Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cat Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Day 2
Cat Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Day 2
Uploaded by
api-168512039Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cat Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Day 2
Cat Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Day 2
Uploaded by
api-168512039Copyright:
Available Formats
CAT
Section 4.2
Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
Day 2
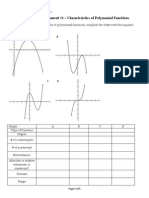
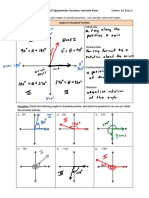
We want to examine the role of the exponent on each factor and its effect on the graph of the
polynomial. Using your calculator make a quick sketch of the graph of each of the following
functions. Use a meaningful window, and mark the x- and y- intercepts with their values. It is not
important to have the heights drawn to scale. Draw smooth flowing curves. Determine the degree of
each polynomial.
For example:
y x 4
x 1
x 1 x 3
Degree = 5
y x 2
Degree = __________________
y x 4
x 1 x 3
Degree = __________________
Under what circumstances did you find a pass-through point? When did you find a bounce point?
Multiplicity If
g ( x) x 1
x a
2
x 53
is a factor of a polynomial f then a is called a zero of multiplicity n of f.
7
zeros are:
x = 1 with multiplicity of 2
x= -3/5 with multiplicity of 7
CAT
Section 4.2
Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
Day 2
Learning Goals:
I can graph polynomial functions using transformations
I can identify real zeros of a polynomial function and their multiplicities.
I can determine the end behavior of a polynomial function.
I can graph polynomial functions using x-intercepts, multiplicities of each zero,& end behavior.
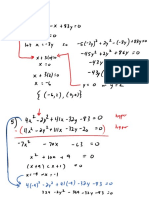
f x 23 x 45
1. Determine the degree of the function
26
x 11 x 5
14
2. Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function.
f x 4 x 6 x 4
x 5
3. Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function.
y x x 6
f x x 1 x 3 x 4 , find the y - intercept.
4. For the polynomial function
2
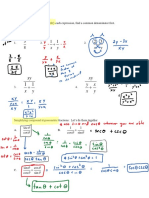
5. Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has the given zeros: -3, 1, 2
6. Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has the given zeros: 0, 4, 10, -12
7. Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has the zeros -3 (with multiplicity 2)
and 5 (with multiplicity 2).
Homework: p. 354: #27-32 (all), 39-51, (x3)
You might also like
- Key Features of Polynomial Graphs: How To Find ThemDocument3 pagesKey Features of Polynomial Graphs: How To Find ThemEthan BaumannNo ratings yet
- Mtc10 0903 q2 Fpf Graphs of PfDocument59 pagesMtc10 0903 q2 Fpf Graphs of PfraignewinsletreyesNo ratings yet
- Motivational Problems On Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotivational Problems On Polynomial FunctionsAnnika SolotkoNo ratings yet
- Sim FunctionDocument16 pagesSim FunctionShuyen AmistadNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions: y - Intercept and The Constant TermDocument6 pages3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions: y - Intercept and The Constant TermJustine WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 3 2 LessonDocument31 pages3 2 Lessonapi-261587850No ratings yet
- SsDocument3 pagesSscristinejoydalag3No ratings yet
- Economía: Universidad Nacional Autònoma de MèxicoDocument3 pagesEconomía: Universidad Nacional Autònoma de Mèxicogerson panochaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument128 pagesCalculusJohn Paul ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.2 Introduction To Polynomial Functions PDFDocument7 pagesLesson 3.2 Introduction To Polynomial Functions PDFmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Evaluating and Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument37 pagesEvaluating and Graphing Polynomial FunctionsAnonymous UyozHgNo ratings yet
- Spcg6e PPT 4 1Document63 pagesSpcg6e PPT 4 1api-334707195No ratings yet
- GenMath M3 W3 Q1Document6 pagesGenMath M3 W3 Q1ariannaclarisse05No ratings yet
- LP1 Math1 Unit1 Edited-082321Document15 pagesLP1 Math1 Unit1 Edited-082321hajiNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Evaluating and Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument15 pages6 2 Evaluating and Graphing Polynomial Functionsapi-200092859No ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDocument22 pagesQuarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Logarithmic FunctionsDocument17 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Logarithmic FunctionsNimfa Plaza100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Functions and Their Graphs - NOTESDocument65 pagesLesson 2 - Functions and Their Graphs - NOTESAilyn DelpuertoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Document19 pagesGrade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Encluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument10 pagesMathsSudarshan NeupaneNo ratings yet
- TLP 8 Polynomial FunctionsDocument13 pagesTLP 8 Polynomial FunctionsMilan WanderlandNo ratings yet
- Section 2.3 Polynomial Functions and Their GraphsDocument31 pagesSection 2.3 Polynomial Functions and Their GraphsdavogezuNo ratings yet
- Mat04 Calculu: Gilbert R. Esquillo, PmeDocument64 pagesMat04 Calculu: Gilbert R. Esquillo, PmeLuis NapolesNo ratings yet
- Exploring Minimum and Maximum ValuesDocument5 pagesExploring Minimum and Maximum ValuesRobert TalbertNo ratings yet
- General Math 11 Q1 LAS Week3Document14 pagesGeneral Math 11 Q1 LAS Week3Ruben Rosendal De Asis100% (1)
- C6fLVI-practice Test Quadratics FunctionsDocument4 pagesC6fLVI-practice Test Quadratics FunctionsPraneewan TunwattanaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Document54 pages2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Urduja Kyle OdiacerNo ratings yet
- CS 546: Module 2: Spring 2014Document73 pagesCS 546: Module 2: Spring 2014drsimrankaurNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledRainiel GanarealNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 LAS Week 1 2 Math 10 (1) 2Document22 pagesQuarter 2 LAS Week 1 2 Math 10 (1) 2Dale DelimNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Hand in Assignment #1Document5 pagesPolynomials Hand in Assignment #1cuteangel_103No ratings yet
- Analyze Graphs of Polynomial Functions: For Your NotebookDocument6 pagesAnalyze Graphs of Polynomial Functions: For Your Notebook미나No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Domain of A Rational FunctionDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Domain of A Rational FunctionJaycint - Rud PontingNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Document4 pagesMath 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation IncDocument17 pagesSupplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation Incjaylyn carasNo ratings yet
- Max/min of A FunctionDocument5 pagesMax/min of A FunctionTrevor ChimombeNo ratings yet
- Final Examination GenMath Q2 Seta STEMDocument3 pagesFinal Examination GenMath Q2 Seta STEMMarjon GarabelNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Functions: Grade 10Document11 pagesPolynomial Functions: Grade 10Mobile legends gamerNo ratings yet
- Section 11. The 1st and 2nd Derivative Tests: y y y y X y y yDocument1 pageSection 11. The 1st and 2nd Derivative Tests: y y y y X y y yEdgar FloresNo ratings yet
- PolyrootDocument4 pagesPolyrooteddy85No ratings yet
- Math 53 Le3 Samplex 02Document1 pageMath 53 Le3 Samplex 02Jonoel TaborNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calc Slides Section 2.2Document16 pagesPre-Calc Slides Section 2.2shamsheer haiderNo ratings yet
- P Q Factors of The Constant Term Factor of Theleading CoefficientDocument2 pagesP Q Factors of The Constant Term Factor of Theleading CoefficientSam MattisNo ratings yet
- 12 Polynomial FunctionsDocument34 pages12 Polynomial FunctionsTitser LaarniNo ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 3 Notes CH 6 CP A2Document47 pages2017 Unit 3 Notes CH 6 CP A2Ross HamiltonNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: F X X 2 F X X 3Document14 pagesGeneral Mathematics: F X X 2 F X X 3Hana LandinginNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 t5 4Document18 pagesAlg 2 t5 4api-261379705No ratings yet
- Q2 - WK 1&2 - Polynomial FunctionDocument67 pagesQ2 - WK 1&2 - Polynomial FunctionJENNALYN RESARENo ratings yet
- 3 2math108selfassessmentDocument1 page3 2math108selfassessmentRondex PabloNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Functions 1Document19 pagesPolynomial Functions 1Arafath Basheer100% (1)
- Finding Equation of Quadratic FunctionDocument2 pagesFinding Equation of Quadratic Functiondiane carol roseteNo ratings yet
- PX Ax A X A X Ax A: Polynomial FunctionsDocument2 pagesPX Ax A X A X Ax A: Polynomial Functionsapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Self Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersDocument14 pagesSelf Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- SIQ Maths 2024 Vivek SirDocument25 pagesSIQ Maths 2024 Vivek SirmangalametaiahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4夏烨No ratings yet
- Calculus: Chapter 6 Transcendental FunctionsDocument82 pagesCalculus: Chapter 6 Transcendental FunctionsFachryal HiltansyahNo ratings yet
- Theme 1Document18 pagesTheme 1GwarraNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
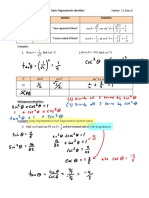
- 1 Sin 1 Sin: CAT 7.1 (Day 3)Document2 pages1 Sin 1 Sin: CAT 7.1 (Day 3)api-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Notes 4/11/16Document2 pagesAAA Notes 4/11/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Notes 4/4/16Document5 pagesAAA Notes 4/4/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- College Algebra and Trig (CAT) Prystalski Chapter 7 - Analytic Trigonometry Number Date Due Read Section Topic AssignmentDocument2 pagesCollege Algebra and Trig (CAT) Prystalski Chapter 7 - Analytic Trigonometry Number Date Due Read Section Topic Assignmentapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Xy X y Xy y X X Y: Section 7.1 Try These Problems Now. Simplify Each Expression, Find A Common Denominator FirstDocument1 pageXy X y Xy y X X Y: Section 7.1 Try These Problems Now. Simplify Each Expression, Find A Common Denominator Firstapi-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Notes 4/6/16Document5 pagesAAA Notes 4/6/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- (Sin) 3 3 Sin 2 4: Sin 3 Sin 2 (Cos) Cos 1 Cos 2 1 1 Cos 2 8Document2 pages(Sin) 3 3 Sin 2 4: Sin 3 Sin 2 (Cos) Cos 1 Cos 2 1 1 Cos 2 8api-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Notes 4/6/16Document5 pagesAAA Notes 4/6/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- REVIEW - 7.1 Basic Trigonometric Identities: Sin Cos 1 Tan 1 Sec 1 Cot CSCDocument2 pagesREVIEW - 7.1 Basic Trigonometric Identities: Sin Cos 1 Tan 1 Sec 1 Cot CSCapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Advanced Algebra A 2015-2016 Prystalski: Date Section Topic HomeworkDocument1 pageAdvanced Algebra A 2015-2016 Prystalski: Date Section Topic Homeworkapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Law of Sines Law of Cosines NeitherDocument3 pagesLaw of Sines Law of Cosines Neitherapi-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Section 8-6 PracticeDocument2 pagesAAA Section 8-6 Practiceapi-168512039No ratings yet
- 6.5 Trig Functions of Nonacute Angles: Mathematician: - PeriodDocument2 pages6.5 Trig Functions of Nonacute Angles: Mathematician: - Periodapi-168512039No ratings yet
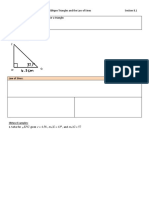
- Review: What Does It Mean To Solve For A Triangle:: CAT Oblique Triangles and The Law of Sines Section 8.1Document3 pagesReview: What Does It Mean To Solve For A Triangle:: CAT Oblique Triangles and The Law of Sines Section 8.1api-168512039No ratings yet
- AAA Notes 3/15/16Document3 pagesAAA Notes 3/15/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- Aaa NotesDocument5 pagesAaa Notesapi-168512039No ratings yet
- CAT Pi Notes 3.14Document3 pagesCAT Pi Notes 3.14api-168512039No ratings yet
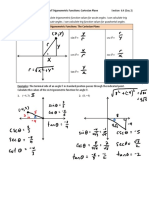
- Learning Goals: I Can Convert Between Degrees and Radians. I Can Calculate The Length of An Arc Along A CircleDocument2 pagesLearning Goals: I Can Convert Between Degrees and Radians. I Can Calculate The Length of An Arc Along A Circleapi-168512039No ratings yet
- CAT Transformations: NameDocument3 pagesCAT Transformations: Nameapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Angular/Linear Velocity ProblemsDocument3 pagesAngular/Linear Velocity Problemsapi-168512039No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledapi-168512039No ratings yet
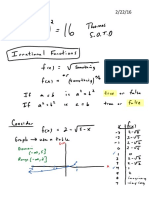
- Aaa Notes 2/22/16Document5 pagesAaa Notes 2/22/16api-168512039No ratings yet
- 1 Full Rotation 360 2 (Degrees) (Radians)Document3 pages1 Full Rotation 360 2 (Degrees) (Radians)api-168512039No ratings yet
- 6.5 - PART 2: 1. Find All Possible Values of Between, Where CotDocument1 page6.5 - PART 2: 1. Find All Possible Values of Between, Where Cotapi-168512039No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Learning Goals: I Can Determine What Angles Result in A Given Trigonometric FunctionDocument1 pageLearning Goals: I Can Determine What Angles Result in A Given Trigonometric Functionapi-168512039No ratings yet
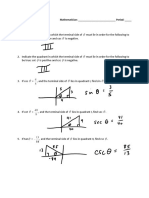
- 6.5 - PART 1: 1. Indicate The Quadrant in Which The Terminal Side of Be True: TanDocument1 page6.5 - PART 1: 1. Indicate The Quadrant in Which The Terminal Side of Be True: Tanapi-168512039No ratings yet
- 6.5 - PART 3: Mathematician: - PeriodDocument1 page6.5 - PART 3: Mathematician: - Periodapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Opposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse: Sin CosDocument2 pagesOpposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse: Sin Cosapi-168512039No ratings yet
- Learning Goals: I Can Plot Angles in Standard Position. I Can Identify Coterminal AnglesDocument2 pagesLearning Goals: I Can Plot Angles in Standard Position. I Can Identify Coterminal Anglesapi-168512039No ratings yet