Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Uploaded by
William CiferCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRemedios Bandong100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- GI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseDocument4 pagesGI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseNerissa Neri NatataNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DMDocument8 pagesDrug Study DMJana Ross Serranilla100% (2)
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of AmoxicillinDocument4 pagesSide Effects of AmoxicillinAphro DhiteNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument44 pagesDrug StudyLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameDocument12 pagesMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127No ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuDocument9 pagesDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Losartan PotassiumDocument3 pagesLosartan Potassiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument16 pagesDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Fosinopril SodiumDocument3 pagesFosinopril Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 pagesDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument4 pagesFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study (AFP)Document10 pagesDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 pagesDrusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Pharm ExamDocument293 pagesPharm ExamTrish HồNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- ValdecoxibDocument3 pagesValdecoxibapi-3797941No ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Tolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideDocument4 pagesTolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideALFATH REFYANUSNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- After Nursing Interventions, Patient Demonstrates Enhanced Body Image and Self-EsteemDocument1 pageAfter Nursing Interventions, Patient Demonstrates Enhanced Body Image and Self-EsteemWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
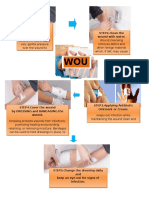
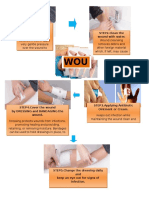
- First Aid For WoundDocument1 pageFirst Aid For WoundWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Strength, AttitudeDocument4 pagesKnowledge, Strength, AttitudeWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- FNCP PrioDocument5 pagesFNCP PrioWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Types of WoundsDocument4 pagesTypes of WoundsWilliam Cifer0% (1)
- WOU ND: STEP1.Control The Bleeding. STEP2.Clean The Wound With WaterDocument1 pageWOU ND: STEP1.Control The Bleeding. STEP2.Clean The Wound With WaterWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- ECG QuestionsDocument4 pagesECG QuestionsWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- ECG QuestionsDocument4 pagesECG QuestionsWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Chicken Empanada Recipe...............Document2 pagesChicken Empanada Recipe...............William CiferNo ratings yet
- 8 SoupDocument60 pages8 SoupWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Emergency Action Plan 05Document33 pagesEmergency Action Plan 05William CiferNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoryDocument13 pagesNursing TheoryWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics PaperDocument14 pagesCode of Ethics PaperWilliam Cifer100% (2)
- The Tripod FractureDocument2 pagesThe Tripod FractureWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- FCP ReviewerDocument4 pagesFCP ReviewerWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- HoR ReviewerDocument6 pagesHoR ReviewerWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument2 pagesCULTUREWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Uploaded by
William CiferOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Clindamycin (: Drug Class
Uploaded by
William CiferCopyright:
Available Formats
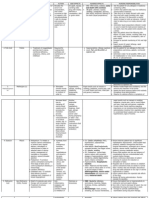
CLINDAMYCIN
(Cleocin)
Drug class
Lincosamide antibiotic
Pregnancy Category B
Therapeutic actions
Nursing considerations
Assessment
Inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria,
causing cell death.
History: Allergy to clindamycin, history of asthma or
other allergies, allergy to tartrazine (in 75- and 150mg capsules); hepatic or renal dysfunction; lactation;
history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis;
history of antibiotic associated colitis
Physical: Site of infection or acne; skin color,
lesions; BP; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds,
output, liver evaluation; complete blood count, renal
and liver function tests
Indications
Serious infections caused by susceptible strains
of
anaerobes,
streptococci,
staphylococci,
pneumococci; reserve use for penicillin-allergic
patients or when penicillin is inappropriate; less
toxic antibiotics (erythromycin) should be
considered
Contraindications
Contraindicated with allergy to clindamycin,
history of asthma or other
allergies, tartrazine (in 75- and 150-mg
capsules); hepatic or renal dysfunction;
lactation.
Side effects
Local: Pain following injection, induration and
sterile abscess after IM injection,
thrombophlebitis after IV use
CV: Hypotension, cardiac arrest (with rapid IV
infusion)
GI: Severe colitis, including pseudomembranous
colitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal
pain, esophagitis, anorexia, jaundice, liver
function changes
Hematologic: Neutropenia, leukopenia,
agranulocytosis, eosinophilia
Hypersensitivity: Rashes, urticaria to
anaphylactoid reactions
Interventions
Culture infection before therapy.
Administer oral drug with a full glass of water or with
food to prevent esophageal irritation.
Do not give IM injections of more than 600 mg; inject
deep into large muscle to avoid serious problems.
Do not use for minor bacterial or viral infections.
Monitor renal and liver function tests, and blood
counts with prolonged therapy.
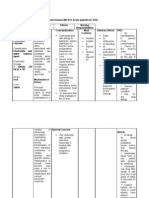
OMEPRAZOLE (Losec,Prilosec)
Drug class
Gastrointestinal agent; proton pump inhibitor
Pregnancy Category C
Therapeutic effects
Suppresses gastric acid secretion relieving
gastrointestinal distress and promoting ulcer
healing.
Report severe diarrhea; drug may need to be
discontinued.
FUROSEMIDE
Indications
Duodenal and gastric ulcer. Gastroesophageal reflux
disease including severe erosive esophagitis (4 to 8
wk treatment). Long-term treatment of pathologic
hypersecretory conditions such as Zollinger-Ellison
syndrome, multiple endocrine adenomas, and
systemic
mastocytosis.
In
combination
with
clarithromycin to treat duodenal ulcers associated
with Helicobacter pylori.
Drug class
Long-term use for gastroesophageal reflux disease,
duodenal ulcers.
Side effects
CNS:Headache, dizziness, fatigue.
GI:Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, mild transient
increases in liver function tests.
Urogenital:Hematuria, proteinuria.
Skin:Rash
Nursing implications
Assessment & Drug Effects
Lab tests: Monitor urinalysis for hematuria and
proteinuria. Periodic liver function tests with
prolonged use.
Patient & Family Education
Report any changes in urinary elimination such as
pain or discomfort associated with urination, or
blood in urine.
Loop diuretic
Pregnancy Category C
Therapeutic effects
Contraindications
(Lasix)
Furosemide inhibits reabsorption of Na and
chloride mainly in the medullary portion of the
ascending Loop of Henle. Excretion of potassium
and ammonia is also increased while uric acid
excretion is reduced. It increases plasma-renin
levels and secondary hyperaldosteronism may
result. Furosemide reduces BP in hypertensives
as well as in normotensives. It also reduces
pulmonary oedema before diuresis has set in.
Indications
Oral, IV: Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis,
renal disease
IV: Acute pulmonary edema
Oral: Hypertension
Contraindications
Severe sodium and water depletion, hypersensitivity
to sulphonamides and furosemide, hypokalaemia,
hyponatraemia, precomatose states associated with
liver cirrhosis, anuria or renal failure.
Addisons disease.
Side effects
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Rashes, photosensitivity, nausea, diarrhoea,
blurred vision, dizziness, headache,
hypotension. Bone marrow depression (rare),
hepatic dysfunction.
Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, ototoxicity.
Potentially Fatal: Rarely, sudden death and
cardiac arrest. Hypokalaemia and magnesium
depletion can cause cardiac arrhythmias.
Nursing implications
Assessment
History: Allergy to furosemide, sulfonamides,
tartrazine; electrolyte depletion anuria, severe renal
failure; hepatic coma; SLE; gout; diabetes mellitus;
lactation, pregnancy
Physical: Skin color, lesions, edema; orientation,
reflexes, hearing; pulses, baseline ECG, BP,
orthostatic BP, perfusion; R, pattern, adventitious
sounds; liver evaluation, bowel sounds; urinary
output patterns; CBC, serum electrolytes (including
calcium), blood sugar, LFTs, renal function tests, uric
acid, urinalysis, weight
Teaching points
Record intermittent therapy on a calendar or dated
envelopes. When possible, take the drug early so
increased urination will not disturb sleep. Take with
food or meals to prevent GI upset.
Weigh yourself on a regular basis, at the same time
and in the same clothing, and record the weight on
your calendar.
Blood glucose levels may become temporarily
elevated in patients with diabetes after starting this
drug.
You may experience these side effects: Increased
volume and frequency of urination; dizziness, feeling
faint on arising, drowsiness (avoid rapid position
changes; hazardous activities, like driving; and
consumption of alcohol); sensitivity to sunlight (use
sunglasses, wear protective clothing, or use a
sunscreen); increased thirst (suck on sugarless
lozenges; use frequent mouth care); loss of body
potassium (a potassium-rich diet or potassium
supplement will be needed).
Report loss or gain of more than 3 pounds in 1 day,
swelling in your ankles or fingers, unusual bleeding
or bruising, dizziness, trembling, numbness, fatigue,
muscle weakness or cramps.
Ampicillin Sulbactam (Unasyn)
Drug class
antibacterial
Pregnancy Category: B
Therapeutic effects
Bactericidal action against sensitive organisms;
inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing
cell death.
Indications
Treatment of skin and skin structure, intraabdominal, and gynecologic infections caused by
susceptible microorganisms.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to penicillins.
Side effects
Dermatologic: Rash (less than 2%); erythema
multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, urticaria.
GI: Diarrhea (3%); black, hairy tongue; Clostridium
difficile associated diarrhea; enterocolitis; gastritis;
pseudomembranous colitis; stomatitis.
Genitourinary: Increased BUN and creatinine;
presence of RBCs and hyaline casts in urine.
Hematologic: Agranulocytosis; decreased Hct, Hgb,
lymphocytes, neutrophils, RBC, platelets, and WBC;
increased basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes,
monocytes, and platelets; positive direct Coombs
tests.
Hypersensitivity:
Hypersensitivity
(anaphylactic)
reactions (sometimes fatal).
Local: Pain at IM injection site (16%); pain at IV
injection site, thrombophlebitis at injection site (3%).
Metabolic: Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase,
ALT, AST, and LDH; reduced serum albumin and total
proteins.
History: Allergies to penicillins, cephalosporins, or
other allergens; renal disorders; lactation
Physical: Culture infected area; skin color, lesion; R,
adventitious sounds; bowel sounds; CBC, LFTs, renal
function tests, serum electrolytes, Hct, urinalysis
Take this drug around-the-clock.
Take the full course of therapy; do not stop taking
the drug if you feel better.
This antibiotic is specific to your problem and should
not be used to self-treat other infections.
You may experience these side effects: Nausea,
vomiting, GI upset (eat frequent small meals),
diarrhea.
Report pain or discomfort at sites, unusual bleeding
or bruising, mouth sores, rash, hives, fever, itching,
severe diarrhea, difficulty breathing.
D5050
Drug class
Rapidly increases blood glucose levels
Transient osmotic diuretic
Indications
Documented hypoglycemia
Seizures of unknown etiology
Cerebral/meningeal edema related to eclampsia
No significant contraindications in the emergency
setting
Side effects
Pain, phlebitis at injection site
Hyperglycemia and glycosuria
Fluid overload
Special Considerations
Teaching points
Therapeutic effects
Assessment
Caloric Agent
Contraindications
Nursing implications
Rapid rates of administration predisposes the patient
to pain and may cause phlebitis if aperipheral vein is
used; to minimize this effect administer slowly
Excessive IV administration may cause fluid
overload, water intoxication, +/or CHF
D50W and Thiamine 100 mg IV (mini bag or IVP)
should be given together when alcoholism or
malnutrition are suspected
CALCIUM CARBONATE
Drug class
Electrolyte replacement
Supplements
Antacid
Therapeutic effects
Essential for nervous, muscular, and skeletal
systems. Maintain cell membrane and capillary
permeability. Act as an activator in the
transmission of nerve impulses and contraction
of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscles. It is
essential for bone formation and blood
coagulation. It is also used a replacement of
calcium in deficiency states. It controls of
hyperphosphatemia in end-stage renal disease
without promoting aluminum absorption.
Indications
Hypercalcemia increases the risk of digoxin
toxicity. Chronic use with antacids in renal
insufficiency may lead to milk-alkali syndrome.
Ingestion by mouth may decrease the absorption
of
orally
administered
tetracyclines,
fluoroquinolones, phenytoin, and iron salts.
Excessive amounts may decrease the effects of
calcium channel blockers, atenolol. Concurrent
use with diuretics may result in hypercalcemia.
ATORVASTATIN
CNS: syncope, tingling
CV: cardiac arrest, arrythmias, bradycardia
GI: constipation, nausea, vomting
GU: calculi, hypercalciuruia
Local: phlebitis (IV only)
Monitor VS especially BP and PR
Obtain ECG result.
Dyslipidaemic Agent
Therapeutic effects
Atorvastatin competitively inhibits HMG-CoA
reductase, the enzyme that catalyses the
conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid. This
results in the induction of the LDL receptors,
leading to lowered LDL-cholesterol
concentration.
Indications
Reduction of risk of stroke and heart attack in
type 2 diabetes patients without evidence of
heart disease but with other CV risk factors, and
revascularization procedures in patients without
evidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) but
with multiple risk factors other than diabetes
(eg, smoking, HTN, low HDL-C, family history of
early CHD) Patients with CHD, to reduce risks of
MI, revascularization procedures, hospitalization
for CHF, and angina
Contraindications
Nursing implications
(Lipitor)
Drug class
Side effects
Asses for heartburn, indigestion, abdominal pain.
Monitor serum calcium before treatment.
Assess for nausea and vomiting, anorexia, thirst,
severe constipation
Hypersensitivity, active liver disease or unexplained
persistent elevations of serum transaminase,
porphyria, pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects
Headache, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,
anorexia,
xerostomia,
angioedema,
myalgia,
rash/pruritus, alopecia, allergy, infection, chest pain
Nursing implications
Contraindications
Stress that atorvastatin is an adjunct to not a
substitute for low-cholesterol diet
Tell patient to take drug at the same time each
day to maintain its effects
Instruct patient to take a missed dose as soon
as possible. If its almost time for his next dose,
he should skip the missed dose.
Advise patient to notify prescriber immediately if
he develops unexplained muscle pain,
tenderness, or weakness, especially if
accompanied by fatigue or fever
(Lanoxin)
Drug class
Cardiac glycoside,
Cardiotonic
Pregnancy Category C
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside which has positive
inotropic activity characterized by an increase in
the force of myocardial contraction. It also
reduces the conductivity of the heart through
the atrioventricular (AV) node. Digoxin also
exerts direct action on vascular smooth muscle
and indirect effects mediated primarily by the
autonomic nervous system and an increase in
vagal activity.
Indications
Extra beats, anorexia, nausea and vomiting.
Diarrhea in elderly, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness,
restlessness, nervousness, agitation and amnesia,
visual disturbances, gynecomastia, local irritation
(IM/SC inj), rapid IV admin may lead to
vasoconstriction and transient hypertension.
Potentially Fatal: Cardiac arrhythmias in combination
with heart block.
Nursing implications
Assessment
Therapeutic effects
Digitalis toxicity, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation,
obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Arrhythmias due to accessory pathways (e.g. WolffParkinson-White syndrome).
Side effects
DIGOXIN
CHF
Atrial fibrillation
History: Allergy to digitalis preparations, ventricular
tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, heart block, sick
sinus syndrome, IHSS, acute MI, renal insufficiency,
decreased K+, decreased Mg2+ increased Ca2+,
pregnancy, lactation
Physical: Weight; orientation, affect, reflexes, vision;
P, BP, baseline ECG, cardiac auscultation, peripheral
pulses, peripheral perfusion, edema; R, adventitious
sounds; abdominal percussion, bowel sounds, liver
evaluation; urinary output; electrolyte levels, LFTs,
renal function tests
Teaching points
Do not stop taking this drug without notifying
your health care provider.
Take pulse rate before administering.
Do not start taking any prescription or over-thecounter products without talking to your health
care provider. Some combinations may increase
the risk of digoxin toxicity and may put you at
risk of adverse reactions.
Report unusually slow pulse, irregular pulse, rapid
weight gain, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea,
vomiting, blurred or yellow vision, unusual
tiredness and weakness, swelling of the ankles,
legs or fingers, difficulty breathing.
ACETYLCYSTEINE
(Fluimucil)
Side effects
Drug class
CNS: fever, drowsiness, abnormal thinking, gait
disturbances
CV: tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension,
flushing, chest tightness
EENT: rhinorrhea, ear pain, eye pain, pharyngitis,
throat tightness
GI: stomatitis, nausea, vomiting
Respiratory: rhonchi, bronchospasm, cough,
dyspnea
Skin: rash, clamminess, diaphoresis, pruritus,
urticaria
Other: angioedema, chills, anaphylactoid
reaction
Mucolytic
Therapeutic effects
Mucolytic that reduces the viscosity of
pulmonary secretions by splitting disulfide
linkages
between
mucoprotein
molecular
complexes. Also, restores liver stores of
glutathione to treat acetaminophen toxicity.
Indications
Treatment of respiratory affections characterized
by thick and viscous hypersecretions: acute
bronchitis,
chronic
bronchitis
and
its
exacerbations;
pulmonary
emphysema,
mucoviscidosis and bronchieactasis.
Nursing implications
Assessment & Drug Effects
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to acetylcesteine. As
Acetylcysteine (Fluimucil) granules and tablets
contain aspartame, it is contraindicated in
patients suffering from phenylketonuria.
During IV infusion, carefully monitor for fluid
overload and signs of hyponatremia (i.e.,
changes in mental status).
Monitor for S&S of aspiration of excess
secretions,
and
for
bronchospasm
(unpredictable); withhold drug and notify
physician immediately if either occurs.
Lab tests: Monitor ABGs, pulmonary functions
and pulse oximetry as indicated.
Have suction apparatus immediately available.
Increased volume of respiratory tract fluid may
be liberated; suction or endotracheal aspiration
may be necessary to establish and maintain an
open airway. Older adults and debilitated
patients are particularly at risk.
Nausea and vomiting may occur, particularly
when face mask is used, due to unpleasant odor
of drug and excess volume of liquefied bronchial
secretions.
Patient & Family Education
Contraindications
Report difficulty with clearing the airway or any
other respiratory distress.
Report nausea, as an antiemetic may be
indicated.
Note: Unpleasant odor of inhaled drug becomes
less noticeable with continued use.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug without
consulting physician.
Side effects
(Ventolin)
Drug class
Therapeutic effects
It relieves nasal congestion and reversible
bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles
of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal
congestion and bronchospasm is made possible
by the following mechanism that takes place
when Salbutamol is administered.
Indications
Treatment & prevention of bronchial asthma,
bronchitis, emphysema w/ associated reversible
airway obstruction.
Nervousness, Restlessness, Tremor, Headache,
Insomnia, Chest pain, Palpitations, Angina,
Arrhythmias,
Hypertension,
Nausea
and
vomiting, Hyperglycemia, Hypokalemia
Nursing implications
SALBUTAMOL
Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines
Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons
Auscultate lungs for presence of adventitious
breath sounds that may signal pulmonary
edema, airway resistance or bronchospasm.
Inspect clients nail bed and oral mucosa for
pallor.
Place client in position of comfort to facilitate
optimum rest and sleep.
Assess pulse for rhythm.
Provide oral care or let patient gurgle after
inhalation to get rid of the unpleasant aftertaste
of the inhalation.
You might also like
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRemedios Bandong100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- GI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseDocument4 pagesGI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseNerissa Neri NatataNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DMDocument8 pagesDrug Study DMJana Ross Serranilla100% (2)
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of AmoxicillinDocument4 pagesSide Effects of AmoxicillinAphro DhiteNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument44 pagesDrug StudyLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameDocument12 pagesMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127No ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuDocument9 pagesDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Losartan PotassiumDocument3 pagesLosartan Potassiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument16 pagesDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Fosinopril SodiumDocument3 pagesFosinopril Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 pagesDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument4 pagesFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study (AFP)Document10 pagesDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 pagesDrusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Pharm ExamDocument293 pagesPharm ExamTrish HồNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- ValdecoxibDocument3 pagesValdecoxibapi-3797941No ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Tolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideDocument4 pagesTolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideALFATH REFYANUSNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- After Nursing Interventions, Patient Demonstrates Enhanced Body Image and Self-EsteemDocument1 pageAfter Nursing Interventions, Patient Demonstrates Enhanced Body Image and Self-EsteemWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Definition of A ?: PlanetWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- First Aid For WoundDocument1 pageFirst Aid For WoundWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Strength, AttitudeDocument4 pagesKnowledge, Strength, AttitudeWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- FNCP PrioDocument5 pagesFNCP PrioWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Types of WoundsDocument4 pagesTypes of WoundsWilliam Cifer0% (1)
- WOU ND: STEP1.Control The Bleeding. STEP2.Clean The Wound With WaterDocument1 pageWOU ND: STEP1.Control The Bleeding. STEP2.Clean The Wound With WaterWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- ECG QuestionsDocument4 pagesECG QuestionsWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- ECG QuestionsDocument4 pagesECG QuestionsWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Chicken Empanada Recipe...............Document2 pagesChicken Empanada Recipe...............William CiferNo ratings yet
- 8 SoupDocument60 pages8 SoupWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Emergency Action Plan 05Document33 pagesEmergency Action Plan 05William CiferNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoryDocument13 pagesNursing TheoryWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics PaperDocument14 pagesCode of Ethics PaperWilliam Cifer100% (2)
- The Tripod FractureDocument2 pagesThe Tripod FractureWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- FCP ReviewerDocument4 pagesFCP ReviewerWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- HoR ReviewerDocument6 pagesHoR ReviewerWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument2 pagesCULTUREWilliam CiferNo ratings yet