Professional Documents
Culture Documents
"Legal" and "Legal Concept" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See
"Legal" and "Legal Concept" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See
Uploaded by
glamoc1987Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
"Legal" and "Legal Concept" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See
"Legal" and "Legal Concept" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See
Uploaded by
glamoc1987Copyright:
Available Formats
"Legal" and "Legal concept" redirect here. For other uses, see Legal (disambiguation).
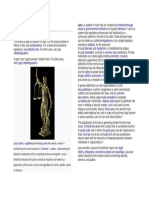
Lady Justice, a goddesssymbolising justice who bears a sword symbolising the coercive power of
a tribunal ,scales representing an objective standard by which competing claims are weighed and a
blindfold indicating that justice should be impartial and meted out objectively, without fear or favor and
regardless of money, wealth, power or identity.[1]
Law is a system of rules that are enforced through social institutions to govern behaviour.[2] Laws can
be made by a collective legislature or by a single legislator, resulting in statutes, by the executive
through decrees and regulations, or by judges through binding precedent, normally in common
law jurisdictions. Private individuals can create legally binding contracts, including arbitration
agreements that may elect to accept alternative arbitration to the normal court process. The
formation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and
the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history and societyin various ways
and serves as a mediator of relations between people.
A general distinction can be made between (a) civil law jurisdictions (including Catholic canon
law and socialist law), in which the legislature or other central body codifies and consolidates their
laws, and (b) common law systems, where judge-made precedent is accepted as binding law.
Historically, religious laws played a significant role even in settling of secular matters, which is still
the case in some religious communities, particularly Jewish, and some countries, particularly Islamic.
Islamic Sharia law is the world's most widely used religious law.[3]
The adjudication of the law is generally divided into two main areas referred to as (i) Criminal law
and (ii) Civil law. Criminal law deals with conduct that is considered harmful to social order and in
which the guilty party may be imprisoned or fined. Civil law (not to be confused with civil law
jurisdictions above) deals with the resolution of lawsuits (disputes) between individuals or
organizations. These resolutions seek to provide a legal remedy (often monetary damages) to the
winning litigant. Under civil law, the following specialties, among others, exist: Contract law regulates
everything from buying a bus ticket to trading on derivatives markets.
You might also like
- Study Material For Legal MethodDocument48 pagesStudy Material For Legal MethodSurabhi Maheshwari100% (2)
- Law Text: Law 30Document73 pagesLaw Text: Law 30Greg100% (3)
- Back To Basics GrammarDocument40 pagesBack To Basics Grammarglamoc198725% (4)
- For Other Uses, See and - This Article Is About A - For The Theory of Law, See - "Legal Concept" Redirects HereDocument2 pagesFor Other Uses, See and - This Article Is About A - For The Theory of Law, See - "Legal Concept" Redirects HereYan Lean DollisonNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence Law (Disambiguation) Legal (Disambiguation)Document2 pagesJurisprudence Law (Disambiguation) Legal (Disambiguation)No OneNo ratings yet
- Law Is A Term Which Does Not Have A Universally Accepted DefinitionDocument1 pageLaw Is A Term Which Does Not Have A Universally Accepted DefinitionGlutton ArchNo ratings yet
- Law Is, Generally, A: Citation NeededDocument2 pagesLaw Is, Generally, A: Citation NeededsalpanditaNo ratings yet
- Awisa: Citation NeededDocument2 pagesAwisa: Citation NeededDavidCruzNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence Statutory Law Law (Disambiguation) : LawisaDocument1 pageJurisprudence Statutory Law Law (Disambiguation) : LawisaJS DSNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About A System of RulesDocument2 pagesThis Article Is About A System of RulesVincent BajaNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See - "Legal" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument2 pagesFor Other Uses, See - "Legal" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeSagarNo ratings yet
- Unknown Details of Boanma Disclosed by ProsDocument2 pagesUnknown Details of Boanma Disclosed by Prosword8gasNo ratings yet
- Name: Fatwa Fitraziah Desiaz Zein Student Id: 010001500156 (CLASS D)Document3 pagesName: Fatwa Fitraziah Desiaz Zein Student Id: 010001500156 (CLASS D)FatwaNo ratings yet
- System Enforced Through Social Institutions Statutes Decrees Regulations Common Law ContractsDocument1 pageSystem Enforced Through Social Institutions Statutes Decrees Regulations Common Law ContractsEuneun BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Law Is Commonly Understood As ADocument2 pagesLaw Is Commonly Understood As AMudau Khumbelo RodneykNo ratings yet
- What Is LawDocument2 pagesWhat Is LawHusayn TamanoNo ratings yet
- What Is Law?: Curs 1Document15 pagesWhat Is Law?: Curs 1Antonio Valentin NegrețNo ratings yet
- 1 o 1.1 o 1.2 2 3 o 3.1 o 3.2 o 3.3 o 3.4 4 5 o 5.1 o 5.2 o 5.3 5.3.1 6 o 6.1 o 6.2 o 6.3 o 6.4 o 6.5Document2 pages1 o 1.1 o 1.2 2 3 o 3.1 o 3.2 o 3.3 o 3.4 4 5 o 5.1 o 5.2 o 5.3 5.3.1 6 o 6.1 o 6.2 o 6.3 o 6.4 o 6.5Joana Loren C. CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Is Law PPT and Philosophy of LawpptxDocument178 pagesWhat Is Law PPT and Philosophy of LawpptxdenyohsylvesterNo ratings yet
- IPR, Media & Cyber Law Assignment 1: Submitted by Pritesh Bohra 10020541055 System and FinanceDocument6 pagesIPR, Media & Cyber Law Assignment 1: Submitted by Pritesh Bohra 10020541055 System and FinanceDeepa BaranwalNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See and - This Article Is About A - For The Theory of Law, See - "Legal Concept" Redirects HereDocument6 pagesFor Other Uses, See and - This Article Is About A - For The Theory of Law, See - "Legal Concept" Redirects HereJohn EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Study Material For Legal MethodDocument85 pagesStudy Material For Legal MethodMeha Bhushan100% (1)
- Breach of ContractDocument26 pagesBreach of ContractAdil HafeezNo ratings yet
- Nass Module 2 .Doc Legal and Parl AffairDocument19 pagesNass Module 2 .Doc Legal and Parl AffairJoel Gwenere100% (4)
- Inbound 3695375915791667941Document2 pagesInbound 3695375915791667941Roselle Luzano GalugaNo ratings yet
- Law Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and AreDocument4 pagesLaw Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and AreSALAH UDDIN AHMED -11No ratings yet
- Law Is, Generally, A System of Rules Which Are Enforced Through Social Institutions To GovernDocument5 pagesLaw Is, Generally, A System of Rules Which Are Enforced Through Social Institutions To GovernSeph InfanteNo ratings yet
- The Administrative LawDocument10 pagesThe Administrative LawNABEEL REHMANNo ratings yet
- Business Law From Acc Department.Document83 pagesBusiness Law From Acc Department.newaybeyene5No ratings yet
- Business LawDocument63 pagesBusiness Lawnatiman090909No ratings yet
- Introduction To Law Dme Master Class.Document5 pagesIntroduction To Law Dme Master Class.Daniel MukelabaiNo ratings yet
- Law Summary - First ExamDocument11 pagesLaw Summary - First ExamROJO- Lourdes TabieresNo ratings yet
- El I - GCL 102Document16 pagesEl I - GCL 102Aman KhokharNo ratings yet
- History of LawDocument19 pagesHistory of LawLeorebelle RacelisNo ratings yet
- Custom Law Sovereign State International Law Juridical Entity Centralised Government SovereigntyDocument2 pagesCustom Law Sovereign State International Law Juridical Entity Centralised Government SovereigntyEunice Flores CatulinNo ratings yet
- Law NotesDocument6 pagesLaw NotesmolxokhanNo ratings yet
- Ohrm 613 NotesDocument128 pagesOhrm 613 NotesgilbertNo ratings yet
- ObliconnnDocument10 pagesObliconnnKier Daniel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Law: Law Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and AreDocument6 pagesPhilosophy of Law: Law Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and AreAngelenemae MohamadNo ratings yet
- CH 1 (1) - Introduction To LawDocument4 pagesCH 1 (1) - Introduction To LawMaria ForkNo ratings yet
- 1) History & SourcesDocument5 pages1) History & SourcesMihle GwadisoNo ratings yet
- Study Material For Legal MethodDocument85 pagesStudy Material For Legal MethodBittu HidkoNo ratings yet
- Study Material For Legal MethodDocument86 pagesStudy Material For Legal MethodOnindya MitraNo ratings yet
- Business Law Lecture Notes (UEBS)Document112 pagesBusiness Law Lecture Notes (UEBS)eholmes8095% (20)
- Unit 1 What Is Meant by LawwDocument31 pagesUnit 1 What Is Meant by LawwsunuuNo ratings yet
- Adnaan Belim LLM (Constitution) 1 SemesterDocument3 pagesAdnaan Belim LLM (Constitution) 1 SemesterSahida ParveenNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument5 pagesINTRODUCTIONHeart Erica AbagNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Law: Law Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and Are Enforceable byDocument45 pagesPhilosophy of Law: Law Is A Set of Rules That Are Created and Are Enforceable byToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Leyes de Laws ResearchDocument5 pagesLeyes de Laws ResearchrednboitesNo ratings yet
- Definition of LawDocument8 pagesDefinition of LawSattar KhanNo ratings yet
- Definition of LawDocument8 pagesDefinition of LawSattar KhanNo ratings yet
- TABL1710 Key TermsDocument4 pagesTABL1710 Key TermsPriscilla YaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - What Is LawDocument29 pagesLecture 1 - What Is LawMUHAMMAD ALIF NAJMI FADZILNo ratings yet
- Lawisa: Lady Justice Tribunal ScalesDocument11 pagesLawisa: Lady Justice Tribunal ScalesA Parel DrNo ratings yet
- AiyubDocument7 pagesAiyubaiyub aliNo ratings yet
- HMM - Busi Law Edit Ver 2Document197 pagesHMM - Busi Law Edit Ver 2Shivam SoamNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentabhilasha maneNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS OF LANGUAGE - Sa ResenjimaDocument1 pageFUNCTIONS OF LANGUAGE - Sa Resenjimaglamoc1987No ratings yet
- MN CLSD MemoDocument1 pageMN CLSD Memoglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Ponedeljak Utorak Sreda Četvrtak PetakDocument2 pagesPonedeljak Utorak Sreda Četvrtak Petakglamoc1987No ratings yet
- University of Novi Sad Faculty of Humanities Department of English Language and Literature Entrance ExaminationDocument9 pagesUniversity of Novi Sad Faculty of Humanities Department of English Language and Literature Entrance Examinationglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Sandra Annette BullockDocument1 pageSandra Annette Bullockglamoc1987No ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument1 pagePhilosophyglamoc1987No ratings yet
- The Modern Olympic Games or OlympicsDocument2 pagesThe Modern Olympic Games or Olympicsglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Married.) : Cleft Sentences (It Was in June We GotDocument2 pagesMarried.) : Cleft Sentences (It Was in June We Gotglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Old Church SlavonicDocument2 pagesOld Church Slavonicglamoc1987100% (2)
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Biology Science Heredity Genes Inheritance Variation Traits Organisms LaboratoryDocument1 pageBiology Science Heredity Genes Inheritance Variation Traits Organisms Laboratoryglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Course Director: Lynda Hazelwood Certed B Phil Tefl: Intesol Worldwide Limited Company No. 5697958Document1 pageCourse Director: Lynda Hazelwood Certed B Phil Tefl: Intesol Worldwide Limited Company No. 5697958glamoc1987No ratings yet
- Non PointDocument1 pageNon Pointglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Pragmatics Is A Subfield ofDocument2 pagesPragmatics Is A Subfield ofglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Reference Book: Book Periodical Its Electronic EquivalentDocument1 pageReference Book: Book Periodical Its Electronic Equivalentglamoc1987No ratings yet
- History: Historical BiographyDocument2 pagesHistory: Historical Biographyglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions Email UsDocument1 pageFrequently Asked Questions Email Usglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Beginnings of Detective Fiction: in Ancient LiteratureDocument2 pagesBeginnings of Detective Fiction: in Ancient Literatureglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Stratosphere Sun Ultraviolet OzoneDocument1 pageStratosphere Sun Ultraviolet Ozoneglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Water Pollution Is The Contamination ofDocument1 pageWater Pollution Is The Contamination ofglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Air Pollution Is The Introduction ofDocument1 pageAir Pollution Is The Introduction ofglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Statutory Law Promulgated Enacted Legislature Governing Body BillDocument1 pageStatutory Law Promulgated Enacted Legislature Governing Body Billglamoc1987No ratings yet
- Writing ClassDocument2 pagesWriting Classglamoc1987No ratings yet