Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis of Visual Texts
Analysis of Visual Texts
Uploaded by
api-299536319Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Visual Texts
Analysis of Visual Texts
Uploaded by
api-299536319Copyright:
Available Formats
ANALYSIS OF VISUAL TEXTS
Creating and analysing meaning using visual
techniques
HOW MUCH DO WE RELY ON
VISUALS?
Scientists agree that at least 75% of
what we learn is derived visually
Sometimes we see more than is there
to see
Have a look at the next two slides to
see what you see and see if it makes
you feel like youre all at sea
THERE ARE MANY FACTORS IN CREATING OR
ANALYSING VISUAL TEXTS AND FEATURES
Symbolism
Colour
Lighting
Proportion/Size
Foreground/Backgro
und
Hyperbole
Lettering/Font
Layout/Position
Body Language
Clothing
Shot Size
SYMBOLISM
The use of signs to carry a message in
a simple picture form. These can be
people used to symbolise particular
parts of society or objects that
symbolise characteristics in a
character.
DESCRIBE WHAT THESE IMAGES MEAN TO YOU
SYMBOLISM
When we analyse images for their symbolic
meaning we dont just identify what the
symbol represents we need to go deeper and
discuss the effect of the symbol on the viewer.
For example the swastika represents Nazi
Germany during WW11. But arguably the
effect of the symbol is to:
Bring to mind the Jewish Holocaust and its horrors.
Represent evil incarnate
Serve as a warning to learn from the past
Remind us that evil regimes must be challenged
COLOUR
Colour can be used to attract attention
to a certain point in a static image or to
create a mood.
It can also be used to represent feelings
or emotions.
COLOUR
Black - Death rebellion, strength and evil. Associated with
the supernatural, it can also suggest inner strength and
determination, as well as power and formality.
White - Purity, chastity and cleanliness.
Black & White - Nostalgia, seriousness, truth, and
detachment.
Brown - Credibilty, stability, and neutrality.
Orange - Warmth and strength of personality. Associated
with Autumn, it also has a broad appeal.
COLOUR
Blue - Peace, tranquility, truth, dignity, power, melancholy, coolness,
heaviness. Regarded as being therapeutic.
Yellow - Happiness, cheerfulness. Can denote caution, decay and
sickness.
Red - Warmth, urgency, passion, heat, blood, excitement, danger and
hostility. Used an accent colour, it can promote expectation and quick
decision-making.
Green - Growth, fertility, health, cheerfulness, vegetation and money.
Signifies life, new growth, energy and faith.
Grey - Cool detachment, bleakness, and lack of intensity.
Purple - Wealth, royalty, sophistication and intelligence. Also the
colour of passion and love.
LIGHTING
Related to colour.
How has a subject been lit?
Is the lighting bright or dim?
Is the subject lit from above
or below?
What is the effect?
Shadows are created by
lighting, which can help
create certain moods, such
as fear.
DISCUSS THE EFFECTS OF LIGHTING ON THESE
IMAGES
PROPORTION / SIZE
Proportion can be used to show
relationships between objects,
by showing one to be larger
than the other or more
dominant than the others.
The size of an object in a
picture often shows how
important that object is
compared to the other things in
the scene.
Larger objects are usually the
most important.
FOREGROUND / BACKGROUND
The part of the scene or picture that is or
seems to be nearest to the one looking at it
is said to be the foreground of the picture.
Objects in the foreground appear bigger
than those in the background.
HYPERBOLE
Deliberate
exaggeration of
particular parts of
the images, or parts
within the image.
For example,
deliberately making
Superman's arms
huge, to show that
he is particularly
strong.
DISCUSS THE EFFECT OF THESE EXAGGERATIONS
LETTERING / FONT
The style that the words
have been written in.
Look at the font, the
colour, the size, the
layout and any variety
within these (not the
actual words
themselves).
SAFETY FIRST
DANGER
HELP DESK
BEWARE
LAYOUT / POSITION
The way components are put together on
the page is called the layout of a static
image.
Usually there is a dominant subject that
takes up the majority of space on the page.
The position of an object in a picture shows
its importance - objects in the foreground
are usually most important.
Objects in the centre a usually more
important than objects to the side.
LAYOUT / POSITION
An example with the important image in the fore
Notice also how the slide is balanced
LAYOUT / POSITION
Which is the dominant image/character?
Notice also how the slide remains balanced
LAYOUT / POSITION
Sometimes images can be unbalanced
but still be effective but you have to
be careful
LAYOUT / POSITION
Dont let your visual presentations get
too busy you lose the impact on the
viewer
LAYOUT / POSITION
Consider the Rule of Thirds which stems
from the theory that the human eye
naturally gravitates to intersection points
that occur when an image is split into
thirds.
In the rule of thirds, photos are divided into thirds with two
imaginary lines vertically and two lines horizontally making
three columns, three rows, and nine sections in the images.
Important compositional elements and leading lines are
placed on or near the imaginary lines and where the lines
intersect.
RULE OF THIRDS
BODY LANGUAGE
People in
images/photographs can
communicate their feelings
through body language.
Body language refers to the way we
use our eyes, our facial expressions,
BODY LANGUAGE
What are these people communicating
with their body language?
BODY LANGUAGE
What are these people communicating
with their body language?
BODY LANGUAGE
What is being communicated by these?
BODY LANGUAGE
What is being communicated whats
happening?
CLOTHING
Clothing and hairstyles often symbolise people's
attitude toward society and their position in it.
What sort of people wear these
clothes?
SHOT / SIZE
Different types of shots
highlight different aspects.
A distant view will
emphasise the setting,
A close-up can concentrate
on specific features such as
a falling tear to emphasise
emotion.
Or you can use a composite
WHAT IS EMPHASIZED IN THESE
SHOTS?
HOW DO WE USE ALL THIS IN CREATING IMAGERY?
We need to do more than just point out
what weve created.
We need to explain the intended or
expected effect on the viewer.
We need to:
highlight why we have used specific images;
why we have laid out the poster, brochure,
pamphlet as we have;
what reaction in the viewer we hoped to
achieve.
AN EXAMPLE LOOK AT THE POSTER BELOW
Write an analysis
of the poster
Comment on as
many features as
you can
In detail
2 minutes!
THIS IS THE LIST OF FACTORS TO
CONSIDER
Symbolism
Colour
Lighting
Proportion/Size
Foreground/Backgroun
d
Hyperbole
Lettering/Font
Layout/Position
Body Language
Clothing
Shot Size
AN EXAMPLE LOOK AT THE POSTER BELOW
Write an analysis
of the poster
Comment on as
many features as
you can
In detail
2 minutes!
THIS IS THE LIST OF FACTORS TO
CONSIDER
Symbolism
Colour
Lighting
Proportion/Size
Foreground/Backgroun
d
Hyperbole
Lettering/Font
Layout/Position
Body Language
Clothing
Shot Size
AN EXAMPLE LOOK AT THE POSTER BELOW
Write an analysis of this poster - 2 minutes!
THIS IS THE LIST OF FACTORS TO
CONSIDER
Symbolism
Colour
Lighting
Proportion/Size
Foreground/Backgroun
d
Hyperbole
Lettering/Font
Layout/Position
Body Language
Clothing
Shot Size
KEEP A LOOKOUT FOR THAT KILLER
IMAGE
You might also like
- Cixous - Portrait of DoraDocument21 pagesCixous - Portrait of DoraYoyoli PerezNo ratings yet
- Philippine Traditional Dance ObtlDocument12 pagesPhilippine Traditional Dance ObtlHilarion Vidal Olimpo100% (5)
- The Everyday Hero PlaybookDocument109 pagesThe Everyday Hero PlaybookCosmina David92% (13)
- Classroom Walkthrough ChecklistDocument1 pageClassroom Walkthrough ChecklistLinh Huynh0% (1)
- THE ROLE OF THE NATIVE LANGUAGE PPT SLADocument9 pagesTHE ROLE OF THE NATIVE LANGUAGE PPT SLAKristiani Simorangkir50% (2)
- Grade 9 EnglishDocument11 pagesGrade 9 EnglishEllen Grace Cepeda ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Competence For Functional SafetyDocument25 pagesCompetence For Functional SafetyRdW992049RdW100% (1)
- Language VariationDocument36 pagesLanguage Variationavid2chat100% (1)
- Oral Presentation 2 1Document34 pagesOral Presentation 2 1AdraidaNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesOral Presentation Rubricapi-377682858No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Descriptivism Vs PrescriptivismDocument15 pagesLesson 6 Descriptivism Vs PrescriptivismJude GrundyNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Consistency and ExerciseDocument3 pagesVerb Tense Consistency and ExerciseNatasha Mills100% (1)
- Course Outline Purposive Communication 2021Document3 pagesCourse Outline Purposive Communication 2021Aljo KimayongNo ratings yet
- Draft Revised Policies Standards and Guidelines For Bachelor of Science in Business AdministrationDocument29 pagesDraft Revised Policies Standards and Guidelines For Bachelor of Science in Business AdministrationKimNo ratings yet
- Integration of Culture Into ESL EFL Clas PDFDocument13 pagesIntegration of Culture Into ESL EFL Clas PDFDanilo de Oliveira100% (1)
- Grammar FinalDocument27 pagesGrammar Finalhuonglanle1230% (1)
- Bics and Calp Cup ReportDocument75 pagesBics and Calp Cup ReportAen Aux100% (1)
- Phonetics Midterm ReviewDocument65 pagesPhonetics Midterm Reviewlavievan99No ratings yet
- Style and Point of View of Narratives, Approaches ToDocument21 pagesStyle and Point of View of Narratives, Approaches ToRetno SuhermenNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument36 pagesLanguageMaya St JusteNo ratings yet
- English Language Learning and TechnologyDocument28 pagesEnglish Language Learning and TechnologyRachel Ann GarciaNo ratings yet
- Grammar BankDocument3 pagesGrammar BankVero VázquezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approach, Strategy, Method, Technique, ModelDocument8 pagesTeaching Approach, Strategy, Method, Technique, ModelSelvia 2005136191100% (1)
- World EnglishesDocument34 pagesWorld EnglishesAbu BurnNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Types of DiscourseDocument2 pagesEvaluating Types of DiscourseNelly Bells100% (1)
- English Composition and Essay WritingDocument43 pagesEnglish Composition and Essay WritingEduaro EllarmaNo ratings yet
- Formal and Informal RegisterDocument11 pagesFormal and Informal RegisterHamidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 On CommunicationDocument15 pagesLesson 1 On CommunicationLyka ElenaNo ratings yet
- World Enlishes 2Document18 pagesWorld Enlishes 2Shahirah ZafirahNo ratings yet
- Bics Vs CalpDocument2 pagesBics Vs CalpAlassfar AbdelNo ratings yet
- SocioDocument23 pagesSocioHasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Teaching Speaking: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesLesson 2: Teaching Speaking: Objectivesmaryrose condesNo ratings yet
- Literature HandoutDocument11 pagesLiterature HandoutJealyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Grammaticalization CardsDocument44 pagesGrammaticalization CardsDaniel Demski100% (1)
- Proficiency of Sophomore English Majors On The Pronunciation of The Structural Variants of "Read" Towards Improved Oral PerformanceDocument12 pagesProficiency of Sophomore English Majors On The Pronunciation of The Structural Variants of "Read" Towards Improved Oral PerformanceAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteNo ratings yet
- A Morphological Analysis of Derivational Suffixes in Short StoriesDocument17 pagesA Morphological Analysis of Derivational Suffixes in Short StoriesIzna Jamz CullenNo ratings yet
- Conversation Analysis by Group 13Document21 pagesConversation Analysis by Group 13Irvink de NaldiNo ratings yet
- History of English Language (Syllabus)Document3 pagesHistory of English Language (Syllabus)jonalyn obinaNo ratings yet
- Language Choice in Multilingual CommunitiesDocument46 pagesLanguage Choice in Multilingual CommunitiesIveth Pereira Rivera100% (1)
- Introduction To SLA in University LevelDocument12 pagesIntroduction To SLA in University LevelNilaNo ratings yet
- The Intercultural Approach To EFL Teaching and Learning - Doc EFLDocument37 pagesThe Intercultural Approach To EFL Teaching and Learning - Doc EFLAntania FieldzahNo ratings yet
- Analyzing LiteratureDocument24 pagesAnalyzing LiteratureLyrah Garcia CagayanNo ratings yet
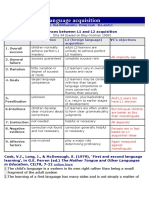
- First and Second Language AcquisitionDocument3 pagesFirst and Second Language AcquisitionHeny AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic Expressions (2nd Demo)Document3 pagesIdiomatic Expressions (2nd Demo)anthonyNo ratings yet
- SemanticsDocument36 pagesSemanticsAlfonso Cárdenas PáezNo ratings yet
- Language in Society - Syllabus 2016 PDFDocument6 pagesLanguage in Society - Syllabus 2016 PDFRyan Lala Rangga SenjayaNo ratings yet
- Gilda CorderoDocument12 pagesGilda CorderoCris TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Esp 1Document13 pagesEsp 1Jan Dave OlacoNo ratings yet
- Language Change & Language Shift: Week 7Document26 pagesLanguage Change & Language Shift: Week 7afiqahNo ratings yet
- Language, Culture and Society: Sherry Mae M. Mingo InstructorDocument31 pagesLanguage, Culture and Society: Sherry Mae M. Mingo InstructorSHERRY MAE MINGONo ratings yet
- Affective Factors in Second Language AcquisitionDocument12 pagesAffective Factors in Second Language AcquisitionAlberto AmaroNo ratings yet
- What Is Discourse AnalysisDocument7 pagesWhat Is Discourse AnalysisRo DoNo ratings yet
- Features of Connected SpeechDocument9 pagesFeatures of Connected Speechbloody777No ratings yet
- Survey of Philippine Literature in EnglishDocument26 pagesSurvey of Philippine Literature in EnglishJesalie NarteaNo ratings yet
- Processes of Word Formation - Morphology-Lane 333-2012 - Dr. ShadiaDocument27 pagesProcesses of Word Formation - Morphology-Lane 333-2012 - Dr. ShadiaDr. Shadia100% (1)
- Investigating Moroccan University Students Difficulties in Dealing With Concrete and Abstract Prepositions: The Case of The English Department in The School of Arts and Humanities, Meknes, MoroccoDocument10 pagesInvestigating Moroccan University Students Difficulties in Dealing With Concrete and Abstract Prepositions: The Case of The English Department in The School of Arts and Humanities, Meknes, MoroccoAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Session 1 Part 2 GrammarDocument40 pagesModule 1 Session 1 Part 2 GrammarMarwa AlashqarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5Raphael SamsonNo ratings yet
- Speaking Skills & Techniques of Assessing Speaking PDFDocument21 pagesSpeaking Skills & Techniques of Assessing Speaking PDFSyafiqah Sabarudin89% (9)
- The History of English: Syrile T. Mangudang Maed/EnglishDocument3 pagesThe History of English: Syrile T. Mangudang Maed/EnglishSyrile MangudangNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Students' Errors in Using Preposition IIDocument22 pagesAn Analysis of Students' Errors in Using Preposition IIAyin KatiliNo ratings yet
- Activity A Multimodality An Introduction 151210Document26 pagesActivity A Multimodality An Introduction 151210MeLanie Miranda CaraanNo ratings yet
- How to Build Self Confidence, Happiness and Health: Part I: Self Confidence Partii: Happiness Pariii: HealthFrom EverandHow to Build Self Confidence, Happiness and Health: Part I: Self Confidence Partii: Happiness Pariii: HealthNo ratings yet
- LeadingInnovationChangeArticle IJIS Praveen August16 PDFDocument11 pagesLeadingInnovationChangeArticle IJIS Praveen August16 PDFmetatah sbyNo ratings yet
- PMI ACP V4 - KnowledgeHut PDFDocument228 pagesPMI ACP V4 - KnowledgeHut PDFVikram Dogra100% (3)
- Performance Guide PDFDocument21 pagesPerformance Guide PDFodescribdNo ratings yet
- Crimsoc 2 Reviewer IIDocument38 pagesCrimsoc 2 Reviewer IIEmerson Tee100% (1)
- Mindsets:: How Beliefs Shape LearningDocument2 pagesMindsets:: How Beliefs Shape LearningHồ Thị Thùy Dung THCS&THPT U Minh Thượng - Kiên GiangNo ratings yet
- Worldview Assessment Instrument Scales - англDocument2 pagesWorldview Assessment Instrument Scales - англsvetlos33No ratings yet
- A History of On Edwin G BoringDocument21 pagesA History of On Edwin G BoringVen PopovNo ratings yet
- The Writer Also Uses Extremely Effective and Influential LanguageDocument2 pagesThe Writer Also Uses Extremely Effective and Influential LanguageDheer Bhanushali100% (2)
- Growth and Development of ChildrenDocument144 pagesGrowth and Development of ChildrenslpheyNo ratings yet
- Assessing The CurriculumDocument34 pagesAssessing The CurriculumDominic Dalton CalingNo ratings yet
- Disorganized SchizophreniaDocument11 pagesDisorganized SchizophreniaDesi Lestari NingsihNo ratings yet
- War and Human Nature - A Realist Approach - Alin G. DiaconuDocument6 pagesWar and Human Nature - A Realist Approach - Alin G. DiaconuAlin DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Developing True Personality-A Scientific ApproachDocument5 pagesDeveloping True Personality-A Scientific Approachsimeonsimon2009No ratings yet
- Major Themes in Heart of DarknessDocument3 pagesMajor Themes in Heart of DarknessM.ZubairNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Sea Change PosterDocument7 pagesLesson 3 - Sea Change Posterapi-323655794No ratings yet
- English Lesson Spelling Pre-TestDocument4 pagesEnglish Lesson Spelling Pre-Testapi-348068009No ratings yet
- I'Ll Be The Matriarch in This LifeDocument3,517 pagesI'Ll Be The Matriarch in This LifeMaria Jessa Paraguya AgangNo ratings yet
- Nanny Wisdom Chapter OneDocument29 pagesNanny Wisdom Chapter OnesusannamNo ratings yet
- Prospectus PhysiotherapyDocument21 pagesProspectus PhysiotherapyHazrat Bilal MalakandiNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers of Coaching 1Document6 pagesNew Frontiers of Coaching 1Garb PoubNo ratings yet
- The 'Erroneous-Zone' Free Life! - Potrait of A Person Who Has Eliminated Erroneous ZonesDocument10 pagesThe 'Erroneous-Zone' Free Life! - Potrait of A Person Who Has Eliminated Erroneous ZonesAim High100% (3)
- Lecture 1Document18 pagesLecture 1Atheena Leerah Agustin LucasNo ratings yet
- Budget Outlay in Research 1Document3 pagesBudget Outlay in Research 1Emcy Clarens Castillo AmorNo ratings yet
- DLL - 1st WK - Electrical Installaiton and MaintenanceDocument28 pagesDLL - 1st WK - Electrical Installaiton and Maintenancemjc100% (1)
- Farah Tahzeeb - ProjectDocument21 pagesFarah Tahzeeb - ProjectFarah JaleelNo ratings yet