Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - 4i Rotational Flow
1 - 4i Rotational Flow
Uploaded by
msmgectOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - 4i Rotational Flow
1 - 4i Rotational Flow
Uploaded by
msmgectCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydraulics
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara
(i) Rotational and Irrotational flow
Flow
Radial motion or Radial flow
Rotary or Vortex Motion
Free vortex
Free Cylindrical Vortex
Forced vortex
Free Spiral vortex
Forced Cylindrical Vortex Forced Spiral vortex
Basically there are two types of motion
(i) Translation and
(ii) Rotation
The two may exist independently or simultaneously.
If now an element is represented, it may be subjected to deformation. This can be linear
or angular.
If the motion of the particles is purely translational and the distortion is symmetrical, the
flow is irrotational and the vorticity
v y vx
=cons tant .
x
y
Example: Flownet application.
Forced vortex is also known as flywheel vortex.
Free vortex is also known as potential vortex.
v
=C
r
vr =C
Compound vortex combination of free and forced vortex also known as Rankine vortex.
Spiral vortex (free vortex and a radial flow).
Rotation of a fluid, moving as a solid, about an axis is called forced vortex motion. Every
particle of fluid will have same angular velocity.
Free vortex motion:
Each particle moves in a circular path with speed varying inversely as the distance from
the centre
vr =cons tant
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Hydraulics
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara
r0
2r2
______
Paraboloid
2g
C
L
Forced vortex
v
=cons tant
r
. Rotation of the fluid in a tea cup is an example of a forced vortex.
Sharp curved orifice
Bath tub vortex
(Basic vortex)
Vortex
Rotational flow
Irrotational flow
Application
(i) Vertical intake in Reservoir
(ii) Horizontal intake
(iii) Pump sump intake
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Hydraulics
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara
surface vortex
subsurface vortex
(submerged or underwater vortex)
1
(a)
(b)
(c)
local vortex
concentric or column vortex
Open air-core
(vortex orifice flow)
dimple
line vortices
Types of vortices due to location of appearance and resulting shape
1
description
due to:
1) increase of circulation
2) development relative to
the intake
3) Physical
explanation
weak
undeveloped
combined potential
and rotational vortex
(Rankine vortex)
critical
critical
critical stage
for air-entrainment
strong
developed
potential vortex or free
spiral vortex with an
open air-core
The different types of stable surface vortices at intakes vertically
downstream (drain vortices), indication and distinction
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Hydraulics
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara
Vt Tangential velocity
Free Vortex
Vt = ____
2-r r
Forced vortex
Vt = r
(vorticity)
2
Combined vortex
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Hydraulics
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara
o
rc
Flow around a 90 bend ___ = 0.5
b
Zone of seperation, Shock waves and Hydraulic jump can be seen
in the downstream of the bend (after Thandaveswara)
(iv) Cyclone.
Rankine vortex is a combination of free and forced vortex.
Forced vortex (inner core region) and Free vortex (in outer core region).
Free vortex tangential velocity
Pressure distribution
Velocity distribution
2ro
Rankine vortex
v = wr
t
C
v =
,r <r
t 2 r o
Vortices can be classified based on vortex strength. A basic vortex also referred as bath
tub vortex.
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
You might also like
- Free & Force Vortex (Full Lab Report)Document39 pagesFree & Force Vortex (Full Lab Report)So Lah Musa75% (8)
- Aerodynamics 1 Question BankDocument24 pagesAerodynamics 1 Question BankSaravanan Durairaj100% (1)
- Free Force VortexDocument25 pagesFree Force Vortexamirul84% (19)
- Experiment 2 (Free and Forced Vortex)Document22 pagesExperiment 2 (Free and Forced Vortex)paan78% (9)
- Free and Forced Vortex PDFDocument4 pagesFree and Forced Vortex PDFRana HanzlaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 02 Forced Vortex MotionDocument2 pagesExperiment No.: 02 Forced Vortex MotionMr Gk meenaNo ratings yet
- FCE 422 Lecture NotesDocument188 pagesFCE 422 Lecture NotesStephanieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Free and Force Vortex Table of ContentDocument33 pagesExperiment 2: Free and Force Vortex Table of Contentmarz95No ratings yet
- Exp 3 Free Vortex N Forced VortexDocument5 pagesExp 3 Free Vortex N Forced VortexAmrun RusrlNo ratings yet
- Swirl FlowDocument5 pagesSwirl Flowahmedmidoo1595No ratings yet
- Fluid Vortex ReportDocument12 pagesFluid Vortex ReportAhmed MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Vortex AssignmentDocument5 pagesVortex AssignmentFaisal GulzarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2212017316301463 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2212017316301463 MainTapas Kumar Pradhan ce19s014No ratings yet
- Free N Forced Vortex ReportDocument18 pagesFree N Forced Vortex ReportAuza100% (1)
- Vortex-Induced Vibration: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesVortex-Induced Vibration: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManoj PradhanNo ratings yet
- Free & Forced Vortices: ManualDocument11 pagesFree & Forced Vortices: ManualMahadevan100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document74 pagesChapter 1Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Two Dimensional Inviscid, Incompressible Flow 2 Marks Question and Answers Aerodynamics 1Document8 pagesUnit 2: Two Dimensional Inviscid, Incompressible Flow 2 Marks Question and Answers Aerodynamics 1sasiaeroNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics and KinematicsDocument17 pagesFluid Dynamics and Kinematicsjohn snowNo ratings yet
- FF Exp 6Document6 pagesFF Exp 62020ch58No ratings yet
- Free and Forced Vortex: ME15B097 ME15B098 ME15B099 ME15B100Document23 pagesFree and Forced Vortex: ME15B097 ME15B098 ME15B099 ME15B100Devashish SoniNo ratings yet
- A Numerical Simulation of Vortex Shedding From An Oscillating Circular CylinderDocument22 pagesA Numerical Simulation of Vortex Shedding From An Oscillating Circular CylinderAshish PawarNo ratings yet
- VortexDocument10 pagesVortexModestyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic MechinesDocument24 pagesHydraulic Mechinesdr hs govardhana swamyNo ratings yet
- A-Jump in Horizontal Inverted Semicircular Open Channels: Ain Shams Engineering JournalDocument8 pagesA-Jump in Horizontal Inverted Semicircular Open Channels: Ain Shams Engineering JournalMiguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Vortex - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesVortex - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSheikh Zakir100% (1)
- 2001 - J Fluid Mechanics - Swirling Flow of Viscoelastic Fluids. Part 1Document49 pages2001 - J Fluid Mechanics - Swirling Flow of Viscoelastic Fluids. Part 1Jason StokesNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Relative To Circular Cylinders: by C. H. WilliamsonDocument34 pagesSinusoidal Relative To Circular Cylinders: by C. H. Williamson李智No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture Notes (10) Fluid KinematicsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture Notes (10) Fluid KinematicsAhmedTahaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Hydraulic JumpDocument26 pagesWeek 2 Hydraulic JumpNickson KomsNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics IDocument15 pagesFluid Mechanics IUsman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Anagnostopoulos 2000Document33 pagesAnagnostopoulos 2000Manu K VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Sloshing in A Baffled Rectangular Tank Under Irregular Excitations 2023Document12 pagesLiquid Sloshing in A Baffled Rectangular Tank Under Irregular Excitations 2023Suresh HubballiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Turbines - Francis and Kaplan PDFDocument16 pagesReaction Turbines - Francis and Kaplan PDFDeva Raj100% (3)
- Lab VortexDocument22 pagesLab VortexaminsubriNo ratings yet
- Rohini 42795977333Document3 pagesRohini 42795977333madesh1047No ratings yet
- Guilmineau JFS 2002 PDFDocument22 pagesGuilmineau JFS 2002 PDFAntonio Martín AlcántaraNo ratings yet
- Vortex Formation in The Wake of An Oscillating Cylinder PDFDocument27 pagesVortex Formation in The Wake of An Oscillating Cylinder PDFAntonio Martín AlcántaraNo ratings yet
- VortexDocument8 pagesVortexZzPumpkingNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-FREE N FORCE VORTEXDocument18 pagesLab 3-FREE N FORCE VORTEXfahmirased100% (1)
- Hydraulic Jump - 1Document3 pagesHydraulic Jump - 1Manmohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Journal of Fluids and Structures: P.W. BearmanDocument11 pagesJournal of Fluids and Structures: P.W. Bearmanshahid fazalNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument7 pagesExperimentShekharNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Kinematics of Fluid FlowDocument50 pagesFluid Mechanics Kinematics of Fluid FlowEngineer yousef mohamedNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report TemplateDocument17 pagesSeminar Report TemplateNasir NaqashNo ratings yet
- Active Flow Control of The Dynamic Wake Behind A Square Cylinder Using Combined Jets at The Front and Rear Stagnation PointsDocument1 pageActive Flow Control of The Dynamic Wake Behind A Square Cylinder Using Combined Jets at The Front and Rear Stagnation Pointscgb2020hit1No ratings yet
- Report 2Document25 pagesReport 2ahmedmidoo1595No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Hydraulic JumpDocument54 pagesUnit 5 Hydraulic JumpS PrathebaNo ratings yet
- Vortex Induced VibrationsDocument7 pagesVortex Induced VibrationsKevin Paredes GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Fluid TutorbinDocument141 pagesFluid TutorbinKhushboo BholeNo ratings yet
- Global Vorticity Shedding For A Vanishing WingDocument24 pagesGlobal Vorticity Shedding For A Vanishing WingCao Xuan CanhNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Vortex-Induced Vibration VIV of Bridge DecksDocument14 pagesAn Overview of Vortex-Induced Vibration VIV of Bridge Decksmohammed nimrNo ratings yet
- A Study of Drag Reduction On Cylinders With DifferDocument21 pagesA Study of Drag Reduction On Cylinders With DifferRida BoualilNo ratings yet
- Vorticity and CirculationDocument43 pagesVorticity and CirculationFabian TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document37 pagesChapter 4Aya HassanNo ratings yet
- AE2251 Part ADocument6 pagesAE2251 Part ARAJASUDHAKAR SNo ratings yet
- AE2251 Aero 2 MarksDocument6 pagesAE2251 Aero 2 MarksShankar NayakNo ratings yet
- Flow-Induced Vibrations of Single and Multiple HeaDocument50 pagesFlow-Induced Vibrations of Single and Multiple HeaAudrey Salsza Maret RoberteNo ratings yet
- Lathe Graphics: Exploring Visual Manipulation in Lathe Graphics through Computer VisionFrom EverandLathe Graphics: Exploring Visual Manipulation in Lathe Graphics through Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- 15 Queries About Form 16 Answered and Its Impact On Tax Filing - Yahoo India FinanceDocument3 pages15 Queries About Form 16 Answered and Its Impact On Tax Filing - Yahoo India FinancemsmgectNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Systems (EMS) : ObjectivesDocument11 pagesEnergy Management Systems (EMS) : ObjectivesmsmgectNo ratings yet
- Leaders at Various Places Centre LeadersDocument1 pageLeaders at Various Places Centre LeadersmsmgectNo ratings yet
- IT and Cyber Laws Study MaterialDocument3 pagesIT and Cyber Laws Study MaterialmsmgectNo ratings yet
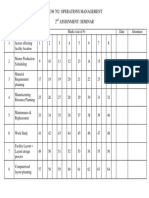
- Me09 702: Operations Management 2 Assignment: SeminarDocument1 pageMe09 702: Operations Management 2 Assignment: SeminarmsmgectNo ratings yet
- Me09 702: Operations Management Study Guide: Topic Chapters Remarks Mahajan PaneerselvamDocument1 pageMe09 702: Operations Management Study Guide: Topic Chapters Remarks Mahajan PaneerselvammsmgectNo ratings yet
- Gurus of Total Quality ManagementDocument1 pageGurus of Total Quality ManagementmsmgectNo ratings yet
- Safety InterlockDocument5 pagesSafety InterlockmsmgectNo ratings yet
- 0, Continuity Equation, W : Mass BalanceDocument1 page0, Continuity Equation, W : Mass BalancemsmgectNo ratings yet
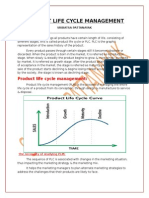
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementmsmgectNo ratings yet
- 7ps Future Trends in MarketingDocument12 pages7ps Future Trends in MarketingPeriyasamy PoovendranNo ratings yet
- Indian History - Chronology of India's Freedom StruggleDocument16 pagesIndian History - Chronology of India's Freedom StrugglemsmgectNo ratings yet
- Tips Tricks and Formulae On Ratio and ProportionDocument6 pagesTips Tricks and Formulae On Ratio and ProportionmsmgectNo ratings yet