Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LSDDLM
LSDDLM
Uploaded by
anothersomeguy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageAn electric circuit requires a power supply, load, and wires to connect them. A circuit diagram uses symbols to represent components. Current (I) is the flow of electric charge. It can flow conventionally from positive to negative, or by electron flow from negative to positive. Instruments like ammeters and voltmeters measure current and voltage respectively. Resistance (R) is a component's opposition to current flow, affected by factors like length, area, temperature and resistivity.
Original Description:
qet qeqt qet qetqb
Original Title
lsddlm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn electric circuit requires a power supply, load, and wires to connect them. A circuit diagram uses symbols to represent components. Current (I) is the flow of electric charge. It can flow conventionally from positive to negative, or by electron flow from negative to positive. Instruments like ammeters and voltmeters measure current and voltage respectively. Resistance (R) is a component's opposition to current flow, affected by factors like length, area, temperature and resistivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageLSDDLM
LSDDLM
Uploaded by
anothersomeguyAn electric circuit requires a power supply, load, and wires to connect them. A circuit diagram uses symbols to represent components. Current (I) is the flow of electric charge. It can flow conventionally from positive to negative, or by electron flow from negative to positive. Instruments like ammeters and voltmeters measure current and voltage respectively. Resistance (R) is a component's opposition to current flow, affected by factors like length, area, temperature and resistivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
24
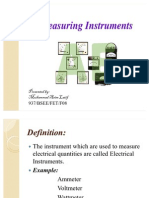
Understandable electric circuits
Basic concepts
Electric circuit: A closed loop of pathway with electric current flowing
through it.
Requirements of a basic circuit:
Power supply (power source): A device that supplies electrical energy
to a load.
Load: A device that is connected to the output terminal of a circuit,
and consumes electrical energy.
Wires: Wires connect the power supply unit and load together, and
carry current flowing through the circuit.
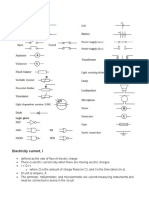
Schematic: A simplified circuit diagram that shows the interconnection of
circuit components, and is represented by circuit symbols.
Circuit symbols: The idealization and approximation of the actual circuit
components.
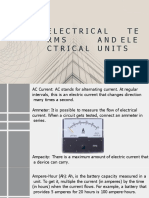
Electric current (I): A flow of electric charges through an electric circuit:
I Q/t (or I dq/dt).
Current direction:
Conventional current flow version: A flow of positive charge
(proton) from the positive terminal of a power supply to its negative
terminal.
Electron flow version: A flow of negative charge (electron) from the
negative terminal of a power supply unit to its positive terminal.
Ammeter: An instrument used for measuring current, represented by the
symbol A . It should be connected in series in the circuit.
Electromotive force (EMF): An electric pressure or force supplied by a
voltage source causing current to flow in a circuit.
Voltage (V) or potential difference: The amount of energy or work that would
be required to move electrons between two points: V W/Q (or v dw/dt).
Source voltage or applied voltage (E or VS): EMF can be called source
voltage or applied voltage. The EMF is supplied by a voltage source and
applied to the load in a circuit.
Load voltage (V): Voltage across two terminals of the load.
Voltage drop: Voltage across a component when current flows from a
higher potential point to a lower potential point in a circuit.
Voltage rise: Voltage across a component when current flows from a lower
point to a higher point in a circuit.
Voltmeter: An instrument used for measuring voltage. Its symbol is V
and it should be connected in parallel with the component.
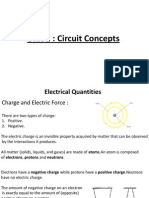
Resistor (R): A two-terminal component of a circuit that limits the flow of
current.
Resistance (R): Measure of a materials opposition to the flow of current.
Factors affecting resistance: R r=A, where cross-sectional area (A),
length (), temperature (T) and resistivity (r).
Ohmmeter: An instrument used for measuring resistance. Its symbol is
and the resistor must be removed from the circuit to measure the resistance.
You might also like
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument17 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringRovick TarifeNo ratings yet
- Thevenin Theorem, Maximum Power TransformDocument17 pagesThevenin Theorem, Maximum Power TransformMomina ShakeelNo ratings yet
- TermsDocument3 pagesTermsivanNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Basic Terminology: A/C CurrentDocument4 pagesElectronics: Basic Terminology: A/C CurrenttowsenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of DC Circuits by PekikDocument27 pagesFundamentals of DC Circuits by PekikAnonymous pCzMEWeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: DC Circuit TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 2: DC Circuit TheoryTaonga NhambiNo ratings yet
- EST 130 BEE Module 1Document94 pagesEST 130 BEE Module 1Gayathri VijayachandranNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument26 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and Definitionspondu888No ratings yet
- Electrical Terms and UnitsDocument28 pagesElectrical Terms and UnitsMichael PachecoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysisthangarajelectres100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument13 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsHazel NantesNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-1Document99 pagesNA Unit-1phani5016No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Wyklad 1Document46 pagesElectrical Circuits Wyklad 1Afaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Aru 302Document34 pagesAru 302Michael PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFDocument8 pagesMohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Back To TopDocument6 pagesBack To TopBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- As Physics Chapter 12 NotesDocument15 pagesAs Physics Chapter 12 NotesYumna AlSuleimaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 ElectricalDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 ElectricalUsamaNo ratings yet
- 21Ees101T-Electrical and Electronicsengineering: Unit 1Document6 pages21Ees101T-Electrical and Electronicsengineering: Unit 1Femi RNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 - 1Document3 pagesUnit 02 - 1raghg2005No ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotesMohammed Ibrahim Lodhi -802797/SLCNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ElectricityDocument24 pagesDynamic Electricitykrabbytom11No ratings yet
- EC100 Elements of ECE: Module - I: RLC CircuitsDocument17 pagesEC100 Elements of ECE: Module - I: RLC CircuitsJustin S BudarpurNo ratings yet
- 21Ees101T-Electrical and Electronicsengineering: Unit 1Document6 pages21Ees101T-Electrical and Electronicsengineering: Unit 1Femi RNo ratings yet
- Definition of Electrical TermDocument2 pagesDefinition of Electrical TermLuis Carlos100% (1)
- Wattmeter 1Document29 pagesWattmeter 1khawar iqbalNo ratings yet
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionDocument31 pages5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics PresentationDocument18 pagesMedical Physics Presentationsamavia sohailNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument9 pagesCurrent ElectricitySayeed SKNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical CircuitssaranphodNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document78 pagesUnit 1Atharva RaksheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Concept NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Basic Concept NotesGangga RobleNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits Part 1Document15 pagesDC Circuits Part 1Soham RaneNo ratings yet
- CLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityDocument63 pagesCLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityannigarwalNo ratings yet
- Transformer:: S P S PDocument4 pagesTransformer:: S P S PMoiz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Review of Basic Circuit ConceptsDocument52 pagesReview of Basic Circuit ConceptsIsmail kabirNo ratings yet
- Verification of Superposition Thereom: Measurement of Power With WattmeterDocument2 pagesVerification of Superposition Thereom: Measurement of Power With Wattmetersateesh83No ratings yet
- As Physics Electricity Chapter 9Document17 pagesAs Physics Electricity Chapter 9LawrenceOnthugaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit SymbolsDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbolsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Basic Eee (Chapter7,8,9)Document14 pagesBasic Eee (Chapter7,8,9)anikNo ratings yet
- Subject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Document30 pagesSubject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Jay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice IIDocument8 pagesWorkshop Practice IISurendra GhalanNo ratings yet
- BEEE (ELT-112) : Ac & DC CircuitsDocument21 pagesBEEE (ELT-112) : Ac & DC CircuitsRocky SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITYou Can Shine AtomNo ratings yet
- For LabDocument2 pagesFor LabjondoeNo ratings yet
- BE Circuit ConceptsDocument15 pagesBE Circuit ConceptsVivekPatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BEEEDocument77 pagesUnit 1 BEEERAMESHBABU SEKARNo ratings yet
- Physics: AssignmentDocument27 pagesPhysics: AssignmentElakkiya Elakkiya0% (1)
- Network Theory: Lecture 1: Introduction 2nd Yr ECE 3rd Semester ECC303Document12 pagesNetwork Theory: Lecture 1: Introduction 2nd Yr ECE 3rd Semester ECC303Sandip DasNo ratings yet
- What Is An Electric Circuit?Document8 pagesWhat Is An Electric Circuit?Josiah ZeusNo ratings yet
- CHMA Unit - IIIDocument6 pagesCHMA Unit - IIISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier and Smoothing FiltersDocument3 pagesDiode Rectifier and Smoothing Filtersppat2006No ratings yet
- AE - 01 - Basic ElectricityDocument24 pagesAE - 01 - Basic ElectricitydhakaeurekaNo ratings yet
- Apuntes TecnologíaDocument1 pageApuntes TecnologíaZaryanGamerNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesCurrent ElectricityKamesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Provided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUODocument53 pagesProvided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUOMuhd AkmalNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Processing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Sa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'JaDocument1 pageSa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'Jaanothersomeguy0% (1)
- A A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsDocument1 pageA A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- F F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordDocument1 pageF F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasDocument1 pageB B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- R R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesDocument1 pageR R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthDocument1 pageA A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyDocument1 pageB B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Y Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeanDocument1 pageY Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- C C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsDocument1 pageC C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- E E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantDocument1 pageE E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- M M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeanDocument1 pageM M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- T T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoDocument1 pageT T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsDocument1 pageVegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- D'fghae (Ruig (OeairDocument1 pageD'fghae (Ruig (OeairanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EanDocument1 pageB B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- L L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceDocument1 pageL L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Humidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureDocument1 pageHumidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- O O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionDocument1 pageO O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- JJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteDocument1 pageJJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Components: Breadboard GuideDocument1 pageEquipment and Components: Breadboard GuideanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeterDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeteranothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageDocument1 page1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Voltage V (Or Potential Difference)Document1 pageVoltage V (Or Potential Difference)anothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceDocument1 page1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Reference Direction of CurrentDocument1 pageReference Direction of CurrentanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsDocument1 page1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaanothersomeguyNo ratings yet