJose luis Arbildo ahuanariNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument50 pagesDNA StructureAngelo LucindoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- DNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDoctor Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesBiomoleculesrajan.11proNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IDocument25 pagesHDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Study Notes - Fall 2018Document10 pagesNucleic Acid Study Notes - Fall 2018ReggieNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bDocument2 pagesCytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- 3 Parts of A NucleotideDocument2 pages3 Parts of A NucleotideGermaeGonzalesNo ratings yet
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Uploaded by
api-297071461Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Is
Uploaded by
api-297071461Copyright:
Available Formats
Damontae Hill
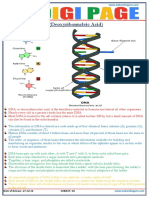
DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as
the main constituent of chromosomes. DNA is the carrier of genetic information. It is made up of
molecules called nucleotides, each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group and a
nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and
cytosine (C). The order of these bases is what determines DNA's instructions, or genetic code
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce. To
carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used
to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.
Each DNA sequence that contains instructions to make a protein is known as a gene.
Conclusion questions
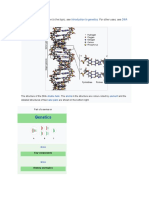
Purines and Pyrimidines are nitrogenous bases that make up the two different kinds of
nucleotides bases in DNA and RNA. The two-carbon nitrogen ring bases (adenine and
guanine) are purines, while the one-carbon nitrogen ring bases (thymine and cytosine) are
pyrimidines.
Bonding between purines and pyrimidines is very unique and specific. Not only can a purine
not bond with anything but a pyrimidine, but specific purines have to bond with specific
pyrimidines. This is because the structure of each is such that it can only bond with the
corresponding one.
Yes, because each stand is specific for instance a purine can only bond with a pyrimidine.
The structure of each is such that it can only bond with the corresponding one.
The model I compared were very similar but not the same. Multiple strands of (A,T) and (G,C)
were in different places. These different sequences of bases encode the information that
determines a human's traits.
You might also like
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- DNA EssayDocument1 pageDNA EssaymartaNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONDocument56 pagesDNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONAmari JeonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument1 pageDNA StructureparaxNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument20 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1ngubobomikaziNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument25 pagesDna Code of Liferaym6270No ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument2 pagesStructure of DNAGuilbert ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Dna 120505163257 Phpapp02Document12 pagesDna 120505163257 Phpapp02Toni Tabi SeunghyunNo ratings yet
- GenBio EssayDocument2 pagesGenBio EssayPrincess Gracel CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA NOTESDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DNA Structure...Document8 pagesIntroduction To DNA Structure...Bhuvan S RamaniNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1survey1hloboNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument1 pageStructure of DNAvuminhtut66No ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Document16 pagesScience-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Azhell VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument2 pagesWhat Is DNAElweelee ElainNo ratings yet
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesStructure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsVignesh Reddy100% (1)
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- Dna SystemDocument2 pagesDna Systemmuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18Document18 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18ADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNADocument20 pagesBiotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNAKimberly Esmelo100% (1)
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Digi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishDocument1 pageDigi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishasdfNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsayesheedattaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocument63 pagesTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeNo ratings yet
- DNA MetalcomplexDocument25 pagesDNA MetalcomplexclrichemNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material - Dna and RnaDocument32 pagesGenetic Material - Dna and Rnaapi-217439283No ratings yet
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Document5 pagesWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Histology - REspiratory SystemDocument5 pagesHistology - REspiratory SystemNusrat HafeezNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument1 pageDNA and RNABea Angela CabajarNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenGan Kah KhengNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument6 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNo ratings yet
- L2 CytoDocument16 pagesL2 CytoDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- What Do You Need To KnowDocument6 pagesWhat Do You Need To Knowrecquelle danoNo ratings yet
- BIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019Document119 pagesBIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019JOHN MVULA IINo ratings yet
- What Is DNA?: Learn MoreDocument2 pagesWhat Is DNA?: Learn Morenikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de ElyDocument8 pagesTrabajo de ElyJose luis Arbildo ahuanariNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument50 pagesDNA StructureAngelo LucindoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- DNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDoctor Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesBiomoleculesrajan.11proNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IDocument25 pagesHDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Study Notes - Fall 2018Document10 pagesNucleic Acid Study Notes - Fall 2018ReggieNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bDocument2 pagesCytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- 3 Parts of A NucleotideDocument2 pages3 Parts of A NucleotideGermaeGonzalesNo ratings yet