Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spongy Bone
Spongy Bone
Uploaded by
api-302547403Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spongy Bone
Spongy Bone
Uploaded by
api-302547403Copyright:
Available Formats
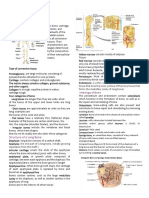
Spongy bone is a network of irregularly-shaped sheets and spikes of bone (trabeculae).
The
trabeculae are only a few cell layers thick. The spaces between the trabeculae contain red or
yellow marrow, depending on a person's age and on which bone it is. The marrow in these
images is red marrow.
Compact bone has a sturdy calcified (meaning calcium deposit) matrix with very few spaces.
This layer not only forms a protective shell around the spongy bone tissue but it also gives our
bones their rigidity, strength, and resistance.
Periosteum and is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the joints
of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of all bones.
There are two types of bone marrow: red marrow (also known as myeloid tissue) and yellow
marrow. Red blood cells, platelets and most white blood cells arise in red marrow; some white
blood cells develop in yellow marrow. The color of yellow marrow is due to the much higher
number of fat cells.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401Document18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401slyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Bones and Cartilage Structure and Types 0F Bones and Cartilage Ossification Bone Growth and ResorptionDocument75 pagesUnit 2: Bones and Cartilage Structure and Types 0F Bones and Cartilage Ossification Bone Growth and Resorptionsourya jyoti dashNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Red and Yellow Bone MarrowDocument2 pagesDifference Between Red and Yellow Bone MarrowWilrenz CastroNo ratings yet
- Bone StructureDocument3 pagesBone Structuresomya mathurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MariebDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mariebmissy23papNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - System AnatomyDocument89 pagesSkeletal - System AnatomysanayaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesSkeletal SystemRaven LacsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue) Is A Hard Tissue, A Type of Dense Connective Tissue. It HasDocument1 pageBone Tissue Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue) Is A Hard Tissue, A Type of Dense Connective Tissue. It HasDean PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Ana PhysioDocument6 pagesAna PhysioZyra ObedencioNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bone Skeletal Chapter 6 Bone SkeletalDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Bone Skeletal Chapter 6 Bone SkeletalTran9716No ratings yet
- ALVEOLAR BoneDocument72 pagesALVEOLAR BoneArchana50% (2)
- PERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 4.2-Learning TaskDocument5 pagesPERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 4.2-Learning TaskEmmalyn PeridaNo ratings yet
- 1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalDocument27 pages1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalAshar AbilowoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesDDNo ratings yet
- Bone and Bone MarrowDocument5 pagesBone and Bone MarrowFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- BC (H) - IV-Human Physiology-Bone Structure and Formation-2 & 3Document32 pagesBC (H) - IV-Human Physiology-Bone Structure and Formation-2 & 3Starco ForeverNo ratings yet
- Femur in Lower Limb) .: Ankle)Document2 pagesFemur in Lower Limb) .: Ankle)Pekeng IlokanoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesHuman Anatomy 4Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdora.ivy892100% (23)
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1donnawugnwsjrzcxt100% (31)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesThe Skeletal SystemrizzamaearancesNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Rzgar F. RashidDocument23 pagesThe Skeletal System: Rzgar F. Rashidyıldız kubeNo ratings yet
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- Functions of BoneDocument7 pagesFunctions of BoneDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument123 pagesSkeletal SystemFernando DisuNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 AnaphyDocument8 pagesChap 6 AnaphyNicholle VelosoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Skeletal System: Skeleton Dried Up BodyDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Skeletal System: Skeleton Dried Up BodyKenn yahweexNo ratings yet
- Histology of BoneDocument20 pagesHistology of Boneyudha anantha khaerul putraNo ratings yet
- Espartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDocument7 pagesEspartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDanelleNo ratings yet
- 1) - Bone As An OrganDocument3 pages1) - Bone As An OrganSofia LoveNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesIntoduction To The Skeletal SystemDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 5Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesHuman Anatomy 5Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJenniferWhitebctr100% (12)
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal Systemnichole2anne2rodriguNo ratings yet
- (Bones 5)Document12 pages(Bones 5)Khan KingNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Document67 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument32 pagesConnective TissuedennymaeperpetuaNo ratings yet
- Histology of A BoneDocument26 pagesHistology of A BoneAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cartilage and BoneDocument27 pages1.2 Cartilage and BonePema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lesson 1 CompletedDocument40 pagesPhysiology Lesson 1 CompletedIkenna OnyewuotuNo ratings yet
- TARI ReferensiDocument13 pagesTARI ReferensitariNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesHuman Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Solutions Manualjillhenrysetcjnzrfp100% (27)
- m5 Skeletal SystemDocument33 pagesm5 Skeletal Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Bone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PDocument75 pagesBone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PAnalhaq ShaikhNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 7 Skeletal SystemDocument163 pagesUNIT - 7 Skeletal SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Bone Anatomy Good NotesDocument16 pagesBone Anatomy Good NotesDENACE JnrNo ratings yet
- SkeletAl SystemDocument18 pagesSkeletAl SystemYen BailadoNo ratings yet
- Functions of The BonesDocument10 pagesFunctions of The BonesAlen OsmanovicNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureDocument54 pagesCh. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureHilary OliverioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONo ratings yet
- 7 - BoneDocument36 pages7 - BoneKhdhir M. SalemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System More On ProcessDocument4 pagesSkeletal System More On Processsayie potatoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument11 pagesBone AnatomyLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument16 pagesCranial Nervesapi-302547403100% (1)
- CircumductionDocument1 pageCircumductionapi-302547403No ratings yet
- ElevationdepressionDocument1 pageElevationdepressionapi-302547403No ratings yet
- Cardiac MuscleDocument1 pageCardiac Muscleapi-302547403No ratings yet
- SarcopeniaDocument10 pagesSarcopeniaapi-302547403No ratings yet