Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsChapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Uploaded by
Erick GonzalezFrom young and freedman
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- PHYS363 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPHYS363 Formula SheetBen MacLellan100% (1)
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation Sheettw2121100% (1)
- Equations SummaryDocument4 pagesEquations SummaryBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- CH 12 A3 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 A3 NoteSam RajibNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Introduction of Vector CalculusDocument19 pagesWEEK 1 - Introduction of Vector Calculuss231032452No ratings yet
- Variable Structure Control Mechanical Systems: Harry G. KwatnyDocument15 pagesVariable Structure Control Mechanical Systems: Harry G. KwatnyChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- ChapteDocument8 pagesChapteMubariz MubarizNo ratings yet
- Bouncing Ball EquationsDocument5 pagesBouncing Ball EquationsFatih TSPNo ratings yet
- Induced Velocity by A Vorticity FieldDocument4 pagesInduced Velocity by A Vorticity FieldKamalkumar1405No ratings yet
- Projectile and Uniform Circular MotionDocument20 pagesProjectile and Uniform Circular Motionbeenilicious100% (1)
- Lectures 4-5 Chapter 4 Fall 2009Document27 pagesLectures 4-5 Chapter 4 Fall 2009tewari_skNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyDocument18 pagesKinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyYasheive saadiNo ratings yet
- FormulasheetDocument3 pagesFormulasheetAnnypaola MartinezNo ratings yet
- Particle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionDocument24 pagesParticle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionTony KaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Motion in Two and Three DimensionsAfnan AziziNo ratings yet
- SIM1003 Chapter 12 NotesDocument5 pagesSIM1003 Chapter 12 NotesMin Hui LeeNo ratings yet
- Me 201 - Dynamics: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument121 pagesMe 201 - Dynamics: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 - Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionDocument11 pagesChapter - 3 - Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensionvishalorisha0075No ratings yet
- 2 - 3D MotionDocument14 pages2 - 3D MotionFatah Imdul Umasugi100% (2)
- Kinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsDocument23 pagesKinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2solutionDocument4 pagesAssignment 2solutionGurraj BhullarNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation SheetKao LimNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two or Three DimensionsDocument58 pagesMotion in Two or Three DimensionsMarc Howard Detera PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathDocument60 pagesKinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathtomodachiNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetOMARNo ratings yet
- Vector Field Theory: 1 Scalar Fields. Vector FieldsDocument9 pagesVector Field Theory: 1 Scalar Fields. Vector FieldsDaNy3lMatheoNo ratings yet
- 5 Vector Valued FunctionsDocument6 pages5 Vector Valued FunctionsslowjamsNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesProjectile Motionapi-285179261No ratings yet
- Mitres 18 001 f17 Manual ch12Document9 pagesMitres 18 001 f17 Manual ch12ClaptrapjackNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDocument18 pagesCalculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDilo Tan100% (1)
- Quantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Document5 pagesQuantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Anoni AnonNo ratings yet
- Basics Solutions ParametrizationDocument4 pagesBasics Solutions Parametrizationrodrigo_trentiniNo ratings yet
- Program:-: This Is Program For Gauss-Siedel Load FlowDocument3 pagesProgram:-: This Is Program For Gauss-Siedel Load FlowVaibhav ChopwadNo ratings yet
- Modul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Document64 pagesModul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Herman_MLNo ratings yet
- Elementary Mechanics and Thermodynamics SOLUTIONS MANUAL - J. Norbury PDFDocument112 pagesElementary Mechanics and Thermodynamics SOLUTIONS MANUAL - J. Norbury PDFsuryaaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion PDFDocument17 pagesProjectile Motion PDFSachin NainNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesProjectile MotionAdrian YasayNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRDocument74 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRameliawenston3No ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasTanisha JainNo ratings yet
- Quick Review of Kinematics Formulas: S.No. Type of Motion FormulaDocument1 pageQuick Review of Kinematics Formulas: S.No. Type of Motion FormulaSaptaswa MunsiNo ratings yet
- Problems PlusDocument4 pagesProblems PlusVendedor OnlineNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Document34 pagesCurvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Mohamed DamraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 New Kinema TicsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 New Kinema TicsAfifudin NazriNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Pratik N ShethDocument37 pagesDifferential Calculus: Pratik N ShethgarvpaulNo ratings yet
- mt1 2013 SolutionsDocument6 pagesmt1 2013 SolutionsdilaytornaciiiNo ratings yet
- Task#147410Document7 pagesTask#147410alexisNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Midterm I IDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Midterm I IDavid ChangNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Remember in PhysicsDocument5 pagesFormulas To Remember in PhysicsBliss JullienneNo ratings yet
- Activity No.3 (Blade Section Forces)Document16 pagesActivity No.3 (Blade Section Forces)Jandrew TanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Vector CalculusDocument26 pagesTopic 1 - Vector Calculusmilinda deshappriyaNo ratings yet
- Ivan Avramidi, MATH 332: Vector Analysis, FormulasDocument4 pagesIvan Avramidi, MATH 332: Vector Analysis, FormulasDestriayu VasistaNo ratings yet
- Homework Vector SolnDocument7 pagesHomework Vector SolnReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument144 pagesVector CalculusramiroNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lecture Accl-VelocityDocument18 pagesDynamics Lecture Accl-VelocityAbhijeeth Nagaraj100% (4)
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- MET 304 Engineering AnalysisDocument31 pagesMET 304 Engineering AnalysisOscar WangNo ratings yet
- Differentiation SummaryDocument1 pageDifferentiation SummaryNishchay BhattNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch07 Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch07 Projectile MotionSaherNo ratings yet
- Erick Gonzalez // CS 1325 - 002 // September 1st 2013 // Homework 2: Program To Solve Quadratic Equation OutputDocument1 pageErick Gonzalez // CS 1325 - 002 // September 1st 2013 // Homework 2: Program To Solve Quadratic Equation OutputErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Motion Along A Straight Line Equations: 1 Velocity, AccelerationDocument1 pageChapter 2: Motion Along A Straight Line Equations: 1 Velocity, AccelerationErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionsDocument1 pageChapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 13 FL2413 GHW10 HDocument2 pages13 FL2413 GHW10 HErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EquationsDocument1 pageChapter 4 EquationsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal TransformationsDocument1 pagePre Cal TransformationsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Uploaded by
Erick Gonzalez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesFrom young and freedman
Original Title
Chapter 3 Equations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFrom young and freedman
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesChapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensions: 1 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Uploaded by
Erick GonzalezFrom young and freedman
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
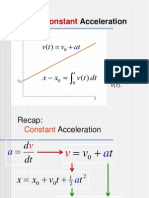
Chapter 3: Motion In 2 or 3 Dimensions
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
~r = xi + yj + z k
~vav =
~r2 ~r1
~r
=
t2 t1
t
~r
d~r
=
t0 t
dt
~v = lim
vx =
dx
dt
~aav =
t0
dy
dt
vz =
dz
dt
~v2 ~v1
~v
=
t2 t1
t
~a = lim
ax =
vy =
~v
d~v
=
t
dt
dvx
dt
ay =
dvy
dt
az =
dvz
dt
Projectile Motion
x = (v0 cos0 )t
1
y = (v0 sin0 )t gt2
2
vx = v0 cos0
vy = v0 sin0 gt
tP =
h=
R=
v0 sin
(Derived Time at Peak)
g
v02 sin2
(Derived Max Height)
2g
v02 sin2
(Range Equation)
g
Uniform and Nonuniform Circular Motion
arad =
v2
R
arad =
4 2 R
T2
Relative Velocity
~vP/A = ~vP/B + ~vB/A
#19
T final
T initial
#23
You might also like
- PHYS363 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPHYS363 Formula SheetBen MacLellan100% (1)
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation Sheettw2121100% (1)
- Equations SummaryDocument4 pagesEquations SummaryBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- CH 12 A3 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 A3 NoteSam RajibNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Introduction of Vector CalculusDocument19 pagesWEEK 1 - Introduction of Vector Calculuss231032452No ratings yet
- Variable Structure Control Mechanical Systems: Harry G. KwatnyDocument15 pagesVariable Structure Control Mechanical Systems: Harry G. KwatnyChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- ChapteDocument8 pagesChapteMubariz MubarizNo ratings yet
- Bouncing Ball EquationsDocument5 pagesBouncing Ball EquationsFatih TSPNo ratings yet
- Induced Velocity by A Vorticity FieldDocument4 pagesInduced Velocity by A Vorticity FieldKamalkumar1405No ratings yet
- Projectile and Uniform Circular MotionDocument20 pagesProjectile and Uniform Circular Motionbeenilicious100% (1)
- Lectures 4-5 Chapter 4 Fall 2009Document27 pagesLectures 4-5 Chapter 4 Fall 2009tewari_skNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyDocument18 pagesKinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyYasheive saadiNo ratings yet
- FormulasheetDocument3 pagesFormulasheetAnnypaola MartinezNo ratings yet
- Particle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionDocument24 pagesParticle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionTony KaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Motion in Two and Three DimensionsAfnan AziziNo ratings yet
- SIM1003 Chapter 12 NotesDocument5 pagesSIM1003 Chapter 12 NotesMin Hui LeeNo ratings yet
- Me 201 - Dynamics: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument121 pagesMe 201 - Dynamics: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 - Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionDocument11 pagesChapter - 3 - Motion in 2 or 3 Dimensionvishalorisha0075No ratings yet
- 2 - 3D MotionDocument14 pages2 - 3D MotionFatah Imdul Umasugi100% (2)
- Kinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsDocument23 pagesKinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2solutionDocument4 pagesAssignment 2solutionGurraj BhullarNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation SheetKao LimNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two or Three DimensionsDocument58 pagesMotion in Two or Three DimensionsMarc Howard Detera PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathDocument60 pagesKinematics of A Particle: Particle Motion Along A Curved PathtomodachiNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetOMARNo ratings yet
- Vector Field Theory: 1 Scalar Fields. Vector FieldsDocument9 pagesVector Field Theory: 1 Scalar Fields. Vector FieldsDaNy3lMatheoNo ratings yet
- 5 Vector Valued FunctionsDocument6 pages5 Vector Valued FunctionsslowjamsNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesProjectile Motionapi-285179261No ratings yet
- Mitres 18 001 f17 Manual ch12Document9 pagesMitres 18 001 f17 Manual ch12ClaptrapjackNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDocument18 pagesCalculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDilo Tan100% (1)
- Quantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Document5 pagesQuantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Anoni AnonNo ratings yet
- Basics Solutions ParametrizationDocument4 pagesBasics Solutions Parametrizationrodrigo_trentiniNo ratings yet
- Program:-: This Is Program For Gauss-Siedel Load FlowDocument3 pagesProgram:-: This Is Program For Gauss-Siedel Load FlowVaibhav ChopwadNo ratings yet
- Modul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Document64 pagesModul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Herman_MLNo ratings yet
- Elementary Mechanics and Thermodynamics SOLUTIONS MANUAL - J. Norbury PDFDocument112 pagesElementary Mechanics and Thermodynamics SOLUTIONS MANUAL - J. Norbury PDFsuryaaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion PDFDocument17 pagesProjectile Motion PDFSachin NainNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesProjectile MotionAdrian YasayNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRDocument74 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 10e Raymond A. Serway John W. Jewett, JRameliawenston3No ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasTanisha JainNo ratings yet
- Quick Review of Kinematics Formulas: S.No. Type of Motion FormulaDocument1 pageQuick Review of Kinematics Formulas: S.No. Type of Motion FormulaSaptaswa MunsiNo ratings yet
- Problems PlusDocument4 pagesProblems PlusVendedor OnlineNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Document34 pagesCurvilinear Motion: Rectangular Components Projectiles (Sections 12.4-12.6)Mohamed DamraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 New Kinema TicsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 New Kinema TicsAfifudin NazriNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Pratik N ShethDocument37 pagesDifferential Calculus: Pratik N ShethgarvpaulNo ratings yet
- mt1 2013 SolutionsDocument6 pagesmt1 2013 SolutionsdilaytornaciiiNo ratings yet
- Task#147410Document7 pagesTask#147410alexisNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Midterm I IDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Midterm I IDavid ChangNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Remember in PhysicsDocument5 pagesFormulas To Remember in PhysicsBliss JullienneNo ratings yet
- Activity No.3 (Blade Section Forces)Document16 pagesActivity No.3 (Blade Section Forces)Jandrew TanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Vector CalculusDocument26 pagesTopic 1 - Vector Calculusmilinda deshappriyaNo ratings yet
- Ivan Avramidi, MATH 332: Vector Analysis, FormulasDocument4 pagesIvan Avramidi, MATH 332: Vector Analysis, FormulasDestriayu VasistaNo ratings yet
- Homework Vector SolnDocument7 pagesHomework Vector SolnReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument144 pagesVector CalculusramiroNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lecture Accl-VelocityDocument18 pagesDynamics Lecture Accl-VelocityAbhijeeth Nagaraj100% (4)
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- MET 304 Engineering AnalysisDocument31 pagesMET 304 Engineering AnalysisOscar WangNo ratings yet
- Differentiation SummaryDocument1 pageDifferentiation SummaryNishchay BhattNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch07 Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch07 Projectile MotionSaherNo ratings yet
- Erick Gonzalez // CS 1325 - 002 // September 1st 2013 // Homework 2: Program To Solve Quadratic Equation OutputDocument1 pageErick Gonzalez // CS 1325 - 002 // September 1st 2013 // Homework 2: Program To Solve Quadratic Equation OutputErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Motion Along A Straight Line Equations: 1 Velocity, AccelerationDocument1 pageChapter 2: Motion Along A Straight Line Equations: 1 Velocity, AccelerationErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionsDocument1 pageChapter 3: Motion in 2 or 3 DimensionsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 13 FL2413 GHW10 HDocument2 pages13 FL2413 GHW10 HErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EquationsDocument1 pageChapter 4 EquationsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal TransformationsDocument1 pagePre Cal TransformationsErick GonzalezNo ratings yet