Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 viewsDiuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Diuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Uploaded by
Andrew AkramDiuretics work by targeting sites in the kidneys to increase urine output and reduce fluid retention. The main classes are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-retaining diuretics, which have different mechanisms and side effect profiles. Diuretics are used to treat edema caused by conditions like heart failure or liver disease, hypertension, and other fluid-related issues. Proper administration is important to balance their effects on electrolytes and acid-base levels while reducing excess fluid. Less common diuretic classes include osmotics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Diuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsDocument22 pagesDiuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsSteven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFDocument422 pagesOxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFvani reddyNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument18 pagesDiureticsChantal CarnesNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of DiureticsDocument46 pagesBasic Pharmacology of DiureticsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- Pharmacology DiureticsDocument32 pagesPharmacology DiureticsIrene WNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument16 pagesDiureticsvinodmedicozNo ratings yet
- Renal Note On DiureticsDocument12 pagesRenal Note On DiureticsLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Cardiovascular System CvsDocument36 pagesLecture 7 Cardiovascular System CvsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Diuretiku TokseDocument22 pagesDiuretiku TokseUgnė ČeponytėNo ratings yet
- Vidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014Document51 pagesVidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014naltrisilvianNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument83 pagesDiureticsKarami BrutusNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticsAnkita TatheNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Diseaseampogison08No ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologyDocument96 pagesDrugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderDocument33 pagesDiuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderNina KerafNo ratings yet
- Diuretics NewDocument21 pagesDiuretics NewPawan RajNo ratings yet
- Cardiac GlycosideDocument24 pagesCardiac Glycosideapi-3708473No ratings yet
- 105 DiureticsDocument18 pages105 DiureticsMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Metabolic & Acid-Base Balance: 1-When Lactic Acid Accumulates, Body Will Respond byDocument8 pagesMetabolic & Acid-Base Balance: 1-When Lactic Acid Accumulates, Body Will Respond byASGHAR ALINo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument40 pagesDiureticsHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213Document19 pagesDiuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213JedoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Usmle SuperDocument239 pagesUsmle SupermaksventileNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02Document45 pagesDiuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02P merugu100% (1)
- Lecture15-Diuretics and AntidiureticsDocument36 pagesLecture15-Diuretics and Antidiureticsharis.18No ratings yet
- Pharmacology I, Diuretics NK-modified 2Document32 pagesPharmacology I, Diuretics NK-modified 289c8g7bvvvNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKDocument46 pagesPharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKRizky Pramata Simamora 19000029No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CVS & RenalDocument116 pagesChapter 3 CVS & RenalKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument31 pagesDiureticsRameez ShamounNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument116 pagesDrugsRyan FlahertyNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowDocument35 pagesDiuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSDocument51 pagesDiuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Haitham Mahmood AlwaliDocument32 pagesDiuretics: Haitham Mahmood Alwaligaurav adhikariNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesPharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFCodyDavistgny100% (9)
- Chapter 13 ElectrolytesDocument115 pagesChapter 13 Electrolytessisay SolomonNo ratings yet
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Document48 pagesPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The KidneysDocument56 pagesDrugs Acting On The Kidneysbetu tufaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument61 pagesDiureticsJoyce WacukaNo ratings yet
- Occupational and EnvironmentalDocument117 pagesOccupational and EnvironmentalGideon K. MutaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular For PharmacologDocument134 pagesCardiovascular For Pharmacologephremtigabie7No ratings yet
- Electrolyte Physiology & The KidneyDocument13 pagesElectrolyte Physiology & The KidneyFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Medicinal_chemistry_2_Unit_2_-1Document11 pagesMedicinal_chemistry_2_Unit_2_-1KevalNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 171130131557Document31 pagesDiuretics 171130131557Lety AgistiniaNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument21 pagesDiureticsShathawe BrgNo ratings yet
- Full Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument31 pagesFull Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptermcddieyorubc400100% (7)
- Presentation On Diuretics+synthesis Final VersionDocument58 pagesPresentation On Diuretics+synthesis Final VersionArkw ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Yuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Document55 pagesYuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Nurul PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Osmo Regulation MCQDocument5 pagesOsmo Regulation MCQKaran PrabaNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid CompartmentsDocument10 pagesBody Fluid CompartmentsAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanDocument54 pagesDiuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanEdi KurniadiNo ratings yet
- GI Disorders - Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument3 pagesGI Disorders - Alcoholic Liver Diseasemollymaheshwari00No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticsmohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Kidney DrugsDocument39 pagesPharmacology - Kidney DrugsSeth-Thomas TateNo ratings yet
- Avocado Nutritional CompositionDocument10 pagesAvocado Nutritional CompositionlizNo ratings yet
- Blood Drugs Used For AneamiasDocument7 pagesBlood Drugs Used For AneamiasMaha KhanNo ratings yet
- MFC GUIDELINES FOR SC T7 LNG 2023 Rev01Document6 pagesMFC GUIDELINES FOR SC T7 LNG 2023 Rev01izik4meNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7359009 20220622112958Document4 pagesLab Report 7359009 20220622112958Nandini PandeyNo ratings yet
- II. Recommendations (Quiambao, Razelle F.) Medications: Contact Your Healthcare Provider IfDocument3 pagesII. Recommendations (Quiambao, Razelle F.) Medications: Contact Your Healthcare Provider IfJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Lipidet BiokimiDocument118 pagesLipidet BiokimiEmir Cerkezi100% (1)
- Problem Lists Patient PlanDocument1 pageProblem Lists Patient Planangel23No ratings yet
- Kualitas Minyak Blend Kelapa Kopra Dan Minyak Kelapa Sawit Ditinjau Dari Kadar Air, Kadar Asam Lemak Bebas Dan Bilangan PeroksidaDocument8 pagesKualitas Minyak Blend Kelapa Kopra Dan Minyak Kelapa Sawit Ditinjau Dari Kadar Air, Kadar Asam Lemak Bebas Dan Bilangan PeroksidaesiNo ratings yet
- 1844 Obesity GuidelineDocument11 pages1844 Obesity GuidelineRohit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates in Our Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates in Our Everyday LifeMadhuri HandeNo ratings yet
- JBLMGH Rates For Laboratory Services: Jose B. Lingad Memorial General HospitalDocument4 pagesJBLMGH Rates For Laboratory Services: Jose B. Lingad Memorial General HospitalApril NNo ratings yet
- Prospectus - Young Star Insurance PolicyDocument26 pagesProspectus - Young Star Insurance PolicyNaveenraj SNo ratings yet
- Probiotic 13 Fr-2021-845 Wulandari Aprl 2023Document11 pagesProbiotic 13 Fr-2021-845 Wulandari Aprl 2023wisnuadi UMBYNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Document3 pagesTop 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Bubu ToNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDocument8 pagesHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountArun DheekshahNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Effects of A Ketogenic Diet in Obese PatientsDocument10 pagesLong-Term Effects of A Ketogenic Diet in Obese Patientsrobertofca2266No ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesDyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyNur HaidagNo ratings yet
- Please Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDocument1 pagePlease Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Fish LipidsDocument31 pagesFish Lipidskolita kamalNo ratings yet
- 3 Lipid MetabolismDocument54 pages3 Lipid MetabolismRahadatul Aisy100% (1)
- HF BrochureDocument23 pagesHF Brochureimran_issufoNo ratings yet
- Benefits of CocozhiDocument3 pagesBenefits of CocozhiGreenplanet CybercafeNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-4 Powerpoint For Hema Lab PT, aPTT, CRT, CFTDocument11 pagesLab 3-4 Powerpoint For Hema Lab PT, aPTT, CRT, CFTElaineNo ratings yet
- Cumin Anti Diabetic 2018Document11 pagesCumin Anti Diabetic 2018srikanth PosaNo ratings yet
- Skenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4Document12 pagesSkenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4ulfahNo ratings yet
- S.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop LocationDocument10 pagesS.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop Locationarindam dasNo ratings yet
- 10 Health Benefits of SpirulinaDocument10 pages10 Health Benefits of Spirulinahkm_gmat4849No ratings yet
- Ehad 814Document11 pagesEhad 814Srinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- LPT 311 PDFDocument190 pagesLPT 311 PDFIbad Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
Diuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Diuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Uploaded by
Andrew Akram0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageDiuretics work by targeting sites in the kidneys to increase urine output and reduce fluid retention. The main classes are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-retaining diuretics, which have different mechanisms and side effect profiles. Diuretics are used to treat edema caused by conditions like heart failure or liver disease, hypertension, and other fluid-related issues. Proper administration is important to balance their effects on electrolytes and acid-base levels while reducing excess fluid. Less common diuretic classes include osmotics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Original Description:
hooo
Original Title
Diuretics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiuretics work by targeting sites in the kidneys to increase urine output and reduce fluid retention. The main classes are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-retaining diuretics, which have different mechanisms and side effect profiles. Diuretics are used to treat edema caused by conditions like heart failure or liver disease, hypertension, and other fluid-related issues. Proper administration is important to balance their effects on electrolytes and acid-base levels while reducing excess fluid. Less common diuretic classes include osmotics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageDiuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Diuretics: Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-Retaining)
Uploaded by
Andrew AkramDiuretics work by targeting sites in the kidneys to increase urine output and reduce fluid retention. The main classes are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-retaining diuretics, which have different mechanisms and side effect profiles. Diuretics are used to treat edema caused by conditions like heart failure or liver disease, hypertension, and other fluid-related issues. Proper administration is important to balance their effects on electrolytes and acid-base levels while reducing excess fluid. Less common diuretic classes include osmotics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
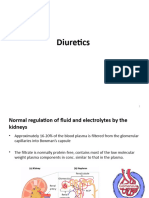
DIURETICS
Common Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop, K-retaining):
Members
Mechanism of action:
1) Site of action of the diuretic
2) How the diuretic reaches its site of action
3) The main diuretic target
a. Thiazides
b. Loop
c. K-retaining
4) Additional non-diuretic actions
Adverse effects:
1) Effects on blood chemistry:
a. Water
b. Electrolytes:
i. Sodium
ii. Potassium & Magnesium
iii. Calcium
c. Acid base balance
d. Glucose
e. Uric acid
2) General adverse effects
3) Special adverse effects
Indications:
1) Oedema
a. Heart failure and acute pulmonary edema
b. Hepatic edema
c. Nephrotic edema
d. Acute renal failure
e. Refractory edema
f. Other types of edema
Practical points about edema
2) Hypertension
3) Additional indications
Administration
Rare Diuretics:
1) Osmotic diuretics
2) Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
You might also like
- Diuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsDocument22 pagesDiuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsSteven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFDocument422 pagesOxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFvani reddyNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument18 pagesDiureticsChantal CarnesNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of DiureticsDocument46 pagesBasic Pharmacology of DiureticsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- Pharmacology DiureticsDocument32 pagesPharmacology DiureticsIrene WNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument16 pagesDiureticsvinodmedicozNo ratings yet
- Renal Note On DiureticsDocument12 pagesRenal Note On DiureticsLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Cardiovascular System CvsDocument36 pagesLecture 7 Cardiovascular System CvsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Diuretiku TokseDocument22 pagesDiuretiku TokseUgnė ČeponytėNo ratings yet
- Vidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014Document51 pagesVidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014naltrisilvianNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument83 pagesDiureticsKarami BrutusNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticsAnkita TatheNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Diseaseampogison08No ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologyDocument96 pagesDrugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderDocument33 pagesDiuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderNina KerafNo ratings yet
- Diuretics NewDocument21 pagesDiuretics NewPawan RajNo ratings yet
- Cardiac GlycosideDocument24 pagesCardiac Glycosideapi-3708473No ratings yet
- 105 DiureticsDocument18 pages105 DiureticsMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Metabolic & Acid-Base Balance: 1-When Lactic Acid Accumulates, Body Will Respond byDocument8 pagesMetabolic & Acid-Base Balance: 1-When Lactic Acid Accumulates, Body Will Respond byASGHAR ALINo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument40 pagesDiureticsHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213Document19 pagesDiuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213JedoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Usmle SuperDocument239 pagesUsmle SupermaksventileNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02Document45 pagesDiuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02P merugu100% (1)
- Lecture15-Diuretics and AntidiureticsDocument36 pagesLecture15-Diuretics and Antidiureticsharis.18No ratings yet
- Pharmacology I, Diuretics NK-modified 2Document32 pagesPharmacology I, Diuretics NK-modified 289c8g7bvvvNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKDocument46 pagesPharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKRizky Pramata Simamora 19000029No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CVS & RenalDocument116 pagesChapter 3 CVS & RenalKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument31 pagesDiureticsRameez ShamounNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument116 pagesDrugsRyan FlahertyNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowDocument35 pagesDiuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Self-Study - Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageDiuretics Self-Study - Revision Questionsedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSDocument51 pagesDiuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Haitham Mahmood AlwaliDocument32 pagesDiuretics: Haitham Mahmood Alwaligaurav adhikariNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesPharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFCodyDavistgny100% (9)
- Chapter 13 ElectrolytesDocument115 pagesChapter 13 Electrolytessisay SolomonNo ratings yet
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Document48 pagesPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The KidneysDocument56 pagesDrugs Acting On The Kidneysbetu tufaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument61 pagesDiureticsJoyce WacukaNo ratings yet
- Occupational and EnvironmentalDocument117 pagesOccupational and EnvironmentalGideon K. MutaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular For PharmacologDocument134 pagesCardiovascular For Pharmacologephremtigabie7No ratings yet
- Electrolyte Physiology & The KidneyDocument13 pagesElectrolyte Physiology & The KidneyFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Medicinal_chemistry_2_Unit_2_-1Document11 pagesMedicinal_chemistry_2_Unit_2_-1KevalNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 171130131557Document31 pagesDiuretics 171130131557Lety AgistiniaNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument21 pagesDiureticsShathawe BrgNo ratings yet
- Full Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument31 pagesFull Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptermcddieyorubc400100% (7)
- Presentation On Diuretics+synthesis Final VersionDocument58 pagesPresentation On Diuretics+synthesis Final VersionArkw ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Yuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Document55 pagesYuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Nurul PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Osmo Regulation MCQDocument5 pagesOsmo Regulation MCQKaran PrabaNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid CompartmentsDocument10 pagesBody Fluid CompartmentsAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanDocument54 pagesDiuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanEdi KurniadiNo ratings yet
- GI Disorders - Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument3 pagesGI Disorders - Alcoholic Liver Diseasemollymaheshwari00No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticsmohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Kidney DrugsDocument39 pagesPharmacology - Kidney DrugsSeth-Thomas TateNo ratings yet
- Avocado Nutritional CompositionDocument10 pagesAvocado Nutritional CompositionlizNo ratings yet
- Blood Drugs Used For AneamiasDocument7 pagesBlood Drugs Used For AneamiasMaha KhanNo ratings yet
- MFC GUIDELINES FOR SC T7 LNG 2023 Rev01Document6 pagesMFC GUIDELINES FOR SC T7 LNG 2023 Rev01izik4meNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7359009 20220622112958Document4 pagesLab Report 7359009 20220622112958Nandini PandeyNo ratings yet
- II. Recommendations (Quiambao, Razelle F.) Medications: Contact Your Healthcare Provider IfDocument3 pagesII. Recommendations (Quiambao, Razelle F.) Medications: Contact Your Healthcare Provider IfJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Lipidet BiokimiDocument118 pagesLipidet BiokimiEmir Cerkezi100% (1)
- Problem Lists Patient PlanDocument1 pageProblem Lists Patient Planangel23No ratings yet
- Kualitas Minyak Blend Kelapa Kopra Dan Minyak Kelapa Sawit Ditinjau Dari Kadar Air, Kadar Asam Lemak Bebas Dan Bilangan PeroksidaDocument8 pagesKualitas Minyak Blend Kelapa Kopra Dan Minyak Kelapa Sawit Ditinjau Dari Kadar Air, Kadar Asam Lemak Bebas Dan Bilangan PeroksidaesiNo ratings yet
- 1844 Obesity GuidelineDocument11 pages1844 Obesity GuidelineRohit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates in Our Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates in Our Everyday LifeMadhuri HandeNo ratings yet
- JBLMGH Rates For Laboratory Services: Jose B. Lingad Memorial General HospitalDocument4 pagesJBLMGH Rates For Laboratory Services: Jose B. Lingad Memorial General HospitalApril NNo ratings yet
- Prospectus - Young Star Insurance PolicyDocument26 pagesProspectus - Young Star Insurance PolicyNaveenraj SNo ratings yet
- Probiotic 13 Fr-2021-845 Wulandari Aprl 2023Document11 pagesProbiotic 13 Fr-2021-845 Wulandari Aprl 2023wisnuadi UMBYNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Document3 pagesTop 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Bubu ToNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDocument8 pagesHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountArun DheekshahNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Effects of A Ketogenic Diet in Obese PatientsDocument10 pagesLong-Term Effects of A Ketogenic Diet in Obese Patientsrobertofca2266No ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesDyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyNur HaidagNo ratings yet
- Please Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDocument1 pagePlease Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Fish LipidsDocument31 pagesFish Lipidskolita kamalNo ratings yet
- 3 Lipid MetabolismDocument54 pages3 Lipid MetabolismRahadatul Aisy100% (1)
- HF BrochureDocument23 pagesHF Brochureimran_issufoNo ratings yet
- Benefits of CocozhiDocument3 pagesBenefits of CocozhiGreenplanet CybercafeNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-4 Powerpoint For Hema Lab PT, aPTT, CRT, CFTDocument11 pagesLab 3-4 Powerpoint For Hema Lab PT, aPTT, CRT, CFTElaineNo ratings yet
- Cumin Anti Diabetic 2018Document11 pagesCumin Anti Diabetic 2018srikanth PosaNo ratings yet
- Skenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4Document12 pagesSkenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4ulfahNo ratings yet
- S.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop LocationDocument10 pagesS.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop Locationarindam dasNo ratings yet
- 10 Health Benefits of SpirulinaDocument10 pages10 Health Benefits of Spirulinahkm_gmat4849No ratings yet
- Ehad 814Document11 pagesEhad 814Srinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- LPT 311 PDFDocument190 pagesLPT 311 PDFIbad Ur RahmanNo ratings yet