Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two Types of Neutral Axis: ST ND
Two Types of Neutral Axis: ST ND
Uploaded by
ajith chandran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesThis document discusses the neutral axis and moment of resistance calculations for reinforced concrete beams. It provides:
1) Equations to calculate the depth of the neutral axis and moment of resistance based on compressive and tensile forces.
2) Descriptions of three section types - balanced, under-reinforced, and over-reinforced - including their failure mechanisms and how to calculate moment of resistance for each.
3) Guidelines that the moment of resistance for over-reinforced sections is limited to that of a balanced section, while under-reinforced sections use a smaller neutral axis depth in calculations.
Original Description:
design of singly & doubly reinforced sections
Original Title
design of beam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the neutral axis and moment of resistance calculations for reinforced concrete beams. It provides:
1) Equations to calculate the depth of the neutral axis and moment of resistance based on compressive and tensile forces.
2) Descriptions of three section types - balanced, under-reinforced, and over-reinforced - including their failure mechanisms and how to calculate moment of resistance for each.
3) Guidelines that the moment of resistance for over-reinforced sections is limited to that of a balanced section, while under-reinforced sections use a smaller neutral axis depth in calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesTwo Types of Neutral Axis: ST ND
Two Types of Neutral Axis: ST ND
Uploaded by
ajith chandranThis document discusses the neutral axis and moment of resistance calculations for reinforced concrete beams. It provides:
1) Equations to calculate the depth of the neutral axis and moment of resistance based on compressive and tensile forces.
2) Descriptions of three section types - balanced, under-reinforced, and over-reinforced - including their failure mechanisms and how to calculate moment of resistance for each.
3) Guidelines that the moment of resistance for over-reinforced sections is limited to that of a balanced section, while under-reinforced sections use a smaller neutral axis depth in calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
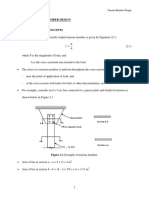
Fe250
Fe415
Fe500
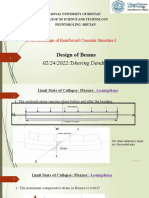
Two types of neutral axis
Xu max
0.53d
0.48d
0.46d
1. Critical NA/maxNA/limiting NA (given in table above)
(NA for a balanced section)
2. Actual NA
Xu =( 0.87*fy*Ast)/(.36*fck* b)
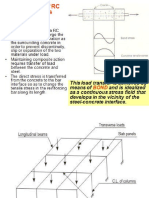
MOMENT OF RESISTANCE
1. Based on compressive forces
Mu = C*leverarm
Mu = 0.36*fck*b*Xu*(d-0.42Xu) eqn 1
2. Based on tensil forces
3. Mu = T*leverarm
Mu = 0.87*fy*Ast*(d-0.42Xu)
eqn 2
Types of sections
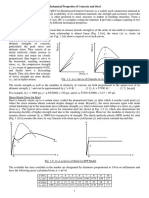
1. Balanced section
Both C & T increase in proportion and both materials fail @ the same
time (assumption)
In practice concrete fails first by crushing (primary compression failure)
and steel yields
Xu = Xu max
MR can be calculated by eqn 1 or eqn 2 with Xu max
Practically balanced section is not possible
2. Under reinforced section
Having steel less than that of balances section
Slow and gradual failure (primary tension failure)
Final collapse is by concrete
Xu < Xu max
MR can be calculated by eqn 1 or eqn 2 with Xu (since Xu is smaller
than Xu max we use a smaller value in the equation and get a small
MR value which is favourable)
3. Over reinforced section
Reinforcement greater than that of balanced section
Concrete fails (primary compression failure)
Sudden failure
Xu > Xu max
Dont design as over reinforced
MR is limited to that of balanced section
MR is calculated by eqn 1 with Xu max
(since Xu max is smaller we use it in calculation and only 1 st
equation.2nd is not used because Ast will be very large and we get a
large value of MR which will not be the true value..)
You might also like
- Solutions Manual Metal Forming MechanicsDocument5 pagesSolutions Manual Metal Forming MechanicsJoão Paulo100% (1)
- Lecture - 4 - Flexure - Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocument25 pagesLecture - 4 - Flexure - Doubly Reinforced BeamsmdaashuNo ratings yet
- AE 321 - Homework #5 Due: Monday March 11, 2019 Chapter 3 and 4: Strain and Mechanics of MaterialsDocument2 pagesAE 321 - Homework #5 Due: Monday March 11, 2019 Chapter 3 and 4: Strain and Mechanics of Materialsbob toodleNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Design of BeamsDocument41 pagesUnit-3 Design of BeamsPema ChodenNo ratings yet
- 3.lecture 3 Flexure Singly Reinforced BeamsDocument59 pages3.lecture 3 Flexure Singly Reinforced BeamsmdaashuNo ratings yet
- Limit State DesignDocument85 pagesLimit State Designkeshav1980No ratings yet
- Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument5 pagesDoubly Reinforced BeamChristineNo ratings yet
- Approved Pre Stressed Concrete Formula Sheet 2Document12 pagesApproved Pre Stressed Concrete Formula Sheet 2Adil ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 8Document15 pages8api-3696315No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Simple Stresses - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument23 pagesStrength of Materials - Simple Stresses - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen100% (1)
- Moment Curvature Relation (6-10)Document26 pagesMoment Curvature Relation (6-10)Nicholas ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 SPMDocument9 pagesTutorial 2 SPMYana JainNo ratings yet
- Lec.2 - Design of Tension Members .Document38 pagesLec.2 - Design of Tension Members .alpegambarliNo ratings yet
- Strengths 9th ChapterDocument20 pagesStrengths 9th Chapteryodahe aberaNo ratings yet
- Mallick Gupta Notes PDFDocument85 pagesMallick Gupta Notes PDFa dutta0% (2)
- Limit State Design FinalDocument53 pagesLimit State Design FinalHariom KhungarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Limit State Design and UltimateDocument85 pagesPrinciples of Limit State Design and UltimateUmar Saba50% (2)
- Lab 4 SolidDocument12 pagesLab 4 SolidSyahmi ChannelNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Stress - Strain ... : 2.1 Rectangular BeamDocument21 pages2.1 Stress - Strain ... : 2.1 Rectangular BeamiffahNo ratings yet
- مقر ةرضاحم 6 خيراتب 4 / 1 / 2021 Riveted (Bolted) JointsDocument8 pagesمقر ةرضاحم 6 خيراتب 4 / 1 / 2021 Riveted (Bolted) JointsroseNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptDocument11 pagesBasic Concept劉建宏No ratings yet
- 02 Rect 1Document28 pages02 Rect 1mengistuberhanu2015No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Simple StressesDocument6 pagesChapter One: Simple StressesAmjed AL-KAHTEEBNo ratings yet
- W14x43 To HSS6x6x1 - 2 Moment ConnDocument21 pagesW14x43 To HSS6x6x1 - 2 Moment ConnrajedmaglinteNo ratings yet
- Pcte Institute of Engineering & Technology, LudhianaDocument1 pagePcte Institute of Engineering & Technology, LudhianaSurjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- RCC Beam3Document18 pagesRCC Beam3Sudip Kumar SwainNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentabdallah amrNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Axial Force Shear Force Bending Moment Diagrams - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument28 pagesStrength of Materials - Axial Force Shear Force Bending Moment Diagrams - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenNo ratings yet
- Stress Block ParameterDocument10 pagesStress Block ParametersanjusamsonNo ratings yet
- Tension MembersDocument39 pagesTension MembersCivil EngineerNo ratings yet
- RC Design I PDFDocument48 pagesRC Design I PDFKaushal GhimireNo ratings yet
- DCS BeamDesign Lect3Document14 pagesDCS BeamDesign Lect3Rahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Turorial 1 PresentationDocument11 pagesTurorial 1 PresentationSujith DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Flexural Analysis and Design of BeamnsDocument15 pagesFlexural Analysis and Design of BeamnsAdil Javed ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Ii - 4 - 06 - 23Document48 pagesStructural Design Ii - 4 - 06 - 23qjh2wwx7smNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 SolidDocument11 pagesLab 4 SolidSyahmi ChannelNo ratings yet
- AISC Design ChecksDocument22 pagesAISC Design ChecksYogeshUndeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument37 pagesStrength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen88% (26)
- CIS221-Design of Concrete Structures: Elements Under FlexureDocument19 pagesCIS221-Design of Concrete Structures: Elements Under Flexurealaa albalahNo ratings yet
- EC2 Bending With or Without Axial ForceDocument11 pagesEC2 Bending With or Without Axial ForceselinaNo ratings yet
- 07 Moment of Inertia For (Columns)Document6 pages07 Moment of Inertia For (Columns)Syed KashifNo ratings yet
- DCS BeamDesign Lect3Document14 pagesDCS BeamDesign Lect3Saket ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Lecture NoteDocument65 pagesAddis Ababa University Lecture NoteTADY TUBE OWNER100% (9)
- Basic Engineering CalculationsDocument12 pagesBasic Engineering Calculationsrheins2000No ratings yet
- RC Design - Sec2 - Analysis of SectionDocument20 pagesRC Design - Sec2 - Analysis of Sectionمختار ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- AZ024 Lecture 7 Steel ConnectionDocument14 pagesAZ024 Lecture 7 Steel ConnectionTong Kin Lun100% (15)
- Microsoft Word - Concrete Lab Handout 2011-12Document8 pagesMicrosoft Word - Concrete Lab Handout 2011-12Yaasiin OozeerNo ratings yet
- PROJECT3Document3 pagesPROJECT3nkjm rtdtNo ratings yet
- 3.5.1 Design Beam Flexural ReinforcementDocument10 pages3.5.1 Design Beam Flexural ReinforcementKaren Esther Acuña VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Flexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMDocument12 pagesFlexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMKallem KiranmayiNo ratings yet
- Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument2 pagesDoubly Reinforced BeamBabu SundararamanNo ratings yet
- Sample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellDocument24 pagesSample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellMaryam ʚiïɞNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Back Workout: SL No Description Number of Sets/ Reps/Time Number Per /setsDocument1 pageDay 1 Back Workout: SL No Description Number of Sets/ Reps/Time Number Per /setsajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Load Combinations - BSDocument6 pagesLoad Combinations - BSajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Gantry Girder LoadingDocument6 pagesGantry Girder Loadingajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Load Calculation: Self-Weight of Materials SL No Material Density (KN/M)Document6 pagesLoad Calculation: Self-Weight of Materials SL No Material Density (KN/M)ajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane Foundation RevisedDocument11 pagesTower Crane Foundation Revisedajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Spacing of The Reinforcement Minimum Distance Between Individual BarsDocument1 pageSpacing of The Reinforcement Minimum Distance Between Individual Barsajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection CheckDocument7 pagesBeam Deflection Checkajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Is 15499Document19 pagesIs 15499ajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Designing of Ground Level Water Tank 2003 FormatDocument4 pagesDesigning of Ground Level Water Tank 2003 Formatajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Deflection Prestressed ConcreteDocument48 pagesDeflection Prestressed Concreteajith chandranNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Modelling Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures - Foundations - Dec2014 - KayniaDocument19 pagesNonlinear Modelling Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures - Foundations - Dec2014 - Kayniaajith chandranNo ratings yet