Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cornell Notes 3
Cornell Notes 3
Uploaded by
api-302904199Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MSDS BriquettesDocument4 pagesMSDS BriquettesKrishnudu NallaNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance Manual: Wheel LoaderDocument31 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual: Wheel LoaderWalter Esteban PeraltaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Document16 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Shiv Ganesh100% (1)
- Aure8 InQuartation Gold Refining EquipmentDocument6 pagesAure8 InQuartation Gold Refining EquipmentAFLAC ............100% (1)
- APES Chapter 3 NotesDocument4 pagesAPES Chapter 3 Noteskhushi100% (1)
- 8.4 Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument16 pages8.4 Biology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point SummaryDocument8 pagesPreliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point Summaryluke0thompsonNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- 2 The Origin of LifeDocument39 pages2 The Origin of LifeRydel GreyNo ratings yet
- 1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's OriginDocument40 pages1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's Originapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Evolutionxii 180730153121 PDFDocument45 pagesEvolutionxii 180730153121 PDFrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- Socratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byDocument5 pagesSocratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byVeronique Plaatjies100% (1)
- Evolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BDocument50 pagesEvolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BtommerraasanneNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument19 pagesOrigin of LifeMary Grace BesinNo ratings yet
- Theories of OriginDocument7 pagesTheories of OriginAbby VillaNo ratings yet
- Evolution Complete ChapterDocument40 pagesEvolution Complete ChapterJairam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Early EarthDocument18 pagesEarly EarthErenst Paul A. BaliuagNo ratings yet
- Module Q.2 ElsDocument4 pagesModule Q.2 Elsaltheaveniceholanda02No ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument25 pagesHistory of LifeMalik Ammar KhawarNo ratings yet
- KISS Notes Life On EarthDocument24 pagesKISS Notes Life On EarthJenniferBackhus100% (2)
- Evolution 9 28 15-10 2 15Document2 pagesEvolution 9 28 15-10 2 15api-300535941No ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 4Document6 pagesEarth Life Science Module 4Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Cell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialsDocument4 pagesCell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialssamNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument10 pagesBiology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Origins of Life Chp15Document107 pagesLecture 12 - Origins of Life Chp15Vicenta UmanaNo ratings yet
- Q2 PPT ELSDocument80 pagesQ2 PPT ELSnheill718No ratings yet
- Early Thoeries About LifeDocument22 pagesEarly Thoeries About LifeAnalyn LampaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemoDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemogladiatornthabiNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument9 pagesHistory of Life On EarthblablaNo ratings yet
- Earthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedDocument17 pagesEarthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedRhea RegaladoNo ratings yet
- How Did Life Begin?: 4 Overlapping StagesDocument16 pagesHow Did Life Begin?: 4 Overlapping StagesDerek GordonNo ratings yet
- 2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSDocument26 pages2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSMickaela MonterolaNo ratings yet
- The History of Life On Earth: - How Did Life Begin???Document39 pagesThe History of Life On Earth: - How Did Life Begin???Ridho SaputraNo ratings yet
- E&L Science SummaryDocument4 pagesE&L Science Summarymissyyours07107No ratings yet
- General Features of The History of Life andDocument59 pagesGeneral Features of The History of Life andcatalanmariegraceNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument73 pagesOrigin of Lifeianespecial0830No ratings yet
- Biology Grade 12 Unit 4 Evolution 01Document25 pagesBiology Grade 12 Unit 4 Evolution 01tewoldeNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument36 pagesOrigin of Life On EarthGuiana Kaila Capito Ibanez100% (1)
- Topic 1 Historical Development of LifeDocument60 pagesTopic 1 Historical Development of Lifealanlomeda505No ratings yet
- History of Life CHP 1sfsDocument20 pagesHistory of Life CHP 1sfsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Life Science: Marilyn P. Mifuel INHS-SHS, Aug.2019Document69 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To Life Science: Marilyn P. Mifuel INHS-SHS, Aug.2019Erren Kyle MadayagNo ratings yet
- Introductiontolifescience 161104052948 PDFDocument48 pagesIntroductiontolifescience 161104052948 PDFZarlene SierraNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity: History of Life On EarthDocument16 pagesEvolution and Origin of Biodiversity: History of Life On EarthMelanie Caliw-caliw ValienteNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument41 pagesThe Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceJerah Mae MacajelosNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesPre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceMarjorie Rose TeodosioNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Document43 pagesThe Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 21 SummaryJamesBlackmanNo ratings yet
- Life On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryDocument10 pagesLife On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryKevin KevinNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Evolution of LifeDocument17 pagesBio-Chemical Evolution of LifeAditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Life Science Lecture 1Document29 pagesLife Science Lecture 1barryjames0528No ratings yet
- The Model School AbudhabiDocument5 pagesThe Model School AbudhabihadiyxxNo ratings yet
- Early EarthDocument16 pagesEarly EarthTIROUVENGADAME TIROUVENGADAMENo ratings yet
- Evolution PDFDocument96 pagesEvolution PDFMendes ArmyNo ratings yet
- Origin and Evolution of LifeDocument40 pagesOrigin and Evolution of LifeMary Grace BesinNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Unit 4 Part One (2016)Document36 pagesGrade 12 Unit 4 Part One (2016)Bekele GonfaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Origins of Life and EvolutionDocument56 pagesUnit 3. Origins of Life and EvolutionFlorencia Escobar BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020Document20 pagesBiodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020tanatswaNo ratings yet
- Early Earth & The Origin of Life (Ch. 26)Document27 pagesEarly Earth & The Origin of Life (Ch. 26)Muhammad Nor RifaniNo ratings yet
- 2) Origin of LifeDocument28 pages2) Origin of LifeAnthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Gbio2-Week 12Document31 pagesGbio2-Week 12Kai SilvanoNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION NotesDocument15 pagesEVOLUTION NotesThanushree.SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life - PPTX DimaporoDocument39 pagesChapter 16 - Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life - PPTX DimaporoRamon Chito S. PudelananNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility TableDocument5 pagesChemical Compatibility TableMindy GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cold Metal Transfer: A Revolution in Mechanised Root Pass Pipeline WeldingDocument3 pagesCold Metal Transfer: A Revolution in Mechanised Root Pass Pipeline Weldingargentino_ar01No ratings yet
- Kinds of RocksDocument4 pagesKinds of RocksDaddyDiddy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- Effective Recovery of Calcium and Sulfur Resources in FGD GypsumDocument12 pagesEffective Recovery of Calcium and Sulfur Resources in FGD GypsumElnathan ValadaresNo ratings yet
- Proposed Additional Content Fire Safety AwarenessDocument50 pagesProposed Additional Content Fire Safety AwarenessMarlon BernardoNo ratings yet
- Coatings 11 01446 v2Document19 pagesCoatings 11 01446 v2Habib AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Polymers: PolymerDocument17 pagesSynthetic Polymers: PolymerdiahpurnamiNo ratings yet
- Brochure ELEMENT-COMPOUND-MIXTUREDocument2 pagesBrochure ELEMENT-COMPOUND-MIXTURElerrie surioNo ratings yet
- SANS1200GADocument14 pagesSANS1200GAMark D VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- PE5623 - Lecture 05 - Natural Gas Hydrates PDFDocument70 pagesPE5623 - Lecture 05 - Natural Gas Hydrates PDFLuis Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- The Nirma Story!: - Vikram U. MoreDocument15 pagesThe Nirma Story!: - Vikram U. Moreamit_12No ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 Prelims H1 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers (For Students) PDFDocument28 pages2019 JC2 Prelims H1 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers (For Students) PDFchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- An In-Vitro Evaluation of MicroleakageDocument6 pagesAn In-Vitro Evaluation of MicroleakageDumitritaNo ratings yet
- SL Paper 2Document19 pagesSL Paper 2Kali stringsNo ratings yet
- Paint Defect Troubleshooting Guide PDFDocument16 pagesPaint Defect Troubleshooting Guide PDFRavi KhoseNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Hazardous Materials SafetyDocument38 pagesChemical and Hazardous Materials SafetyardodotNo ratings yet
- Specification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperedDocument4 pagesSpecification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperededwinbadajosNo ratings yet
- 16-ERASM Environmental Fact Sheet Cocamide DiethanolamineDocument5 pages16-ERASM Environmental Fact Sheet Cocamide DiethanolamineKuan Yau HoongNo ratings yet
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Commercial Kerosene Stoves Using Waste Cooking Oil-Kerosene BlendsDocument8 pagesPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Commercial Kerosene Stoves Using Waste Cooking Oil-Kerosene BlendsPrakash SpNo ratings yet
- Saes L 110Document12 pagesSaes L 110Karu 2No ratings yet
- NapGard - Brochure Final 8-6-15 PDFDocument4 pagesNapGard - Brochure Final 8-6-15 PDFPietro ViganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Biochemistry LectureDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Biochemistry Lecturetyler_4No ratings yet
- BethanyDocument4 pagesBethanyMama's VirgoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and TeratogensDocument7 pagesPregnancy and TeratogensLE NGNo ratings yet
Cornell Notes 3
Cornell Notes 3
Uploaded by
api-302904199Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cornell Notes 3
Cornell Notes 3
Uploaded by
api-302904199Copyright:
Available Formats
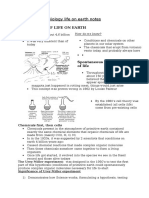
Cornell Notes
Topic/Objective:
Name: Hugo Bustamante
Class/Period: P5
The general names of what we learned
Date:10/4/15
Essential Question: To investigate how Earth and its inhabitants have changed over time
Questions:
How many years
ago did mammals
start to develop?
Who were the first
living organisms?
When did oxygen start to
come?
What were the first
conditions on
earth?
What is a species?
Notes:
What is Life?
-First we have to define Life
-Organized as cells
-Respond to stimuli
-Regulate internal processes
-Homeostasis
-Use energy to grow
-Metabalism
-Develop
-Change & mature within lifetime
-Reproduce
-Heredity
-DNA/RNA
-Adaptation & evolution
-Special Creation
-Was life created by a supernatural or driven force? (Not
Testable)
-Estraterrastrial Orgin
-Was the orginal source of organic (carbon) materials comets &
meteorites striking early earth? (Testable)
-Spontaneous Abiotic Orgin
-Did life evolve spontaneously from inorganic molecules?
-Bacteria
-Archaea
-Extremophiles = Live in extreme env.
-methanogens
-halogens
-thermophiles
-Eukarya
-eukaryotes
-protists
-fungi
-plants & animals
Summary: What I learned from this week is that how much little the time human started to develop. All the other
parts of the time had a big gap. 4 bya the earth developed and had some different conditions. They all had to do
with oxygen. Oxygen played a big factor for things to develop. So this week was more about of development.
Questions:
Notes:
-Kingdom Bacteria
-Kingdom Archaebacteria
-Kingdom Protista
-Kingdom Plantae
-Kingdom Animallea
Conditions on Early Earth
-Atmosphere full of gases
-Water vapor(H2O)
-Lots of available H
-No free oxygen
-Energy source
-Lightning, UV radiation, volcanic
Key Events in Origin of Life
-Key events in evolutionary history of life on Earth
-3.5 to 4 bya
-Prokaryotes: first living organisms
Oxygen Atmosphere
-Oxygen begins to accumulate 2.7 bya
-oxidizing atmosphere
-evidence in banded iron in rocks=rusting
-Photosynthetic bacteria (blue- green alge)
First Eukaryotes
-Development of internal membrance
-Endosymbiosis
-Evolution of eukaryotes
-Orgin of mitochondria
-Engulfed aerobic bacteria, but did not digest them
-Mutually benetical relationship
Cambrian Explosion
-Diversification of Animals
-Early Mammal Evolution
-125 mya mammals began to radiate out and fill inches
-Gradualism: evolutionary change is slow, gradual, and continuous
-Punctuated Equilibrium: A theory of the time frame required for
evolution that assumes that evolutionary change occurs in burts
with long periods of relative stability
-Species: A group of living organisms consisting of similar
individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding
-Extinction: Occurs when the environment changes and the
adaptive characteristics of a species of a species are insufficient to
allow its survival
Summary:
You might also like
- MSDS BriquettesDocument4 pagesMSDS BriquettesKrishnudu NallaNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance Manual: Wheel LoaderDocument31 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual: Wheel LoaderWalter Esteban PeraltaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Document16 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Shiv Ganesh100% (1)
- Aure8 InQuartation Gold Refining EquipmentDocument6 pagesAure8 InQuartation Gold Refining EquipmentAFLAC ............100% (1)
- APES Chapter 3 NotesDocument4 pagesAPES Chapter 3 Noteskhushi100% (1)
- 8.4 Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument16 pages8.4 Biology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point SummaryDocument8 pagesPreliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point Summaryluke0thompsonNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- 2 The Origin of LifeDocument39 pages2 The Origin of LifeRydel GreyNo ratings yet
- 1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's OriginDocument40 pages1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's Originapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Evolutionxii 180730153121 PDFDocument45 pagesEvolutionxii 180730153121 PDFrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- Socratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byDocument5 pagesSocratic Questions:: Questions and General Answers Created and Compiled byVeronique Plaatjies100% (1)
- Evolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BDocument50 pagesEvolusi - Asal Usul & Evolusi Awal Kehidupan BtommerraasanneNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument19 pagesOrigin of LifeMary Grace BesinNo ratings yet
- Theories of OriginDocument7 pagesTheories of OriginAbby VillaNo ratings yet
- Evolution Complete ChapterDocument40 pagesEvolution Complete ChapterJairam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Early EarthDocument18 pagesEarly EarthErenst Paul A. BaliuagNo ratings yet
- Module Q.2 ElsDocument4 pagesModule Q.2 Elsaltheaveniceholanda02No ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument25 pagesHistory of LifeMalik Ammar KhawarNo ratings yet
- KISS Notes Life On EarthDocument24 pagesKISS Notes Life On EarthJenniferBackhus100% (2)
- Evolution 9 28 15-10 2 15Document2 pagesEvolution 9 28 15-10 2 15api-300535941No ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 4Document6 pagesEarth Life Science Module 4Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Cell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialsDocument4 pagesCell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialssamNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument10 pagesBiology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Origins of Life Chp15Document107 pagesLecture 12 - Origins of Life Chp15Vicenta UmanaNo ratings yet
- Q2 PPT ELSDocument80 pagesQ2 PPT ELSnheill718No ratings yet
- Early Thoeries About LifeDocument22 pagesEarly Thoeries About LifeAnalyn LampaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemoDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemogladiatornthabiNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument9 pagesHistory of Life On EarthblablaNo ratings yet
- Earthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedDocument17 pagesEarthlife Science q2 Week 1 EditedRhea RegaladoNo ratings yet
- How Did Life Begin?: 4 Overlapping StagesDocument16 pagesHow Did Life Begin?: 4 Overlapping StagesDerek GordonNo ratings yet
- 2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSDocument26 pages2nd-qrt. Week-12 ELSMickaela MonterolaNo ratings yet
- The History of Life On Earth: - How Did Life Begin???Document39 pagesThe History of Life On Earth: - How Did Life Begin???Ridho SaputraNo ratings yet
- E&L Science SummaryDocument4 pagesE&L Science Summarymissyyours07107No ratings yet
- General Features of The History of Life andDocument59 pagesGeneral Features of The History of Life andcatalanmariegraceNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument73 pagesOrigin of Lifeianespecial0830No ratings yet
- Biology Grade 12 Unit 4 Evolution 01Document25 pagesBiology Grade 12 Unit 4 Evolution 01tewoldeNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument36 pagesOrigin of Life On EarthGuiana Kaila Capito Ibanez100% (1)
- Topic 1 Historical Development of LifeDocument60 pagesTopic 1 Historical Development of Lifealanlomeda505No ratings yet
- History of Life CHP 1sfsDocument20 pagesHistory of Life CHP 1sfsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Life Science: Marilyn P. Mifuel INHS-SHS, Aug.2019Document69 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To Life Science: Marilyn P. Mifuel INHS-SHS, Aug.2019Erren Kyle MadayagNo ratings yet
- Introductiontolifescience 161104052948 PDFDocument48 pagesIntroductiontolifescience 161104052948 PDFZarlene SierraNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity: History of Life On EarthDocument16 pagesEvolution and Origin of Biodiversity: History of Life On EarthMelanie Caliw-caliw ValienteNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument41 pagesThe Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceJerah Mae MacajelosNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesPre Final Module Earth and Life ScienceMarjorie Rose TeodosioNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Document43 pagesThe Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 21 SummaryJamesBlackmanNo ratings yet
- Life On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryDocument10 pagesLife On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryKevin KevinNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Evolution of LifeDocument17 pagesBio-Chemical Evolution of LifeAditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Life Science Lecture 1Document29 pagesLife Science Lecture 1barryjames0528No ratings yet
- The Model School AbudhabiDocument5 pagesThe Model School AbudhabihadiyxxNo ratings yet
- Early EarthDocument16 pagesEarly EarthTIROUVENGADAME TIROUVENGADAMENo ratings yet
- Evolution PDFDocument96 pagesEvolution PDFMendes ArmyNo ratings yet
- Origin and Evolution of LifeDocument40 pagesOrigin and Evolution of LifeMary Grace BesinNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Unit 4 Part One (2016)Document36 pagesGrade 12 Unit 4 Part One (2016)Bekele GonfaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Origins of Life and EvolutionDocument56 pagesUnit 3. Origins of Life and EvolutionFlorencia Escobar BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020Document20 pagesBiodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020tanatswaNo ratings yet
- Early Earth & The Origin of Life (Ch. 26)Document27 pagesEarly Earth & The Origin of Life (Ch. 26)Muhammad Nor RifaniNo ratings yet
- 2) Origin of LifeDocument28 pages2) Origin of LifeAnthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Gbio2-Week 12Document31 pagesGbio2-Week 12Kai SilvanoNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION NotesDocument15 pagesEVOLUTION NotesThanushree.SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life - PPTX DimaporoDocument39 pagesChapter 16 - Origin and Evolution of Microbial Life - PPTX DimaporoRamon Chito S. PudelananNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility TableDocument5 pagesChemical Compatibility TableMindy GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cold Metal Transfer: A Revolution in Mechanised Root Pass Pipeline WeldingDocument3 pagesCold Metal Transfer: A Revolution in Mechanised Root Pass Pipeline Weldingargentino_ar01No ratings yet
- Kinds of RocksDocument4 pagesKinds of RocksDaddyDiddy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- Effective Recovery of Calcium and Sulfur Resources in FGD GypsumDocument12 pagesEffective Recovery of Calcium and Sulfur Resources in FGD GypsumElnathan ValadaresNo ratings yet
- Proposed Additional Content Fire Safety AwarenessDocument50 pagesProposed Additional Content Fire Safety AwarenessMarlon BernardoNo ratings yet
- Coatings 11 01446 v2Document19 pagesCoatings 11 01446 v2Habib AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Polymers: PolymerDocument17 pagesSynthetic Polymers: PolymerdiahpurnamiNo ratings yet
- Brochure ELEMENT-COMPOUND-MIXTUREDocument2 pagesBrochure ELEMENT-COMPOUND-MIXTURElerrie surioNo ratings yet
- SANS1200GADocument14 pagesSANS1200GAMark D VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- PE5623 - Lecture 05 - Natural Gas Hydrates PDFDocument70 pagesPE5623 - Lecture 05 - Natural Gas Hydrates PDFLuis Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- The Nirma Story!: - Vikram U. MoreDocument15 pagesThe Nirma Story!: - Vikram U. Moreamit_12No ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 Prelims H1 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers (For Students) PDFDocument28 pages2019 JC2 Prelims H1 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers (For Students) PDFchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- An In-Vitro Evaluation of MicroleakageDocument6 pagesAn In-Vitro Evaluation of MicroleakageDumitritaNo ratings yet
- SL Paper 2Document19 pagesSL Paper 2Kali stringsNo ratings yet
- Paint Defect Troubleshooting Guide PDFDocument16 pagesPaint Defect Troubleshooting Guide PDFRavi KhoseNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Hazardous Materials SafetyDocument38 pagesChemical and Hazardous Materials SafetyardodotNo ratings yet
- Specification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperedDocument4 pagesSpecification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperededwinbadajosNo ratings yet
- 16-ERASM Environmental Fact Sheet Cocamide DiethanolamineDocument5 pages16-ERASM Environmental Fact Sheet Cocamide DiethanolamineKuan Yau HoongNo ratings yet
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Commercial Kerosene Stoves Using Waste Cooking Oil-Kerosene BlendsDocument8 pagesPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Commercial Kerosene Stoves Using Waste Cooking Oil-Kerosene BlendsPrakash SpNo ratings yet
- Saes L 110Document12 pagesSaes L 110Karu 2No ratings yet
- NapGard - Brochure Final 8-6-15 PDFDocument4 pagesNapGard - Brochure Final 8-6-15 PDFPietro ViganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Biochemistry LectureDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Biochemistry Lecturetyler_4No ratings yet
- BethanyDocument4 pagesBethanyMama's VirgoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and TeratogensDocument7 pagesPregnancy and TeratogensLE NGNo ratings yet