Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDF
Resultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDF
Uploaded by
Sara Jones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
147 views1 pageResultant force and terminal velocity
Original Title
Resultant force and terminal velocity.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentResultant force and terminal velocity
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
147 views1 pageResultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDF
Resultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDF
Uploaded by
Sara JonesResultant force and terminal velocity
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 1
28
Resultant Force and Terminal Velocit
Resultant Force is Real Im, int — Fspecially for "F = ma"
The notion of resultant force is @ real important one for you to get your head round.
W's not especially tricky, it's just that it seems to ge? kind of ipnored.
In most real situations there are at least two forces acting on an object along any direction.
The overall affect of these forces will decide the motion of the object — whether i will accelerate,
decelerate or ctay at a steedy speed. The "overall effect” is found by just adding or ubtracting the
forces which point along the same direction. The overall force you get is celled the resultant force.
‘And when you use the formula "F = ma’, F rnust always be the resultant force.
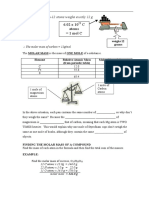
EXAMPLE: A car of mase of 1760kg has an engine which provides driving force of 5,200N.
‘At 70mph the drag force acting on the car is 5,150N.
Find its acceleration a) when first setting off from rest b) at 7Omph.
ANSWER: — I) First draw a force diagram for both cases (no need to show the vertical forces):
nest <«<<—$§ €
seyipe” Og S200N gp
2) Work out the resultant force in each case, and apply “F Using the formula triangle:
Resultant force = 5,200N Resultant force = 5,200 - 5,150
a = F/m = 6,200+1750 = 3.0 m/s* 8 = F/m = 50 +1750 = 0.08 m/s’
Cars and Free-Fallers all Reach a Terminal Velocii
When cars and free-flling objects first set off they have much more
force accelerating them than resistance slowing them down. As the
speed increases the resistance builds up. This gradually reduces the
‘agceleration until eventuslly the resistance force is equal to the
accelerating force and then it won't be able to accelerate any more.
It will have reached its maximum speed or terminal velocity.
The Terminal Velocity of fallit their Shape and Are.
The accelerating force acting on all falling objects is gravity and it would ..
make therm all fall et the same rate, If if wasn't for ait resistance.
To prove thio, on the moon, where there's no air, hamsters and feathers
dropped simultaneously will bit nd together.
However, on Earth, ait resistance causes things to fall at different speeds,
and the ferminal velocity af any object is determined by its drag in...
compatison to the weight of i. The dreg depends on its shape and area
The most important example ic the human skydiver. Without his parachute
open he has quite gmall area and a force of *W=mg" pulling him down.
+ | He reaches a terminal velocity of about 120mph.
‘age. But with the perachute open, there's much more ait resistance (at any given
The difference is speed) and still only the same force “W=mg" pulling him down.
the speed ot which This means hie terminal velocity comes right down to about 1Smpb, which Is
that happens.
Learning ab: ir resistance — it can be a real drag...
It looks like mini-essay time to me. There's a lot of details swirling around here, so definitely the
best way of checking how much you know is to scribble down a mini~eseay for each of the
three sections. Then check back and see what you misse shen ry again sat keer tng
8 safe speed to hit the ground at.
“Section Two — Forces and Motion
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Psychology Units 1 & 2Document408 pagesPsychology Units 1 & 2Sara Jones100% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Molar MassDocument3 pagesMolar MassSara Jones100% (1)
- Evolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsDocument2 pagesEvolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Writing A Literature Review AssignmentDocument2 pagesWriting A Literature Review AssignmentSara Jones100% (1)
- RMIT, Note Taking For LecturesDocument2 pagesRMIT, Note Taking For LecturesSara JonesNo ratings yet