Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disas Chemistry Year 09 Test2
Disas Chemistry Year 09 Test2
Uploaded by
Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Disas Chemistry Year 09 Test2
Disas Chemistry Year 09 Test2
Uploaded by
Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleCopyright:
Available Formats
DISAS CHEMISTRY YEAR 09 TEST2
TOPIC: ATOMIC STRUCTURE SUB TOPIC(S) DISCOVERY OF THE STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM
1. Two parts of an atom are: ...................................................... and
....................................(2mks)
2. Put a tick () in the box of an element below that has only one electron and one proton:
-
Helium [ ]
Hydrogen [ ]
Nitrogen [ ]
(1mk)
3. Complete the table below by stating the characteristics of atomic particles on the table.
Particle
Charge
Mass
Location
Electron
Neutron
Proton
(9mks)
4. Complete the table by matching each observation to a conclusion drawn by Lord Ernest
Rutherford gold foil experiment. An example is already done for you.
Statements
Conclusion
More than 90% of the alpha
particles passed through the gold
foil undeflected
The centre of an atom called the
nucleus is very small.
Some alpha particles bounce
back
The nucleus is positively
charged.
A few alpha particles were
deflected
The nucleus is massive
A few alpha particles deviated
from their path of incident
An atom is mostly made up of
large empty space
(3mks)
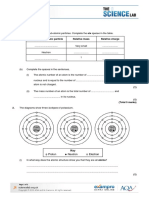
5. Identify A to D on the diagram below for Rutherford gold foil experiment.
B
C
A:
D
CHM YEAR 09 TEST2 Page 1 of 3
B:
C:
D:
(4mks)
6. Complete the table by linking a particular atomic model to the scientist who proposed it.
An example is already done for you.
Model of atom
Scientist who proposed it
Solid sphere model
James Chadwick
The nuclear model
Joseph John (J.J) Thomson
Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford
John Dalton
(2mks)
7. The diagram in Figure 1 shows the behaviour of the three sub-atomic particles when
passed through an electric field.+
A
B
C
Figure 1
(i)
Identify the particles represented by A, B, and C.
A ....................................................... B ............................................................
C .......................................................
(ii) Explain the why each of the particles A, B or C behaves as shown on in figure 1.
Explanation for behaviour of particle A in electric field.
....................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................... ........................
CHM YEAR 09 TEST2 Page 2 of 3
Explanation for behaviour of particle B in electric field.
....................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................... ........................
Explanation for behaviour of particle C in electric field.
....................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................... ............... (6mks)
END !!!
[Grand total = 27 mks]
CHM YEAR 09 TEST2 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Atomic Structure Past Paper QuestionsDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure Past Paper QuestionsOshan Dissanayake75% (4)
- IB Topic 3 Thermal Physics Question BookletDocument19 pagesIB Topic 3 Thermal Physics Question Bookletpixelhobo67% (3)
- Disas Chemistry Year 09 Test1Document2 pagesDisas Chemistry Year 09 Test1Nkemzi NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Pp2Document8 pagesSet 1 Pp2collinsaroniofficialNo ratings yet
- Form 2 2023 End T3 Chemistry QN - TeacherDocument12 pagesForm 2 2023 End T3 Chemistry QN - TeacherDaniel KibetNo ratings yet
- 2. Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions (1)Document7 pages2. Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions (1)Sangita Das BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSEDocument6 pagesWorksheet IGCSEsiennaNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 11 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDocument9 pagesBritish International College: Year 11 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonNo ratings yet
- Grade 08 CambDocument6 pagesGrade 08 CambShohani HapuarachchiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formulae and EquationsIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeNo ratings yet
- f2 Endterm 1 Series 2Document70 pagesf2 Endterm 1 Series 2abu326274No ratings yet
- Chem F2Document13 pagesChem F2Qiash JontezNo ratings yet
- Modul KimiaDocument57 pagesModul KimiaAZIE207No ratings yet
- Form 2 Chem End Term 1 2024Document11 pagesForm 2 Chem End Term 1 2024blueivyl872No ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY-QDocument15 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY-Qjuicetabp1No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY F2 QN Teacher - Co - .Ke End Term 2Document10 pagesCHEMISTRY F2 QN Teacher - Co - .Ke End Term 2KevinNo ratings yet
- James Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsDocument12 pagesJames Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsLisWeiNo ratings yet
- C2 3 1 Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesC2 3 1 Atomic StructureKirsty HewittNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) JUJ 2010 Chemistry PDFDocument197 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) JUJ 2010 Chemistry PDFKak Ngah FienaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 4 4S Ping XinDocument2 pagesQUIZ 4 4S Ping XinWen YaoNo ratings yet
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Document27 pagesStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Chem F2Document8 pagesChem F2Festus NanokNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Exam ET 2014Document20 pages5th Form Exam ET 2014NIRVAN RAMESHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Topic 1 TestDocument8 pagesChemistry - Topic 1 TestAnonymous ANo ratings yet
- Revision Session I - End Semester ExaminationDocument5 pagesRevision Session I - End Semester ExaminationAyanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR Tugasan f5Document7 pagesNUCLEAR Tugasan f5Nurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- H2 Quantum Physics - Part 1 Tutorial 2014 - StudentDocument17 pagesH2 Quantum Physics - Part 1 Tutorial 2014 - StudentweinengxxNo ratings yet
- Test On Electrolysis Grade IXDocument13 pagesTest On Electrolysis Grade IXkrisnuNo ratings yet
- Form 3 ChemDocument6 pagesForm 3 ChemFestus NanokNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerDocument36 pagesUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- Chemist f5 Paper 3 2015Document7 pagesChemist f5 Paper 3 2015putri_latifahNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assignment 2Document6 pagesAtomic Structure Assignment 2misbah shahidNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry CIE Question 1Document3 pagesAs Chemistry CIE Question 1danielmahsaNo ratings yet
- F2 Chem Et2 QNDocument11 pagesF2 Chem Et2 QNJOSEPH MWANGINo ratings yet
- CHEM PAPER 1 FORM 3 T3 2023 Kcse RevDocument9 pagesCHEM PAPER 1 FORM 3 T3 2023 Kcse ReveastnetdigitalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F3 QNSDocument5 pagesChemistry F3 QNSangelinenyaboke360No ratings yet
- C2 Structures and Bonding HigherDocument14 pagesC2 Structures and Bonding HigherdownendscienceNo ratings yet
- 3perep Final PDFDocument14 pages3perep Final PDFMohamed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY FORM TWO Holiday Assignment Term1Document16 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM TWO Holiday Assignment Term1jackemmanuel771No ratings yet
- g10 Review WorkbookDocument16 pagesg10 Review WorkbookAnh Quân NghiêmNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Document14 pagesFinal Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Norzilah MazaharNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Document2 pagesActivity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chem Endterm 1 2024Document9 pagesForm 3 Chem Endterm 1 2024blueivyl872No ratings yet
- CI 9 Co Science Paper 4 Paper 6Document21 pagesCI 9 Co Science Paper 4 Paper 6Jyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 8.2Document12 pagesElectrochemistry 8.2sumathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper TWODocument12 pagesChemistry Paper TWOMBUGUA GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Kcse Extra-County Mocks s1Document235 pagesKcse Extra-County Mocks s1micah isabokeNo ratings yet
- Form 3 - Chemistry - Question PaperDocument14 pagesForm 3 - Chemistry - Question Papermiles computersNo ratings yet
- 09 JJ H2 Prelim P2Document15 pages09 JJ H2 Prelim P2etherfoxxNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Language School Worksheets First Term (2023 - 2024)Document10 pagesEgyptian Language School Worksheets First Term (2023 - 2024)joudyabdalla014No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 16+ Chemistry PDFDocument12 pages16+ Chemistry PDFKhyzer HayyatNo ratings yet
- Electron StructureDocument13 pagesElectron Structuredejla67No ratings yet
- Atoms, Electron Structure and Periodicity HWDocument15 pagesAtoms, Electron Structure and Periodicity HWrojersymondsNo ratings yet
- F3 ChemDocument12 pagesF3 ChemFred ObotaNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT2Document2 pagesPeriodicity (ANNEX) - CN - STDT2Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry (CURRENT) - STDT6Document2 pagesElectrochemistry (CURRENT) - STDT6Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibria 01-TEXTBOOK - TCHADocument4 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria 01-TEXTBOOK - TCHANkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Document2 pagesActivity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Document2 pagesActivity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Nkemzi Elias Nzetengenle100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDocument6 pagesStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- T3HQDocument9 pagesT3HQNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- 2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Document3 pages2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Form Three ChemitryDocument1 pageForm Three ChemitryNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDocument4 pagesSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Activity 17 (Preparation of Salts)Document4 pagesActivity 17 (Preparation of Salts)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Reaction Rates' Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument12 pagesFactors Affecting Reaction Rates' Chemical Kinetics PDFNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Percent CompositionDocument2 pagesWorksheet Percent CompositionNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Solu Bility Curve WorksheetDocument2 pagesSolu Bility Curve WorksheetNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet