Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lymphatics and Respiratory System
Lymphatics and Respiratory System
Uploaded by
ellekaye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views66 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views66 pagesLymphatics and Respiratory System
Lymphatics and Respiratory System
Uploaded by
ellekayeCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt
You are on page 1of 66
The Lymphatic System
Includes the lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymph
nodes, lymphoid organs (tonsils, spleen and
thymus)
Primary Functions:
1. Maintains fluid homeostasis
2. Absorbs lipids from the GIT
3. Filters blood (spleen)
4. Contains lymphocytes participating in
immunity
The Lymph
Fluid similar to composition as
plasma
Without RBC and less proteins
Special Lymph from the GIT is
loaded with fats and is called
CHYLE
Fig. 14.2
The Lymph vessels
Carry fluid away from tissues into
the venous circulation
These are NOT present in the
central nervous system, Bone
marrow, epidermis and cartilage
They resemble vein because they
have valves
3 mechanisms of edema
formation
1. Decrease oncotic pressure
cirrhosis and kwashiorkor
2. Increased hydrostatic pressure
CHF and prolonged standing
3. Lymphatic obstruction or
destruction filiariasis, lymph node
dissection
Lymphatic duct
1. Right lymphatic duct- drains
the right side of the head and
the upper right side of the
thorax and the right extremities
2. Thoracic duct- drains the rest
of the body
The Lymphatic organs
1. Tonsils
A. palatine
B. pharyngeal
C. lingual
D. tubal
The lymphatic organs
2. Lymph nodes
Small round structures of lymphoid tissue
Major lymph nodes are the axillary,
inguinal and cervical
Filters lymph
Activates the immune system
Removes microorganisms from the blood
The lymphoid organs
3. The spleen
Reddish, flat organ lying next to the 9th and 10th rib
in the left upper quadrant
Functions:
Repository of old RBC
Activates the immune system
Storage of Blood
Sequesters bacteria
MOST COMMONLY INJURED
in BLUNT abdominal trauma
The lymphoid organs
4. Thymus
Bilobed organ in the superior mediastinum
Lymphocytes from the bone marrow
mature and grow as T-lymphocytes
Positive selection= T-cells that react to
foreign antigen are selected
Negative selection= T-cells that do not
react to the self-antigen are selected
IMMUNITY
Innate or Non-specific Specific Immunity
1. Mechanical- skin, 1. Cellular
mucus, saliva, urine
Immunity- T-cell
2. Chemical- enzymes,
lysozymes
system
3. Vascular Blood cells- 2. Humoral
Neutrophils and Immunity- B-cell
macrophages system
4. Inflammation
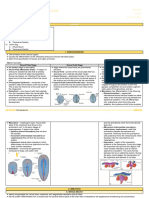
Non-specific Immunity
Inflammatory response
Reaction of the vacularized living tissues to
injury
Classic signs:
1. Rubor- redness
2. Calor- heat
3. Tumor- swelling
4. Dolor- pain
5. Functio laesa- loss of function
Inflammation
Initial reaction Vasoconstriction!
VC VD VP (due to HISTAMINE)
VD Redness and Heat
VP Swelling
Bradykinin, Prostaglandin,
compression of tissues pain
Specific Immunity: T cell
T-cells originate in the bone marrow and
mature in the thymus
4 types of T-cells
1. Cytotoxic T cells- kill infected cells, cancer
cells and transplanted cells
2. Helper T cells- help the humoral immunity
3. Suppressor T cells- suppress that actions of
cytotoxic and Helper cells
4. Memory T cells- for recall and specificity
Specific Immunity: B cells
B cells are produced and
mature in the bone marrow
B cells helped by Helper
cells turn into Plasma cells
secrete ANTIBODIES
ANTIBODIES
Are proteins that can combine
with antigens and function for:
1. Opsonization
2. Neutralization
3. Activation of complement
system
ANTIBODIES types
Five classes
1. Ig M- priMary response, pentaMer
2. Ig G- secondary response, most
abundant, can cross placenta
3. Ig A- secreted by the body (sIgA)
4. Ig D- receptor for B cells
5. Ig E- allergic and parasitic reactions
TYPES OF IMMUNITY
1. Natural Immunity
Active natural
Passive natural
2. Artificial Immunity
Active artificial
Passive artificial
Fig. 14.18
End of Immune System
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The Respiratory System
Composed of the air conducting
system and the respiratory unit
(lungs)
Major function is RESPIRATION
Commonly divided into UPPER
RESPIRATORY tract and LOWER
RESPIRATORY tract
Ventilation and Respiration
VENTILATION- movement of air from the
atmosphere into the lungs and out of the
lungs
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION- exchange of
gases between the alveoli and the blood
INTERNAL RESPIRATION- exchange of
gases between the blood and the tissues
The Respiratory System
Commonly divided into
UPPER RESPIRATORY tract and
LOWER RESPIRATORY tract
The UPPER Respiratory tract
The nose, pharynx and larynx
The LOWER respiratory tract
Composed of The trachea
down to the Lungs
The NOSE
Made up of nasal bones and
cartilages
The NASAL cavity is made up of
bones, cartilages and turbinates or
conchae
The nostril is the external opening
The choanae is the internal opening
Functions of the nose
1. Hairs or vibrissae filter
large particles
2. Blood vessels warm the air
3. Mucus serves to humidify
the air
4. Phonation
The Pharynx
Musculo-membranous tube from
behind the nasal cavity to the
level of the cricoid cartilage (C6)
The Pharynx
3 component parts
1. Nasopharynx
2. Oropharynx
3. Laryngopharynx
The Larynx
Upper expanded portion of the trachea
Made up of cartilages
3 Unpaired- Cricoid, Thyroid and
Epiglottis ( cUte)
6 Paired- Cuneiform, Corniculate and
Arytenoid (pACC)
Function: air passageway and phonation
The vocal cords
1. False vocal cords
2. True vocal cords
3. Glottis- the space between the
true vocal cords and is the
narrowest portion of the adult
airway
Fig. 15.4
Lower airway: Trachea
Called windpipe
Made up of 15-20 C-shaped
cartilage
10-11 inches
Lined with pseudostratified
ciliated epithelium
Bronchus
RIGHT Bronchus Left bronchus
Wider Narrower
Shorter Longer
More vertical More horizontal
Bronchioles
Primary bronchussecondary
bronchustertiary bronchus terminal
bronchioles
Respiratory bronchioles belong to the
respiratory unit
Respiratory unit
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts
Alveolar sacs
alveolus
The Pleura
Surrounds the lungs and provide
protection
1. Parietal pleura- in the chest wall
2. Visceral pleura- intimately attached
to the lungs
3. Pleural space- in between the two
Diaphragm
Respiratory Physiology
1. Ventilation and gas exchange
2. Mechanics of breathing
3. Gas transport
4. Pulmonary volumes and capacities
5. Respiratory control
Ventilation
Ventilation is the movement of air into
the lungs
Air (oxygen) moves by the process of
diffusion from the higher concentration
in the alveoli to the pulmonary
capillaries
Mechanics of breathing
Gas exchange
Respiratory membrane is thin which
facilitates gas exchange
Rate of diffusion depends on the
thickness of the membrane, surface
area and partial pressure of gases
Gas transport
1. OXYGEN- majority is transported in
the blood loosely bound to hemoglobin-
oxyhemoglobin
2. CARBON DIOXIDE- majority is
transported in the blood in the RBC as
BICARBONATE
Fig. 15.8
LUNG VOLUMES
1. Tidal volume – TV
2. Inspiratory Reserve Volume- IRV
3. Expiratory Reserve Volume- ERV
4. Residual volume- RV
LUNG CAPACITIES
Lung volume + another lung volume
1. Inspiratory Capacity- IC
2. Functional Residual Capacity- FRC
3. Vital capacity- VC
4. Total Lung capacity- TLC
NOT CLINICALLY measured
1. Residual volume
2. Functional residual volume
3. Total lung capacity
Control of Respiration: Central
Respiratory center in the medulla
Controls the rate and depth of
respiration
Increased CO2 is the most potent
stimulus
Control of Respiration:
Peripheral
1. Chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic
bodies
Sensitive to changes in pH and O2
Decreased O2 increase respiration
Decreased pH (acidosis) increase respiration
2. Herring-Breurer reflex
Stretch receptors in the lungs limit the inspiration
ASSESSMENT
Normal Breathing pattern:
12-21 respiratory rate
Active inspiration with contraction of
diaphragm
Passive expiration with relaxation of
diaphragm
Steady rhythm and regular rate and size
I:E ratio is 1:2
Abnormal breathing pattern
1. Cheyne-Stoke’s
2. Biot’s
3. Kussmaul’s
4. Agoral
Breathing rates
1. Eupnea- 12-21
2. Bradypnea- 11 and below
3. Tachypnea- 22 and above
4. Dyspnea- difficulty of breathing
Breathing Position
1. Platypnea- inability to breath in an
upright position
2. Orthopnea- difficulty in breathing in
any position except upright
Breath sounds: Normal
1. Bronchial or Tracheal- in the sternum
2. Bronchovesicular- in the interscapular
area
3. Vesicular- lung periphery
Adventitious Breath sounds
1. Rales or crackles
2. Stridor
3. Wheeze
4. Rhonchi
5. Friction rub
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Growth Evaluation of Ornamental Foliage Plants in Response To Light Intensity Levels Under Continuous Lighting ConditionsDocument13 pagesChlorophyll Fluorescence and Growth Evaluation of Ornamental Foliage Plants in Response To Light Intensity Levels Under Continuous Lighting ConditionsSai RaisaNo ratings yet
- Eals ReviewerDocument12 pagesEals ReviewerEms TeopeNo ratings yet
- Tesis MaquiDocument20 pagesTesis MaquiBastian SeguelNo ratings yet
- Muscle Energy Technique: Concepts & MethodsDocument24 pagesMuscle Energy Technique: Concepts & MethodssandipandassarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 9-Biology-Lesson 11-Sense Organs-EarDocument10 pagesClass 9-Biology-Lesson 11-Sense Organs-EarShlok JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaDocument4 pages4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaM Syarifuddin Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice in BiotechnologyDocument15 pagesMultiple Choice in Biotechnologyjohn.kate1120No ratings yet
- Blood ChemistryDocument24 pagesBlood Chemistryflorabelvelasco2No ratings yet
- Fluids in Surgery 1 1Document43 pagesFluids in Surgery 1 1محمد عماد عليNo ratings yet
- Manuale Radiometer OSM3Document5 pagesManuale Radiometer OSM3assistenza tecnicaNo ratings yet
- MORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Document20 pagesMORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Luiza MartinsNo ratings yet
- " The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotDocument7 pages" The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotNargess OsmanNo ratings yet
- Factors Regulating BreathingDocument15 pagesFactors Regulating BreathingShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Fish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Document293 pagesFish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Rodolfo Velazco100% (1)
- DLL in Science 10 Third QuarterDocument16 pagesDLL in Science 10 Third QuarterAlfred NeriNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- MCBN 111 2023Document12 pagesMCBN 111 2023nika35908No ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocument7 pagesChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- D. Cardiac EnlargementDocument10 pagesD. Cardiac EnlargementNuhad Bou Mosleh100% (1)
- Cell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesCell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Strive ShashaNo ratings yet
- Sept 22 Neonatal HypothermiaDocument23 pagesSept 22 Neonatal Hypothermiaf.abrahamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology II Lab Manual New - Updated2.0Document70 pagesPharmacology II Lab Manual New - Updated2.0Bella AstilahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12shabanaNo ratings yet
- M2 Rad AnaDocument11 pagesM2 Rad AnaramilccabrigaNo ratings yet
- Summative Practice 3: Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneDocument14 pagesSummative Practice 3: Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneDewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sensation and PerceptionDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - Sensation and PerceptionKaiNo ratings yet
- Try Out - Bahasa InggrisDocument13 pagesTry Out - Bahasa InggrisAditya JbNo ratings yet
- Sandip Mardhekar: Emoly Code Blood Group D.O.B D..O.J Designa OnDocument36 pagesSandip Mardhekar: Emoly Code Blood Group D.O.B D..O.J Designa Onprint xeroxNo ratings yet
- Vasoactive DrugsDocument14 pagesVasoactive DrugsTushar GhuleNo ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet