Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
Uploaded by
Nikki DavisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Concept Malaysia PDFDocument14 pagesConcept Malaysia PDFNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Development of Multimedia Learning PackageDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Multimedia Learning PackageNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Weekly Scheme of Work: English Year 2Document6 pagesWeekly Scheme of Work: English Year 2Nikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work (Year 4) 25 JANUARY 2016 - 23 MARCH 2016 Theme/ Unit Listening & Speaking Reading Language Arts Writing Grammar Notes DateDocument6 pagesScheme of Work (Year 4) 25 JANUARY 2016 - 23 MARCH 2016 Theme/ Unit Listening & Speaking Reading Language Arts Writing Grammar Notes DateNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Topic 1)Document1 pageChapter 1 (Topic 1)Nikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyDocument1 pageChanges in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Old MC Donald Had A FarmDocument8 pagesOld MC Donald Had A FarmNikki DavisNo ratings yet
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
Uploaded by
Nikki DavisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
T11 - Edited-Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning-Final-090113
Uploaded by
Nikki DavisCopyright:
Available Formats
EDU3105
TOPIC 11
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
INTEGRATION OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY (ICT) IN TEACHING AND LEARNING
SYNOPSIS
This topic discusses the concepts, theories and practices in the integration of information
and communication technology (ICT) skills in teaching and learning; selection and use,
as well as the technical skills of a number of computer applications including word
processing, electronic presentations, spreadsheets, databases and authoring tools. Also
discussed is the production and use of the multimedia learning packages and the use of
interactive media in teaching and learning.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By doing the learning activities in this topic, hopefully the teacher will be able to:
i. Describe the roles and implications of using ICT in teaching and learning
ii. Select and apply appropriate computer applications with the teaching and learning
process to be executed
iii. Apply a variety of computer applications in teaching and learning
iv. Produce appropriate teaching and learning media in line with the learning standards
v. Integrate information and communication technology skills in teaching and learning.
TOPIC FRAMEWORK
11.1 Introduction to the Integration of ICT in Teaching And Learning
11.2 Word Processing
11.3 Electronic Presentation
11.4 Electronic sheet
11.5 Database
11.6 Use of Software Authoring Tools
11.7 Production of Multi Media Learning Packages
11.8 Use of Interactive Media in Teaching and Learning
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
11.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE INTEGRATION OF ICT IN TEACHING AND
LEARNING
Traditional educational practices no longer provide students with all the knowledge and
skills necessary to enable them to compete in the current job scenario. To stay
competitive, they need to apply their problem-solving strategies, using appropriate tools,
and act collaboratively and communicate, in order to learn. Thus the present learning
environment should involve a variety of strategies, media, software and ICT-related tools
that will prepare students for their future.
11.1.1 Integrating ICT in teaching and learning
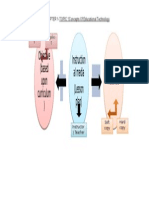
Production and use of ICT-based instructional and learning media has now become a
standard for the integration of technology in teaching and learning. Integration of ICT in
teaching and learning demands teachers to understand all aspects of instructional
planning, learning theory, instructional design, and master the skills of various computer
applications to produce media that can support teaching and learning.
The use of ICT in teaching and learning, aims to improve the effectiveness and efficiency
of the teaching and learning process. Hence the teacher should be able to use it in a
thoughtful, well-planned and appropriate manner. The learning environment should
improve for the better when technology is used in teaching and learning
Traditional Learning Environment
New Era Learning Environment
Teacher-centered instruction
Student-centered learning
Single sense stimulation
Multisensory stimulation
Single path progression
Multipath progression
Single media
Multimedia
Isolated work
Collaborative work
Information delivery
information exchange
Passive learning
Critical thinking and informed decision- making
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Factual, knowledge-based
Active/exploratory/inquiry-based learning
Reactive response
Proactive/planned action
Isolated, artificial context
Authentic, real-world
Source : National Educational Technology Standards for Students (June, 1998), published
by the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE), NETS Project.
Discussion
Discuss the development of technology you have used in the classroom.
Think
How to integrate ICT in teaching and learning?
11.1.2 The Teachers Role in the Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning
Integration of ICT in teaching and learning does not require a teacher to master high
levels of ICT skills. What is more important is which is how teachers can create and use
materials and teaching and learning media suitable for students' learning.
To produce teaching and learning media suitable for optimum learning, teachers should
know and understand instructional planning) instructional design and the learning theory
that underlines both. Something to keep in mind is, when integrating ICT in teaching and
learning, the teacher shoukd not be teaching how to use the technology - what is done is
to use technology as a vehicle to help facilitate delivery and facilitate students to
understand knowledge and develop their skills.
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Think
What software applications that can be used for teaching and learning?
11.1.3 Requirements for Integrating ICT in Teaching and Learning
The use of ICT in a smart way to enrich the learning environment can enable students to
achieve skills that can be used in the working environment. Thus the educators need to
consider the potential for integrating ICT in teaching and learning.
ICT is more than a teaching tool. Its potential for improving the quality
and standards of students educationis significant. Equally, its potential is
considerable for supporting teachers, both in their everyday classroom
role, for example by reducing the time occupied by administration
associated
with
it,
and
in
their
continuing
training
and
development.(DfEE 1998)
The use of ICT in teaching and learning is necessary for the following purposes:
i.
Engaging students
ii. Motivate students
iii. Support new approaches to teaching and learning, such as cooperative learning,
higher order thinking, problem-solving-based learning and project-based learning.
iv. Engage students through the production of works
v.
Increasing students control ove their own learning
vi. Help teachers connect students to learning resources
vii. Help teachers keep track of students' learning progress
viii. Prepare students for the ever-changing world
1.1.4 The Effects of Using ICT in Teaching and Learning
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
There are studies which show intensive use of ICT can improve student achievement.
Project Apple Classrooms of Tomorrow (ACOT) (1995) found that students who use ICT
intensively during the school have the following characteristics:
i. can explore and communicate dynamically in various forms
ii. higher self-confidence and social skills
iii. can communicate effectively about complex matters
iv. have the skills and autonomy of self access
v. discover their abilities and can share with others
vi. can work collaboratively, and
vii. better prepared for the future.
11.1.5 Standard Features of Students in the Aspect of ICT Use
The extent to which ICT can help in shaping the quality of students, who have critical
and creative thinking, and skilled in problem solving, a lot depends on the role of
teachers. An effective learning environment is a combination of traditional approaches
with new approaches to guide the students to master the subject content, while taking
into account individual needs. The combination can provide capable students sho can
(International Society for Technology in Education 1998):
i.
communicate using various forms of media
ii.
access and exchange information in a variety of ways
iii. collect, analyze, organize and synthesize information
iv. make conclusions based on the information collected
v.
using the information and use the appropriate tools to solve problems
vi. know the subject matter and able to reach necessary information when required
vii. become self-directed student
viii. collaborate with others and work effectively as a team
ix. interact with others appropriately and in an ethical manner
11.1.6 Approach to Learning Using ICT
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Curriculum Development Division of the Ministry of Education (BPK) has outlined three
methods of how ICT can be incorporated into the student's learning (Bahagian
Pembangunan Kurikulum 2011: Buku panduan teknologi maklumat dan komunikasi
merentas kurikulum):
11.1.6.1 Learninng ABOUT ICT
Learning about ICT require the students to acquire specific knowledge and skills in the
field of ICT, including computer systems, networks, information systems, multimedia and
programming. Exposure to students is carried performed using strategies which is
appropriate with their cognitive levels and abilities.
11.1.6.2 Learning WITH ICT
Learning with ICT means students use ICT as a tool for learning, such as using ICT
hardware and software. The hardware can be about
printers, scanners and digital
cameras. While software can be MS Word, MS PowerPoint, MS Excel, MS Paint,
Geometer's Sketchpad and free software. Teaching and learning will be more effective,
interesting and fun. The use of ICT as a tool in teaching and learning in primary schools
will be able to produce creative and innovative students.
11.1.6.3 Learning THROUGH ICT
Learning through ICT is the use of ICT to access information using ICT media such as
CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, software and Internet courses. Examples of learning through ICT
can be seen through the use of materials such as encyclopedias, dictionaries, video
learning, EDUWEBTV and Google Earth.
Learning about ICT, Learning with ICT and
Learning THROUGH ICT can be
incorporated into teaching and learning strategies. ICT integration can be implemented
effectively when students have mastered ICT skills. It is recommended that teachers
integrate ICT through project-based activities such as assignments or tasks. For
example, in the production of greeting cards, children can insert images and write a
speech or poem. Students are also able to improve their skills and self-confidence when
6
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
they make a presentation of their work, especially in the form of multimedia. They will be
excited to learn and demonstrate their creativity through performance using a variety of
software features such as use of color, font type, font size and animation.
11.1.7 ICT Mode to be Used in Teaching and Learning
Curriculum Development Centre, Ministry of Education has categorized the use of ICT in
teaching and learning to four modes (Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum 2001:
Penggunaan Teknologi Maklumat dan Komunikasi (ICT) dalam Pengajaran dan
Pembelajaran), namely:
i. Tutorial Mode
ii. Exploration Mode
iii. Application Mode, and
iv. Communication Mode
11.1.7.1 Tutorial Mode
In the tutorial mode, ICT is used to deliver learning content based on a predetermined
sequence and includes;
i.
Disclosure of content
ii. Demonstration of a phenomenon - using a control system
iii. Training or drills that can be accessed - using control system
11.1.7.2 Exploration Mode
Through the exploration mode, students can determine and control the information
received from the tutorial mode where students only receive learning materials that are
determined and controlled by the system. The main purpose of the exploration mode is
not to find answers, but to focus on student involvement in shaping a concept or
understanding of a matter.
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
In the exploration mode, ICT is used as a medium to:
i.
find and access information through resources such as CD ROMs and internet
information portals
ii. learn and study the demonstration of a phenomenon under the students own control
iii. experience, learn and study a phenomenon through simulations controlled by the
system
Examples of technologies that can be used in the mode of exploration include:
Access to a variety of resources on the Internet through search engines
Courseware with a wide range of options including exploration, simulation and games
11.1.7.3 Aplication Mode
In application mode, ICT is used as a medium to help students perform learning tasks
and disseminate information to others (as compared to the tutorial and exploration mode
where ICT is used as a mechanism for the dissemination of information from the source
to the students). With the help of software applications students can focus on the actual
learning activities.
Examples of technologies that can be used in the exploration mode include:
word processor to produce essays
spreadsheet to display chart
graphics editor, sound editor, movie editor, electronic presentation software,
and web editor to deliver a presentation
computer-aided design software to create the design of materials.
11.1.7.4 Communication Mode
In the communication mode, ICT is used as a communication medium by teachers and
students in different locations to send and receive information between them.
Information sharing can occur through the form of text, graphics, audio, video, or various
combinations.
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Examples of technologies that can be used in the communication mode include:
Chat
Audio conference
Video conference
Building a website for access over the Internet
11.1.8 Execution Modes for ICT Use in Teaching and Learning
Curriculum Development Division has set three modes of how ICT can be used by
teachers and students (Bahagian), namely:
i.
Teachers and Students together
ii. Teachers Only
iii. Students Only
11.1.8.1 Teachers and Students together
Teachers can implement interactive teaching and learning in the school computer lab.
During the teaching and learning in the classroom, teachers can use a laptop, software
courses and LCD projectors. Teachers can ask students to try activities that are included
in the teacher laptops. Teachers can also download material from the website in
advance and use the site during lessons.
11.1.8.2 Teachers Only
Teachers teach with the aid of teaching and learning and teachers teaching module
which has provided the material before entering the classroom.
11.1.8.3 Students Only
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
By using the courseware is interactive and based on the learning modules, students can
perform the learning activities using the computer without the help of a teacher. In this
situation, the teacher acts as a facilitator for student learning.
Exercise
Download Buku Panduan Penggunaan Teknologi Maklumat dan Komunikasi
(ICT) dalam Pengajaran dan
Pembangunan
Pembelajaran dari laman
Kurikulum
(http://www.moe.gov.my/bpk/bsk/bpanduan/).
Kementerian
Read
web
Pelajaran
carefully the
Bahagian
Malaysia
advantages and
disadvantages of each mode of use of ICT. Select a document standard content
standard for the subject you are teaching. Prepare a lesson plan using one of the
proposed ICT modes.
10
EDU3105
11.2
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
WORD PROCESSING
Word processing refers to the use of computer applications to build, manipulate, save,
edit and print a text document. A word processor is a computer application for creating a
document file, store it electronically, display it on the computer screen, edit it through
instruction and characters from the keyboard and print it using the printer. Word
processing applications also allow the user to insert a word or paragraph in a document
or to another document.
Word processing applications can support many of the tasks associated with teaching
and learning processes that were once made by typewriter or by hand. These
applications provide the space and opportunity for educators to integrate ICT in teaching
and learning.
Examples of word processing applications include Microsoft Word from Microsoft
Corporation, Word Perfect, Word Star, Chiwriter, Kingsoft Office Writer, Atlantis Word
Processor, while Macintosh-based is iWork and open source applications are
OpenOffice, AbiWord and EZ Word.
Figure 11.1.1: Various Word Processing Applications
Think
11
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
To what extent is word processing software important in the process of
building teaching and learning resources?
11.2.1 Features of word processing applications
Some common features of word processors are:
i.
Insert text - lets you insert text in a document.
ii.
Delete text - allows you to delete the words, text, line and paragraph
easily.
iii.
Cut and paste - allows you remove words or paragraphs from one place
and move them to another place.
iv.
Copy - allows you to copy word, text or paragraph if needed.
v.
Save allows a document to be saved and edited again.
vi.
Font - you can change the font type of your text
vii.
Page size and margins allow you to set the page size, so that the
document will be adjusted automatically.
viii.
Find and replace - lets you direct the word processor to search for a word
or a phrase and you can also replace the word or sentence with other
words in your text.
ix.
Word wrap - word processing application will automatically move words to
the next line after the line has reached the page margin.
x.
Print - lets the printer print your document.
xi.
Font Specifications - allows you to change the font features such as italic,
bold, size, color and shadow.
xii.
Graphics - allows you to insert shapes, images and charts in your
document.
xiii.
Spell check - a facility to check the correct spelling of a word.
12
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
xiv.
Thesaurus - allows you to find the synonyms of words in your document.
xv.
Headers, footers and pagination allow you to edit the top (header) or
bottom (footer) of your document sheet.
xvi.
Table - lets you insert tables in your document to support the compilation
of your data in the form of rows and columns
The above features are part of the word processor capabilities. Teachers can use this
word processors to make materials such as handouts, worksheets and tests to improve
teaching effectiveness.
What are the features of a word processing application you
Think
11.1.2
normally use that causes you to continously use the application?
Integration of Word Processing Application in Teaching and Learning
Teachers can use for word processing applications to support their role in the activities
and matters relating to the management teaching and learning. Here are some
advantages of using word processing in teaching and learning:
i.
Saves time - word processing applications help teachers manage their time more
efficiently, especially for modifying text (material) repeatedly, reduces the need to
rewrite text, and make corrections and revisions quicker and more efficiently.
ii.
Document are more organised and attractive - teaching materials produced using
word processing applications are more organized, neat, and attractive, making it
easier to understand.
13
EDU3105
iii.
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Information sharing - teachers can share lesson plans, reading materials, tables,
text, templates and other questions of teaching materials. Friends can copy,
modify, improve material produced word processing applications.
iv.
Support the management of teaching and learning - the use of word processing
applications can help teachers in teaching and learning, especially the for the
production of teaching materials such as handouts, worksheets, test papers and
other instructional support materials such as daily lesson plans, reports, and
bulletins.
v.
Strengthen teaching and learning activities - students can be stimulated to use
the word processing application in most writing tasks previously written by hand.
Students will be more motivated to perform the task if the results obtained by
them more organised, neat, attractive and saves time.
vi.
Support the writing process - students can use word processing application to
write, edit, illustrated stories, produce presentation materials for the topics they
are learning and make notes as a reference. Students can be stimulated to
create ideas in creative writing using a variety of fonts, colors, layout, insert
images and various graphics.
vii.
Strengthen language skills - students can learn the language through a variety of
word processing application features including spell check, grammar checker and
thesaurus.
PRACTICAL
By using a word processing application of your choice, prepare a handout suitable
for attracting students to learn a learning standard for a subject that you teach.
Provide appropriate worksheets to assess student achievement.
Your work should take into consideration the following points:
i.
The learning content corresponds to an appropriate learning standard
ii. Theme to be used: Sustainable environment
iii. product should use a variety of fonts and graphics, neat and attractive, and
presented using variable layouts
14
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
15
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
11.3 ELECTRONIC PRESENTATION
Electronic presentation is a computer application that delivers textual and visual
information that can be integrated with other multimedia elements such as audio, video,
animation. According to Gregory (2012), electronic presentation is "A computergenerated program capable of communication, text, drawings, photos, video, and audio."
It usually displays the information in a presentation display. It is also able to provide a
link (hyperlink) to external sources of information such as images, documents,
spreadsheets, video, audio and websites. Electronic presentation can enrich viewers'
reference sources to obtain appropriate information about the topic or concept described
by the presenter.
Electronic presentations are used in business, medicine, education and various other
fields for demonstration purposes, make explanations, digest the facts, presenting the
report, the message, sharing ideas and others. Examples of commonly used electronic
presentation applications include Microsoft PowerPoint, Harvard Graphics, Open Office
Impress, and Kingsoft Presentation.
Think
What are the advantages of using electronic presentation in teaching and
learning compared to other media such as posters, pictures, slides and
charts?
11.3.1 Electronic presentation features
Most electronic presentations applications have basic features that allow presenters to
include elements of text, graphics, audio, video and a variety of special effects to attract
the attention of the audience to the main idea. Answer.com (2012) has listed some of the
basic features of electronic presentation as follows:
i.
Word processing feature that allows its users to enter and modify text format.
16
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Figure 11.3.1: Examples of text editing features in Microsoft PowerPoint.
ii.
Features for editing graphic images, and creating animation effects.
Figure 11.3.2: Examples of graphic editing features are available in
Microsoft PowerPoint.
iii.
Slide-based display presentation (slide show engine) that can display on the
screen the order of the slides.
Electronic presentation applications also
provides an option to preview animation effects before you make the final
selection.
Figure 11.3.3: Examples of features that are available to preview a presentation
in Microsoft PowerPoint 2010
iv.
Layout management system which allows you to select predefined
templates and customize it according to current needs.
17
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Figure 11.3.4: Examples of layout templates available in
Microsoft PowerPoint 2010.
Think
Based on your experience of using electronic presentation application,
what features are available in an electronic presentation applications other
than the above? How do you attract the attention of students or the
audience to an electronic presentation that you use?
11.3.2 Criteria for making a good electronic presentation
Good electronic presentations have the following features:
i. The graphic design help make the electronic presentation easy to read and have
aesthetic value. Among the principles of graphic design include:
a. Simplicity
Use a simple background, so the audiences interest is not in the of colorful or
more complex background compared to the content (Smaldino et al., 2012;
Jones, 2005).
Figure 11.3.5 shows three displays A, B and C with dfferent
backgrounds.
Display A is most effective in highlighting the message and best
facilitates viewers to read and understand the text.
C
Figure11.3.5
18
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
b. Contrast
The contrast of colors used in the display should result in the main message
appear more prominent (Jones, 2005; Smaldino, 2012). Using a dark background
and bright colored text also would produce good contrast (Clark, 2004). In Figure
11.3.6, the first line shows a combination of background and text colors that
create contrast while the second line shows color combinations that should be
avoided.
1 Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
2 Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Kontras
Figure11.3.6: Aplication of Contrast
c. Emphasis
The use of a larger font size or larger objects, and contrasting colors may
highlight the main subject or idea. In Figure 11.3.7, the use of a large font size
and color contrast in the display A is more effective in attracting the attention of
the viewer to the main idea compared to display B.
B
Figure 11.3.7: Application of Emphasis
d. Space
19
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Use a lot of empty space around the subject or the main idea so that it can attract
the attention of the audience.
In Figure 11.3.8, Display A is compact display
with a lot text while display B has more space between the texts. The design of
Display B facilitates viewers to read and understand the text.
B
Figure 11.3.8: Use of Space
e. Focus
Each display should focus on the main concept only. In Figure 11.3.9,
Display A focusses on several concepts while Display B focusses on
one
concept only. Display B facilitates viewers to read and understand the text.
B
Figure 11.3.9: Comparison of views in terms of Focus
ii. Make your message accurate and as simple as possible (Smaldino, 2012; Microsoft,
2012; Markowitz, 2011; Mayer 1998).
Short messages in the form of keywords makes a presentation easier to read and
understand compared to lengthy sentences.
The Six by Six Rule (Rule of Sixes), a
guide for the preparation of the display suggests the use a simple bulleted text to
20
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
facilitate optimal information acquisition. This rule recommends the use of bulleted text in
each display does not exceed six lines while in each row contains no more than six
words per line (Clark, 2004).
B
Figure 11.3.10: Short messages in the form of keywords (Display B) makes it easier
to read and understand compared to lengthy sentences (Display A).
iii. Submit an idea or information according to a logical sequence. Practice the display
principle of simple to complex, from the known to the unknown, and from the concrete
to the abstract. Use visual graphics to represent abstract concepts or when text and
figures may seem complex and confusing. In Figure 3.11.11,
visual diagrams and
images in display B are able to explain a concept or process better than using a text-only
display such as display A.
B
Figure 3.11.11: Using graphics represent text.
21
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
iv. Integrate multimedia elements in your delivery to stimulate multiple sensory organs.
Mayer (1998) in his multimedia learning theory, has suggested the following principles
as preparation guidelines for the development of multimedia learning materials:
a. Multimedia Representation Principle:
Better make explanations with text and image combination of text only.
b. Spatial Contiguity Principle:
The effect of learning involves a combination of text and image nearby is
better than made separately.
c. Visual Split-Attention Principle:
Use oral explanation to replace lengthy text on the display
d. Chunking Principle:
Use minimal text and images
e. Coherent Principle :
Avoid using words or terms that are irrelevant.
e. Auditory Split-Attention Principle:
When making a verbal explanation along with animation on the display, avoid
using excessive background music and sound effects so that students can
relate to the animation to the description presented.
v. Make explanations, introduce concepts progressively.
vi. Avoid excessive use of animation effects (Smaldino, 2012; Clark, 2004).
Think
(A)
(B)
22
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Display A load all the steps in display while Display B exposes each step in
phases. Which one is more helpful for students attain the concept taught?
What is the justification for your answer?
Further Reading
Read reference as set out below for explanation about electronic
presentation applications.
Mayer, Richard. (1999). Multimedia aids to problem-solving transfer. In
International Journal of Educational Research 31 (1999). 611-623.
through the following URL
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?
doi=10.1.1.58.6023&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
11.3.3 Principles of electronic presentations production
Electronic presentation is a popular medium of instruction amongst teachers. It
can be produced quickly with the availability of electronic information resources
such as ebooks, articles surfed through web pages, and multimedia elements in
digital form that are produced through a variety of electrical and electronic
equipment. However, the production of quality electronic presentation are
necessarily produced through careful planning and preparation.
The application of the ADDIE Model in the development of instructional media
and the use of the ASSURE Model when implementing the teaching and learning
processes in the classroom are crucial to the successful dissemination of
information and behavioral change among students. However each material
produced caters only to the specific target group. Thus if the same instructional
material is to be applied to other target groups, the material needs to be modified
according to abilities, interests and preferences of the new target group.
Step-by-step planning, creation and use of electronic presentation can be
described briefly as follows:
23
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
i. Make a needs analysis of the requirements in terms of the scope of the
syllabus content, learning outcomes, learning objectives, needs and abilities of
students.
ii. Design electronic presentation. Set the approach to be used, the learning
activities, the storyboard and features that can attract attention and increase
concept attainment etc.
iii. Collect materials,media and appropriate applications, and make a literature
review of the topic being studied.
iv. Select materials, media, approaches and methods that suits your target group
and the topic being studied.
v. Produce electronic presentations in compliance with the desing principles for
graphic and message delivery so that it is able to attracted the attention of
students and help them keep it in long-term memory and retrieve the information
efficiently.
vi. Preview your product. You need to ensure the accuracy of relevant facts and
the language use is in line with existing knowledge and ability of your students.
Rehearse to ensure the material can be used smoothly.
vii. Use the electronic presentation with the student. Practice the ASSURE Model
and involve students actively in the learning process.
viii. Evaluate and revise to make appropriate improvements.
Think
24
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
How do you integrate electronic presentation in teaching and learning?
What are the principles of electronic presentation production that can be
used to convey an idea, concept, skill or specific values in the teaching and
learning of a topic in a subject that you are teaching?
Discussion
Discuss the effective use of electronic presentation when compared with
the use of concrete materials in the process of delivering new ideas,
concepts and specific skills?
Would you agree that electronic presentations are much more effective
than media such as video and movie playback? What are the arguments
that support your answer?
Could electronic presentation be made as a learning medium that can be
used by students without the presence of the teacher? What are the
arguments that support your answer?
Practical
By using electronic presentation application of your choice, create a
presentation to enable you to deliver learning content related to a learning
standard subjects you teach. Presentation produced should include a
variety of features, elements and characteristics of the design and
development of electronic presentation discussed in this topic.
25
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
11.4 ELETRONIC SHEET
Electronic sheet (spreadsheets) organize information into software-defined rows and
columns. The rows and columns of a spreadsheet make up cells that form a grid. The
user enters data in the cells and types in formulas (or uses pre-programmed formulas
called functions) to perform mathematical calculations on the data (ehow.com 2012).
Basic Features of Electronic Spreadsheet:
i.
ii.
iii.
Manage data in rows and columns
Provide a platform for users to enter data
Allow users to do mathematical calculations such as adding and subtracting; and
iv.
v.
vi.
vii.
formulated of mathematical calculations on data
Allow users to use mathematical functions on data
Allow users to copy mathematical formulas and;
Allow users to redo the calculation automatically when they change the data
Users are able to present data in charts and graphs format.
Advantages of Using Electronic Spreadsheet Rather Than Manual Spreadsheets:
i.
ii.
Data entry error can be detected and corrected easily using the edit feature
Allow users to get through the answer without typing complex mathematical
formula or function. Users may use the mathematical formula or function
iii.
provided in application to do the calculation automatically
Save a lot of processing time as data on several spreadsheets may be
iv.
v.
vi.
vii.
viii.
ix.
processed simultaneously
Present neat and interesting data through automatic formatting function
Interpretation of the data is more easily done through graph features
Provide a method to locate and present the information in a manageable form
Save computation time if need to do recalculation.
Quick and easy data access because the data is saved in the digital files form
Data and information can be shared easily using the internet access because
x.
the data is saved in the digital files form
Files can be locked using a password to prevent unauthorized data changes
Example of spreadsheet applications :
Microsoft Excel
Apple VisiCalc
Kingsoft Spreadsheets
OpenOffice Calc
LibreOffice Calc Corel
Quattro Pro
26
EDU3105
T11 - PENGINTEGRASIAN TMK
27
EDU3105
T11 - PENGINTEGRASIAN TMK
Further Reading
By surfing internet, get information on how to use spreadsheets
in the process of teaching and learning?
Practical
By using a spreadsheet application of your choice, create a
suitable chart to show the media composition in your school
resource center.
28
EDU3105
T11 - PENGINTEGRASIAN TMK
11.5 DATABASE
A database is a collection of information that is organized so that it can be
accessed, managed, and updated easily
(http://searchsqlserver.techtarget.com/definition/database).
A database is a data structure that saves organized information. Most
databases contain multiple tables, which may each include several different
fields. Each of these tables would have different fields that are relevant to the
information saved in the table. Database applications are software programs
designed to collect, manage and disseminate information efficiently
(techterms.com 20012b).
i.
11.5.1 Database Applications Features
Formed from a table or several tables that can be linked to each other. Each
ii.
table has fields for data entry
Saves data in a field in the table. One field can save a data and an entire data
iii.
about an object or thing is known as a record
Allow users to save, edit and retrieve data
11.5.2 The Uses of Database in Teaching and Learning
i.
Students data and information can be saved and managed in order to make the
ii.
managing process more efficient and accurate
Information can be accessed using keywords and pupils records can be displayed
automatically. Students information can be filtered and formulated automatically.
Teacher can save a lot of time compared to the old method of saving student
iii.
information using fails and papers
Can be used to save the test questions and if the collection becomes too large,
teachers have opportunity to retrieve the relevant questions through the filtering
iv.
process
Teachers can use database for teaching and learning activities such as
encouraging higher-order thinking skills by asking the students to study the filtered
report from database.
29
EDU3105
T11 - PENGINTEGRASIAN TMK
Examples of database applications :
30
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Microsoft Access
MySQL
Oracle
Discussion
Explore and discuss the key features of database applications.
Practical
By using a database application of your choice, create a
question bank for the subjects you teach. The questions stored
in the question bank need to be questons suitable for test
purposes when needed.
11.6 THE USES OF AUTHORING TOOLS
Authoring tools usually enable you to create multimedia courseware merely
by linking together objects, such as a paragraph of text, an illustration, or a
song. By defining the objects' relationships to each other, and by sequencing
them in an appropriate order, authors (those who use authoring tools) can
develop attractive and useful graphics applications. Most authoring systems
also support a scripting language for more sophisticated applications.
In the context of education, authoring tool refers to the software used to
develop courseware for e-learning purposes. Most authoring tool
applications allows teachers to integrate a variety of media in courseware
development with the purpos of encourage student participation and
interactivity (Lectora.com 2012).
31
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Types of Authoring Tools
Based on icon design
1. Multimedia elements and interactive
instruction managed as objects in a
Software Example
AUTHORWARE
structured framework or process
framework
2. Show flowchart about the activities
that occurred on the branches frame
Timeline-based
1. Multimedia elements and events
DIRECTOR
TOOLBOOK
(Based on Page)
(event) is managed on a time line
2. Events happened are based on the
timeline
3. Events speed can be controlled
4. Disclosure of elements can be
performed at any time or place on the
timeline
5. Can be linked to any part on the
timeline
Based on Page or Card
32
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Types of Authoring Tools
1. Element is managed as the
pages of a book or group of cards
2. Pages are arranged like the
pages in a book
3. Links to a page or a card are in
sequence
4. Can be linked to any page or
other cards based on interactive
commands
Software Example
HYPERSTUDIO
(Based on Card)
Think
i.
Table 11.6.1: Types of Authoring Tools
What are the examples of the other software that can be
categorized as an authoring tool?
Common Authoring Tools Features
Manage and edit
create, edit and convert multimedia element format
33
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
manage and design, based on the storyboard and flowchart
ii. Programming
Using high level but easy to use programming language because of the
visualize format
iii. Interactive
Complex programming becomes easy by using the concept of structured
programming. Using IF-THEN and GO TO programming command may
allow users to control the flow of the information and content
iv.
Playback
Development can be done according to the segments and each segment
can be built and tested separately
Time frame for each implementation of the element can be fix neatly and
accuracy
v. Delivery across multiple platforms and internet
Standalone product
products may across multiple platforms
The format of the products can be converted to run on an internet
platform
11.7 Development of Multimedia Learning Package
Multimedia Definition
As the name implies, multimedia is the integration of multiple forms of media.
This includes text, graphics, audio, video, etc. For example, a presentation
involving audio and video clips would be considered a "multimedia
presentation." Educational software that involves animations, sound, and text
is called "multimedia software." CDs and DVDs are often considered to be
34
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
"multimedia formats" since they can save a lot of data and most forms of
multimedia require a lot of disk space (techterms.com 20012a).
In the context of ICT, a multimedia material is an integration of a variety of
multimedia elements including text, graphics (including images), audio, video
and animation, is subset to the hypermedia. Hypermedia combine multimedia
elements with hipertext (also known as hyperlink) that creates a link between
the elements (Microsoft Press 1994).
In the context of education, a multimedia package is a package that
combines the learning strategy with learning contents and is presented using
a variety of multimedia elements to enable the learning objectives to be
achieved by the pupils.
Prepare a storyboard for developing a multimedia learning
package for a learning standard from a subject that you
teach.
Pr
11.8
Use of Interactive Media in Teaching and Learning
Interactive Media
Interactive media is the integration of a variety of media, including text,
graphics, images, audio, and video in a structured environment so that users
can interact for a specific purpose. Interactive media usually requires control,
input, and active user response. Most interactive media are now using digital
technologies. Examples of interactive media are websites, digital video
recorder (DVR), computer games, online forum, E-Mail and social
networking.
Interactive Multimedia
35
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
When users are able to control the type, time and manner of elements in the
multimedia package, it will become an interactive multimedia. The specific
uses of interactive multimedia are for;
Drill and exercise to master basic skills
Development of writing skills
Problem Solving
Understanding the concepts of mathematics and science
data manipulation
mastering computer skills
access and communication
remote access by teachers and students
individual and cooperative learning
administration and management of classroom activity
How important is interactive multimedia packages for students
and teachers in teaching and learning process?
Development of Multimedia Interactive Learning Package
Development of Interactive Multimedia involves a systematic and thorough
process. There are many models that can be used in interactive multimedia
developments project. ADDIE model is a popular model used in the design of
teaching and learning project. In the context of the development of interactive
multimedia packages education, this model is an ideal choice. The model
consists of the following phases:i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
v.
Analysis
Design
Development
Implementation
Evaluation
36
EDU3105
i.
ii.
iii.
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
WORKING PROCESS
A Analysis Phase:-
Analyse your pupils (make assumptions about the condition of your students);
Think about the students attitude, existing knowledge, skills, and learning styles
Analyse the syllabus, topic or sub-topic for the teaching and learning aids that
vii.
will be constructed
Examine the structure of the titles concept
Think about the sequence should be mastered by students
Think about the support materials needed
Think about the materials (media) can be built or found according to the
viii.
major content and support materials
Ensure the learning outcomes of the subject is comply with curriculum and
ix.
x.
based on what can be done by the students
Dsiscuss the way of learning suppose to be conduct
Think about the appropriate activities and assignments to develop a meaningful,
iv.
v.
vi.
fun, relevant learning and achieve the learning outcomes.
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
B. Design Phase:
Consider aspects such as the design, contents, arrangement/layout for the
display and interface
Build navigation plan
Build storyboard
Define the interactivity level
C. Development Phase:
i.
ii.
iii.
Find and select the appropriate materials / media
Modify the existing media if necessary
Build your own media if deemed necessary with appropriate audio; graphics;
iv.
v.
vi.
vii.
animation; video; etc.
Use appropriate software to edit graphics, Audio, Video and Animation
Convert all media materials into digital form
Choose an appropriate authoring tool
Based on the storyboard, compose by using authoring software that was
viii.
ix.
x.
selected
Input the element multimedia you had fixed
Build a menu to access the topics, activities, training and resources
Create a link from title, activities, assignments, training, and other resources; and
link back to the menu
D. Implementation Phase:
37
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
i.
Run the multimedia packages that have been developed to find bugs. This test
ii.
level called 'Alpha Testing'
Apply your multimedia Package to your students and correct the bugs. This test
level called Beta Testing
i.
ii.
E. Evaluation Phase:
Conduct an assessment about the effectiveness of the media you had prepared
Conduct an assessment about the teaching and learning process that you have
planned.
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
v.
vi.
Interactivity Design
Multimedia interactivity design consists of six major components (Shedroff,
1994) :-
Feedback (user performance response)
Control (navigation and interactivity)
Creativity (users develop something)
Productivity (content)
Communication (communication with others)
easily adapted
Practical
Choose an educational software and identify the elements had
included in the interactive media?
Advantages of Using Interactive Media
Using interactive media in education have brought many advantages. Such
as:
It facilitates the student-centered learning. Provide many options for learning and
introducing a lot of new material.
It fulfill the requirements of a variety learning styles to provide a large selection of
learning approaches
It motivate interaction, experimentation and students cooperative learning
It helps the learning process based on the theme
It enhances constructivist learning
38
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Interactive media are very suitable to use in complex learning situations
as follows :-
Material or content that is difficult to visualize such as complex processes.
The learning of three-dimensional content which is usually difficult if done using
two-dimentional materials
Dynamic processes that require an understanding of the relationship between
moving objects
Comprehensive content where some ideas have to be combined to understand
the entire content
Simulation of a complex or expensive process in which no opportunity to use real
equipment
Further Reading
By surfing the internet, get additional ideas about the ways to use
interactive media in teaching and learning process
Practical
Using an authoring tool of your choice, create an
Interactive multimedia presentation suitable for teaching
and learning of a topic from a primary school subject.
SUMMARY
This topic describes the integration of ICT in teaching and learning, as well as
sub-topics related to computer applications including word processing,
39
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
electronic presentations, electronic sheets, databases and authoring tools.
Also described are the production of multimedia learning packages and the
use of interactive media in teaching and learning.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
Answer.com (2012). What are the features of presentation softwares? Akses
pada November 11, 2012 daripada
[http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_are_the_features_of_presentation_software
]
Apple Classrooms of Tomorrow (ACOT) (1995). A report on 10 years of
ACOT research. Cupertino, CA: Apple Computers Inc.
Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum (2011). Buku panduan teknologi
maklumat dan komunikasi merentas kurikulum. Malaysia: Bahagian
Pembangunan Kurikulum. Akses pada November 8, 2012 daripada
[web access:
http://kssr.bpk.my/dokumen_kurikulum/emk_kemahiran_menaakul]
Bowling Green State University (n.d.). Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 tutorial.
Akses pada Oktober 22, 2012 daripada [
http://www.bgsu.edu/downloads/cio/file85354.pdf]
Clark, Nancy B. (2004). Criteria for professional presentations. Akses pada
November 11, 2012 daripada [http://www.dmu.edu/wpcontent/uploads/2011/02/Criteria-for-Professional-Presentations-withPowerPoint.pdf]
Customeguide.com (2011). Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 quick reference
card.Akses pada October 22, 2012 daripada [http://customguide.com/wpcontent/themes/customguide/pdf/qr/powerpoint-quick-reference-2010.pdf]
DfEE. (1998) Teaching: high status, high standards. Requirements for
courses of initial teacher training. Circular 4/98.
40
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
ehow.com (2012). What Is an Electronic Spreadsheet? Akses pada
November 13, 2012 daripada
[http://www.ehow.com/facts_6736821_electronic-spreadsheet_.html]
Gregory, Hamilton (2012). Public speaking for college and career. 6th ed.
Akses pada 11 November 2012 daripada
[http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072400536/student_view0/glossary.html]
Heinich, R., Molenda, M., Russell, J.D., & Smaldino, S.E. (1996). Instructional
media and technologies for learning. Edisi ke 5. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
International Society for Technology in Education (1998). National education
technology standards for students. Eugene, Oregon: ISTE
Jones, David (2005). How to make good presentation. Akses pada
November 11, 2012 daripada [http://www.cmos.ca/presentationse.html]
Lectora.com (2012), What is an Authoring Tool? Akses pada November 13,
2012 daripada
[http://lectora.com/resources/authoring-tool/ ]
Markowitz, Eric (2011). How to create a great PowerPoint presentation.
Akses pada November 11, 2012 daripada
[http://www.inc.com/guides/201102/how-to-create-a-great-powerpointpresentation.html]
Mayer, Richard (1999). Multimedia aids to problem-solving transfer. dalam
International Journal of Educational Research 31 (1999). 611-623. Akses
pada November 12, 2012 daripada
[http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?
doi=10.1.1.58.6023&rep=rep1&type=pdf]
Mayer, Richard & Moreno, Roxana (1998).A cognitive theory of multimedia
learning: Implications for design principles. Akses pada November 12, 2012
daripada [http://spnd423.com/SPND%20423%20Readings/A%20Cognitive
%20Theory.pdf]
41
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Microsoft (2012). 12 tips for creating better PowerPoint presentations. Akses
pada November 11, 2012 daripada
[http://www.microsoft.com/atwork/skills/presentations.aspx#fbid=ddC-
RB9pjwi]
Microsoft Office.com (2012). What is presenter view? Akses pada October
22, 2012 daripada
[http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/powerpoint-help/what-is-presenter-viewHA010360578.aspx]
Microsoft Press (1994). Computer dictionary. 2nd Edition. Washington:
Microsoft Press
Mohd Jizat Abdol,Abdul Razak Idris dan Jessnor Elmy (2006). Teknologi
pengajaran dan pembelajaran. UTM.
Ngui Kuan Sang (1989). Teknologi Pendidikan:penggunaannya dalam
pengajaran geografi, Kuala Lumpur: Fajar Bakti.
Norasiah Abdullah, Nor Risah Jamilah Mat Lazim & Rosnah Ahmad Zain
(2009). Teknologi dalam pengajaran dan pembelajaran. Puchong: Penerbitan
Multimedia.
Noriati A.Rashid, et. al. (2009).Teknologi dalam pengajaran dan
pembelajaran. Shah Alam. Oxford Fajar.
Noriati, A.Rashid (2012). Teknologi dalam pengajaran dan pembelajaran.
Kuala Lumpur: Oxford Fajar.
Percival , H.T., Ellington, H.I. dan Race, P. (1993).Handbook of educational
technology. Edisi ke 3. London: Kogan Page.
Poh Swee Hiang, Mokhtar Affandi Amran & Tajuddin Hassan (1996).
Pengurusan sumber pengajaran pembelajaran 2. Kuala Lumpur: Kumpulan
Budiman Sdn. Bhd.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum (2001). Penggunaan teknologi maklumat
dan komunikasi (ICT) dalam pengajaran dan pembelajaran. Malaysia: Pusat
Perkembangan Kurikulum . Akses pada November 4, 2012 daripada
[web access: http://www.moe.gov.my/bpk/bsk/bpanduan/ict_in_pnp.pdf
]
42
EDU3105
T11 INTEGRATION OF ICT
Razali Nor (1995). Teknologi pendidikan: media unjuran dan media
elektronik. Kuala Lumpur: Kumpulan Budiman Sdn. Bhd.
Safian bin Abd. Rashid (2002). Pengurusan sumber: Komponen teknologi
pendidikan.
Sharifah Alwiah Alsagoff (1987). Teknologi pengajaran. Kuala Lumpur:
Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
Shedroff, Nathan (1994). Interaction Design. Akses pada November 13,
2012 daripada [http://www.nathan.com/thoughts/recipe/inter.html]
Smaldino, S. E., Russell, J. D., Heinich, R.& Molenda, M. (2002). Instructional
technology and media for learning. Edisi ke 7. New Jersey: Pearson & Merrill
Prentice-Hall.
Smaldino,S.,Russell,J.,Heinnich, R,& Molenda, M. (2005). Instructional
technology and media for learning, edisi ke-8. New York: Pearson Prentice
Hall.
Smaldino, Sharon E., Lowther, Deborah L. & Russell, James D. (2012).
Instructional technology and media for learning. Edisi ke 10. Boston:
Pearson.
Techtarget.com. SearchSQLserver. Akses pada November 13, 2012
daripada
[http://searchsqlserver.techtarget.com/definition/database]
techterms.com 2012a. The tech terms computer dictionary. Akses pada
November 13, 2012 daripada
[http://www.techterms.com/definition/multimedia]
techterms.com 2012b . The tech terms computer Dictionary. Akses pada
November 13, 2012 daripada
[http://www.techterms.com/definition/database]
Wah Wan Ali et al. (2008). HBEM3103. Prinsip teknologi pengajaran. Kuala
Lumpur: OUM.
43
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Concept Malaysia PDFDocument14 pagesConcept Malaysia PDFNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Development of Multimedia Learning PackageDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Multimedia Learning PackageNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Weekly Scheme of Work: English Year 2Document6 pagesWeekly Scheme of Work: English Year 2Nikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work (Year 4) 25 JANUARY 2016 - 23 MARCH 2016 Theme/ Unit Listening & Speaking Reading Language Arts Writing Grammar Notes DateDocument6 pagesScheme of Work (Year 4) 25 JANUARY 2016 - 23 MARCH 2016 Theme/ Unit Listening & Speaking Reading Language Arts Writing Grammar Notes DateNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Topic 1)Document1 pageChapter 1 (Topic 1)Nikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyDocument1 pageChanges in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Old MC Donald Had A FarmDocument8 pagesOld MC Donald Had A FarmNikki DavisNo ratings yet