Professional Documents
Culture Documents
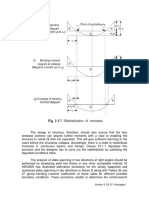
1.2.7 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers
1.2.7 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers
Uploaded by
scr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageReinforced concrete consists of plain concrete and steel reinforcement, which allows architects and structural engineers to work together in a unified way. Concrete is strong in both tension and compression when reinforced with steel, and its moldability and monolithic nature enable new architectural visions. However, the strength and durability of concrete depends on the properties of its constituent materials - cement, sand, gravel, water, and sometimes mineral admixtures - as well as how they are proportioned, prepared, transported, placed, compacted, and cured. Similarly, the quality and durability of steel reinforcement, influenced by environmental effects, also impacts the strength of reinforced concrete. Adequate concrete cover protects the embedded steel from rusting. Inspection,
Original Description:
x
Original Title
31 Pdfsam Conc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentReinforced concrete consists of plain concrete and steel reinforcement, which allows architects and structural engineers to work together in a unified way. Concrete is strong in both tension and compression when reinforced with steel, and its moldability and monolithic nature enable new architectural visions. However, the strength and durability of concrete depends on the properties of its constituent materials - cement, sand, gravel, water, and sometimes mineral admixtures - as well as how they are proportioned, prepared, transported, placed, compacted, and cured. Similarly, the quality and durability of steel reinforcement, influenced by environmental effects, also impacts the strength of reinforced concrete. Adequate concrete cover protects the embedded steel from rusting. Inspection,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 page1.2.7 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers
1.2.7 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers
Uploaded by
scrReinforced concrete consists of plain concrete and steel reinforcement, which allows architects and structural engineers to work together in a unified way. Concrete is strong in both tension and compression when reinforced with steel, and its moldability and monolithic nature enable new architectural visions. However, the strength and durability of concrete depends on the properties of its constituent materials - cement, sand, gravel, water, and sometimes mineral admixtures - as well as how they are proportioned, prepared, transported, placed, compacted, and cured. Similarly, the quality and durability of steel reinforcement, influenced by environmental effects, also impacts the strength of reinforced concrete. Adequate concrete cover protects the embedded steel from rusting. Inspection,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
The reinforced concrete consisting of plain concrete and steel
reinforcement opened a new vista fulfilling the imaginations of architect with a
unified approach of the architect and structural engineer. This has been made
possible due to mouldability and monolithicity of concrete in addition to its
strength in both tension and compression when reinforced with steel. However,
concrete is produced by mixing cement, sand, gravel, water and mineral
admixtures, if needed. Therefore, the final strength of concrete depends not only
on the individual properties of its constituent materials, but also on the
proportions of the material and the manner in which it is prepared, transported,
placed, compacted and cured. Moreover, durability of the concrete is also largely
influenced by all the steps of its preparation.
Steel reinforcement though produced in steel plants and made available in
form of bars and rods of specific diameter also influences the final strength of
reinforced concrete by its quality and durability due to environmental effects.
Concrete cover provides the protective environment to embedded steel
from rusting that would need presence of both oxygen and moisture. Not only the
extent of cover but the quality of cover is important for this reason.
Accordingly, inspection of concrete work, sample testing of specimens,
core tests, load tests and non-destructive tests are very important to maintain the
quality, strength and durability of reinforced concrete structures. Moreover, it is
equally important to remove small defects or make good of it after removing the
formwork before it has thoroughly hardened.
Thus, starting from the selection of each constitutive material to the
satisfactory construction of the structure, the designer's responsibility will only
produce the desired concrete structure which will satisfy the functional
requirements as well as will have its aesthetic values exploiting all the good
properties of this highly potential material.
1.2.7 Practice Questions and Problems with Answers
Q.1: What are the constituent materials of plain concrete?
A.1: The constituent materials of plain concrete are cement, sand (fine
aggregate), gravel (coarse aggregate), water and mineral admixtures in
some special cases.
Q.2: Define characteristic strength fck of concrete.
Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instructional Objectives:: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument1 pageInstructional Objectives:: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurscrNo ratings yet
- LWH Technical Paper 071219Document12 pagesLWH Technical Paper 071219ahmad tarmiziNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: 2.0 Literature ReviewDocument17 pagesChapter Two: 2.0 Literature ReviewRayyan Darwisy100% (1)
- CMT Research 2Document5 pagesCMT Research 2Fred RecaldeNo ratings yet
- By: Nirmla G.F. Lecturer Civil BKN Govt. Polytechnic NarnaulDocument53 pagesBy: Nirmla G.F. Lecturer Civil BKN Govt. Polytechnic NarnaulAshish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Procem SlidesDocument29 pagesProcem Slideskevin iyeseNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 PreambleDocument33 pagesChapter One 1.1 PreambleRAHMON RAUF OYEDOKUNNo ratings yet
- Seminar Technical Report (1903024,1903023, 1903043)Document10 pagesSeminar Technical Report (1903024,1903023, 1903043)vivekkumarsingh7980No ratings yet
- Cec 313 Lect NoteDocument10 pagesCec 313 Lect NoteSamson Mide FolorunshoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Basics PDFDocument30 pagesConcrete Basics PDFDarshan Rokztar100% (1)
- Portland Cement Construction Aggregate Rebar: Reinforced ConcreteDocument1 pagePortland Cement Construction Aggregate Rebar: Reinforced ConcreteIshwarya SrikanthNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Cocncrete at Hardened StageDocument1 page2.1 Properties of Cocncrete at Hardened StageKanchana HarikaranNo ratings yet
- Design of Structures.hDocument95 pagesDesign of Structures.hAsiimwe Moses KasirikaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Rusting Prevention PDFDocument6 pagesReinforcement Rusting Prevention PDFJitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement Construction Aggregate RebarDocument1 pagePortland Cement Construction Aggregate RebarClarenceNo ratings yet
- Civil Concrete Technology Lectures Notes DownloadDocument12 pagesCivil Concrete Technology Lectures Notes DownloadMildred Ivy Bangoy Pangilinan0% (1)
- Plain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Document48 pagesPlain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Adil Javed Chaudhary100% (1)
- 236763-Article Text-572027-1-10-20221124Document7 pages236763-Article Text-572027-1-10-20221124WalterGentileNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: M.R. Head of Civil Engineering Department, For Inspiring Take This Project. I Also ExpressedDocument18 pagesAcknowledgement: M.R. Head of Civil Engineering Department, For Inspiring Take This Project. I Also ExpressedRicky RickxNo ratings yet
- Lec-1-Introduction ACI 318-19 - ACI 214r-11Document48 pagesLec-1-Introduction ACI 318-19 - ACI 214r-11Muhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- Causes of Deterioration of StructuresDocument5 pagesCauses of Deterioration of StructuresDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Arc 022 Building Technology 1: Department of ArchitectureDocument19 pagesArc 022 Building Technology 1: Department of ArchitectureLenard UsonNo ratings yet
- Report On Summer RainingDocument16 pagesReport On Summer RainingAr G S YadavNo ratings yet
- Project Journal-MagiDocument11 pagesProject Journal-MagiItsme PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument10 pagesResearch ArticlePankaj MunjalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 FINAL YEAR ProjectDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 1 FINAL YEAR ProjectdejayzNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete 2Document2 pagesReinforced Concrete 2MJ MacalamNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Hybrid Fibre Reinforced Concrete Beam Column Joints Under Reverse Cyclic Loads 2014 Materials and DesignDocument8 pagesBehaviour of Hybrid Fibre Reinforced Concrete Beam Column Joints Under Reverse Cyclic Loads 2014 Materials and DesignAlper BuyukkaragozNo ratings yet
- Name:Muhammad Huzaifa ROLL NO: 21AR104 Submitted To: Ma'Am Rida Rarenstation TopicDocument8 pagesName:Muhammad Huzaifa ROLL NO: 21AR104 Submitted To: Ma'Am Rida Rarenstation TopicAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Plain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Document19 pagesPlain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Manoj BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- TN 3 ADocument10 pagesTN 3 ARoy H Mayo JrNo ratings yet
- Types of Concrete - WikipediaDocument11 pagesTypes of Concrete - WikipediaAndi SilalahiNo ratings yet
- A Robust Composition of Polymers and Fly AshDocument30 pagesA Robust Composition of Polymers and Fly AshlazamNo ratings yet
- Plain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Document52 pagesPlain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Lecture # 1Muhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- Subject:: "Building Materials & Construction"Document42 pagesSubject:: "Building Materials & Construction"Yash DhabaliaNo ratings yet
- Ecs268 L11Document2 pagesEcs268 L11HazeyyNo ratings yet
- Concrete Repair and Protection System1 - CeresitDocument12 pagesConcrete Repair and Protection System1 - CeresitJill Jim LivestockNo ratings yet
- Material HandoutDocument77 pagesMaterial Handoutgebretsadikaraya211626No ratings yet
- Reinforcement Corrosion in Concrete Structures and Service Life Predictions - A ReviewDocument5 pagesReinforcement Corrosion in Concrete Structures and Service Life Predictions - A ReviewAdnan BuljubasicNo ratings yet
- Durability of Concrete With Differential Concrete Mix DesignDocument10 pagesDurability of Concrete With Differential Concrete Mix Designshoyeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Ref2 Beton SpallingDocument14 pagesRef2 Beton SpallingGresy Yosepha Banjarnahor100% (1)
- Stress Strain From Saenz ModelDocument7 pagesStress Strain From Saenz ModelKorrapati Pratyusha 19PHD0497No ratings yet
- Engineered Cementitious CompositesDocument8 pagesEngineered Cementitious CompositesSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Strength and Workability of Reinforced Concrete Using Lathe WasteDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Strength and Workability of Reinforced Concrete Using Lathe WasteyunuskolaNo ratings yet
- Repair and Rehabilitation of Reinforced ConcreteDocument15 pagesRepair and Rehabilitation of Reinforced ConcreteebinVettuchirayil100% (2)
- Module 04 NMDocument5 pagesModule 04 NMmiratif19_860027847No ratings yet
- Properties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete: Rajiv Gandhi Technological University, BhopalDocument21 pagesProperties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete: Rajiv Gandhi Technological University, Bhopalmuhammad irfanNo ratings yet
- Materials and Conbstructioib Technology 4.Document21 pagesMaterials and Conbstructioib Technology 4.AmmarNo ratings yet
- Kshuboo 2nd PaperDocument5 pagesKshuboo 2nd PaperPriyanshiNo ratings yet
- Concrete Types and UsesDocument2 pagesConcrete Types and UsesKaouter BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Tn3a PDFDocument10 pagesTn3a PDFlukasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document8 pagesLecture 8Mask KingNo ratings yet
- Typologies of CementDocument250 pagesTypologies of CementRHYME KIDSNo ratings yet
- 01 Cotm 2103 HandoutDocument102 pages01 Cotm 2103 HandoutDëø VølëñtëNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 IntroductionDocument19 pagesLec 1 IntroductionManoj BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Concrete ProjectionDocument28 pagesConcrete ProjectionMooneer El AssaadNo ratings yet
- DRCE NotesDocument127 pagesDRCE NotesAyush GargNo ratings yet
- 314 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page314 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 320 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page320 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 315 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page315 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Step 5c: Calculation Of: R R EffDocument1 pageStep 5c: Calculation Of: R R EffscrNo ratings yet
- 7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IDocument1 page7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IscrNo ratings yet
- 321 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page321 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 323 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page323 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Step 6: Checking of The Requirements of IS 456:) (PermDocument1 pageStep 6: Checking of The Requirements of IS 456:) (PermscrNo ratings yet
- 318 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page318 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 2.3.8 Summary of This Lesson: TQ.6: Give Four Reasons To Justify The Design of Structures by Limit State MethodDocument1 page2.3.8 Summary of This Lesson: TQ.6: Give Four Reasons To Justify The Design of Structures by Limit State MethodscrNo ratings yet
- 7.17.9 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers: F o W FDocument1 page7.17.9 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers: F o W FscrNo ratings yet
- 332 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page332 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Step 1: Properties of Plain Concrete SectionDocument1 pageSolution 1:: Step 1: Properties of Plain Concrete SectionscrNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Deflection: Step 1Document1 pageCalculation of Deflection: Step 1scrNo ratings yet
- 59 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page59 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 56 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page56 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 329 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page329 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 333 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page333 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 334 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page334 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 58 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page58 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 60 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page60 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 70 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page70 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 55 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page55 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 57 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page57 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 52 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page52 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 2.3.7 Test 3 With Solutions: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument1 page2.3.7 Test 3 With Solutions: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurscrNo ratings yet
- 51 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page51 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 49 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page49 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 50 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page50 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 48 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page48 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet