Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research 5
Research 5
Uploaded by
api-297205880Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research 5
Research 5
Uploaded by
api-297205880Copyright:
Available Formats
Marina Farag
ISM Period 1
Borton, Chloe, Dr. "Placenta and Placental Problems. Information Page. |
Patient." Patient. Web. 13 Sept.2015.
< http://patient.info/doctor/placenta-and-placental-problems>
The placenta provides exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products between
the mother and fetus.
Acts as an endocrine organ for synthesis of hormones and neurotransmitters.
Acts as a barrier to toxins and infection.
Comprises a large number of functional units called villi, which are branched
terminals of fetal circulation, allowing transfer of metabolic products.
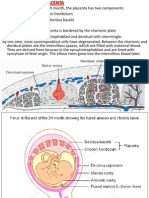
A normal placenta is blue-red in color and discoid in shape, 22 cm in diameter,
2.5 cm thick in the center, weighs 450 g on average, has a maternal surface that is
divided into lobules or cotyledons with irregular grooves or clefts, has a smooth,
shiny, translucent fetal surface, the chorionic plate, covered in amniotic
membrane, and has a basal plate which is the maternal surface and is created at
the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall at delivery.
A normal umbilical cord is 51-60 cm long and 2-2.5 cm in diameter, should have
abundant Wharton's jelly with no true knots, contains two umbilical arteries and
one umbilical vein, and arises from the center of the placenta.
Women who have had a previous caesarean section who also have either placenta
praevia or an anterior placenta underlying the old caesarean section scar at 32
weeks of gestation, are at increased risk of placenta accreta and should be
managed as if they have placenta accrete.
Abruption is the premature separation of a normally placed placenta before
delivery of the fetus, with blood collecting between the placenta and the uterus.
It is one of the two most important causes of antepartum haemorrhage.
Marginal haemorrhage occurs with a painless bleed and clot located along the
margin of the placenta with no distortion of its shape.
Velamentous cord insertion is the term for where the placenta has developed away
from the attachment of the cord and the vessels divide in the membrane. If the
vessels cross the lower pole of the chorion, this is known as vasa praevia and
there is high risk of fetal haemorrhage and death at rupture of membranes.
In the presence of bleeding vasa praevia, delivery should be achieved by
emergency caesarean section.
This source goes in depth about what causes the placenta or the umbilical cord to be abnormal
depending on diseases that are genetic and the diseases that are caused due to drugs or different
surroundings, who has greater risks and what has to be done in those cases. The source also
shows and describes the difference in placentas and umbilical cords that are abnormal versus the
normal.
You might also like
- Project Synopsis DnheDocument15 pagesProject Synopsis Dnheahmed85% (13)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Concept MapDocument1 pageBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Concept MapJason A. AdoyoganNo ratings yet
- Placental PathologyDocument39 pagesPlacental PathologyconstantinilieNo ratings yet
- Placental ExaminationDocument13 pagesPlacental ExaminationAnuradha Maurya67% (3)
- A Case of Vasa Previa Diagnosed PrenatallyDocument5 pagesA Case of Vasa Previa Diagnosed PrenatallydeadcorpsesNo ratings yet
- Umblical Cord AbnormalitiesDocument54 pagesUmblical Cord AbnormalitiesKeerti Patel100% (6)
- Pathology of Preeclampsia (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document59 pagesPathology of Preeclampsia (Autosaved) (Autosaved)ck4realNo ratings yet
- Courtney Mashburn Bilobed Placenta With Velamentous Cord Insert PaperDocument8 pagesCourtney Mashburn Bilobed Placenta With Velamentous Cord Insert Paperapi-307030551No ratings yet
- Placental Development - Implantation - Transfer - Clinical RelevanceDocument3 pagesPlacental Development - Implantation - Transfer - Clinical RelevanceLiridon SopajNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Placental ProblemsDocument13 pagesPlacenta and Placental ProblemsLuvita Ronteltap100% (1)
- PlacentaDocument35 pagesPlacentaDrsmcsi dept of radiodiagnosisNo ratings yet
- 2.demoplacental ExaminationDocument7 pages2.demoplacental ExaminationKuleshwar SahuNo ratings yet
- 11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidDocument35 pages11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Anomalies of The Placenta and The CordDocument38 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and The CordDN Sly Litang DumangasNo ratings yet
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaDocument150 pagesFetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaKripa SusanNo ratings yet
- Placenta - WikipediaDocument19 pagesPlacenta - Wikipediasoft hutNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LabourDocument21 pagesAbnormal LabourbetablockersNo ratings yet
- Bio PresentationDocument17 pagesBio PresentationkamiiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation: Group 2Document12 pagesCase Study Presentation: Group 2Anna Marie Donaire0% (1)
- Clin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordDocument13 pagesClin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordTami Selvi100% (2)
- Plac Pathology - Drucilla RobertsDocument11 pagesPlac Pathology - Drucilla RobertsconstantinilieNo ratings yet
- Care of The Umbilicus and Management of Umbilical Disorders - UpToDateDocument31 pagesCare of The Umbilicus and Management of Umbilical Disorders - UpToDateJulio Leal100% (1)
- Abnormalities of Placenta and CordDocument47 pagesAbnormalities of Placenta and CordShrooti Shah75% (4)
- Final BioDocument24 pagesFinal Biosayedsaifullah.knbossNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine SegmentDocument11 pagesPredisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine Segmentjhachers100% (1)
- 8 Disorders of The Umbilical Cord 2018Document12 pages8 Disorders of The Umbilical Cord 2018Yan Zhen YuanNo ratings yet
- Chorioangioma of PlacentaDocument13 pagesChorioangioma of Placentagibson kumwendaNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities: Placenta Accreta, Placenta Increta, and Placenta PercretaDocument11 pagesPlacental Abnormalities: Placenta Accreta, Placenta Increta, and Placenta PercretaLiza M. PurocNo ratings yet
- 67Document57 pages67Neeruam Ellehcim Aled ZurcNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordDocument53 pagesAbnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordPraveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics V10 Common Obstetric Conditions Chapter Placenta Previa and Placenta Abruption 1665345717Document17 pagesObstetrics V10 Common Obstetric Conditions Chapter Placenta Previa and Placenta Abruption 1665345717Mauricio Lopez MejiaNo ratings yet
- MANUAL OF PLACENTAL PATHOLOGY FinaleDocument24 pagesMANUAL OF PLACENTAL PATHOLOGY FinaleAnonymous wE02eRNo ratings yet
- PlacentationDocument15 pagesPlacentationKomal SinghNo ratings yet
- The Placenta BDocument48 pagesThe Placenta BLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Case 5Document18 pagesCase 5Brian Arthur LeysonNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDocument66 pagesPlacenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionmadyNo ratings yet
- Benign Cervical Lesions and Congenital Anomalies of The Cervix - UpToDateDocument33 pagesBenign Cervical Lesions and Congenital Anomalies of The Cervix - UpToDatecriswesi23No ratings yet
- Perkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdDocument18 pagesPerkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument71 pagesMultiple PregnancyAndre PutraNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Document22 pagesAbruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Marzo, Cecille JoyceNo ratings yet
- Placenta ExaminationDocument18 pagesPlacenta ExaminationAbi RajanNo ratings yet
- Delivery of PlacentaDocument8 pagesDelivery of PlacentaAbdullahi Suleiman MakaNo ratings yet
- Williams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Document57 pagesWilliams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- MC Pregnancy Version 12 17 5 10Document13 pagesMC Pregnancy Version 12 17 5 10Ram ParepalliNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The UterusDocument7 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Uterusمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Placental AbruptionDocument5 pagesPlacental Abruptioncamdao.huynh187No ratings yet
- Science Direct Cord CareDocument7 pagesScience Direct Cord CareFatma ElzaytNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Placenta OutlineDocument7 pagesAbnormalities of The Placenta OutlineSteve ShirmpNo ratings yet
- Placental AbruptionDocument7 pagesPlacental AbruptionNavora, Bryle TrixthaneNo ratings yet
- Maternity Study Guide 1Document14 pagesMaternity Study Guide 1Rob Davila100% (2)
- Embryology, Yolk Sac - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pagesEmbryology, Yolk Sac - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfr9fch8mws7No ratings yet
- DR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and GrowthDocument42 pagesDR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and Growthhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Placenta AccretaDocument37 pagesImaging of Placenta AccretaDhanush P BNo ratings yet
- OB Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesOB Definition of TermsWarrenSandovalNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesStages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentGrant KhangabNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument32 pagesPlacentaAbedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Maternal Placental Foetal UnitDocument10 pagesMaternal Placental Foetal UnitFestus SinoNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta FullDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta FullChester ManaloNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- Journal Entry 11-9Document1 pageJournal Entry 11-9api-297205880No ratings yet
- Research 1Document1 pageResearch 1api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 11-2Document1 pageJournal Entry 11-2api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 10-19Document1 pageJournal Entry 10-19api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 10-26Document1 pageJournal Entry 10-26api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 10-5Document1 pageJournal Entry 10-5api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 9-14Document1 pageJournal Entry 9-14api-297205880No ratings yet
- Journal Entry 9-21Document1 pageJournal Entry 9-21api-297205880No ratings yet
- Episodic Focused SOAP NoteDocument7 pagesEpisodic Focused SOAP NoteSam Odoo100% (1)
- Application of Antidepressants in Depression. A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument14 pagesApplication of Antidepressants in Depression. A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisCésar Vásquez CohelloNo ratings yet
- Preview Newman and Carranzas Clinical PeriodontologyDocument142 pagesPreview Newman and Carranzas Clinical PeriodontologyBala SubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- Swamedikasi DemamDocument25 pagesSwamedikasi DemamrosawpNo ratings yet
- UofA Application Pack Clinical Elective Students 2017 2018Document10 pagesUofA Application Pack Clinical Elective Students 2017 2018abhi1648665No ratings yet
- HCM 2337 Vector, Vermin and Rodent ControlDocument13 pagesHCM 2337 Vector, Vermin and Rodent ControlMokua FedinardNo ratings yet
- CPT Modifier NewDocument10 pagesCPT Modifier NewSeenuvasanLeeManiNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument21 pagesBlood TransfusionAnup GouravNo ratings yet
- Veterinarians 09-2022Document28 pagesVeterinarians 09-2022PRC Baguio100% (1)
- Quackery, The 20 Million Dollar DuckDocument20 pagesQuackery, The 20 Million Dollar DuckAustin Macauley Publishers Ltd.No ratings yet
- Cahps Strategy Section 6 GDocument6 pagesCahps Strategy Section 6 Gnatxla07No ratings yet
- Plate Removal Following Orthognathic SurgeryDocument7 pagesPlate Removal Following Orthognathic SurgeryAdam HaytoumiNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Working Long Hours Kill Hundreds of ThousandsDocument4 pagesWorking Long Hours Kill Hundreds of ThousandsTuấn Kiệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Programa Simposio Aorta Compleja Oviedo Noviembre 2022Document8 pagesPrograma Simposio Aorta Compleja Oviedo Noviembre 2022Francisco Álvarez MarcosNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2590059523001930 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2590059523001930 MainHarithaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy: Jorge H. MDDocument23 pagesHyperthyroidism in Pregnancy: Jorge H. MDRashid HussainNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Plasma TherapyDocument80 pagesAdverse Effects of Plasma TherapyShaiji ShahidNo ratings yet
- Rubber Dam - 07 - HandoutDocument12 pagesRubber Dam - 07 - HandoutOmar Al-AboodNo ratings yet
- Vesicovaginal FistulaDocument7 pagesVesicovaginal Fistuladrnareshkumar3281No ratings yet
- OSCE - Acute AsthmaDocument3 pagesOSCE - Acute AsthmaNicu EnachiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Syphilis - Evaluation, Management, and Prevention - UpToDate PDFDocument18 pagesCongenital Syphilis - Evaluation, Management, and Prevention - UpToDate PDFcuenta personalNo ratings yet
- EndophthalmitisDocument30 pagesEndophthalmitisNazmiNo ratings yet
- Orl CuricullumDocument53 pagesOrl CuricullumRaynard ShNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Gangrene Cure by Carbon VegDocument5 pagesDiabetic Foot Gangrene Cure by Carbon Vegpratibha mishraNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For Module 1.5Document17 pagesHand Out For Module 1.5weissNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka FinalDocument8 pagesDaftar Pustaka FinalBayu DestiawanNo ratings yet
- Eastern Visayas Regional Medical Center: Tacloban City, Philippines, 6500Document1 pageEastern Visayas Regional Medical Center: Tacloban City, Philippines, 6500Marimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet