Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ductility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability and
Ductility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability and
Uploaded by
Ravi TarunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ductility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability and
Ductility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability and
Uploaded by
Ravi TarunCopyright:
Available Formats
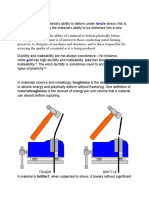
Ductility describes the property of the ability to stretch a metal, without
being damaged
Ductility and malleability- *The difference between malleability and
ductility is that malleability is the ability to deform easily upon the
application of a compressive force, and ductility is doing the same with
tensile force.
*Ductility is a mechanical property used to describe the extent to which
materials can be deformed plastically without fracture.
In material science, ductility specifically refers to a material's ability to
deform under tensile stress; this is often characterized by the material's
ability to be stretched into a wire.
Malleability, a similar concept, refers to a material's ability to deform under
compressive stress; this is often characterized by the material's ability to
form a thin sheet by hammering or rolling. Ductility and malleability do not
always correlate with each other; for instance, gold is both ductile and
malleable, but lead is only malleable.
Commonly, the term "ductility" is used to refer to both concepts, as they are
very similar.
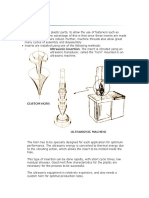
-Ductility and malleability are two properties of metals that describe specific
tendencies in certain metals. Ductility describes the property of the ability to
stretch a metal, without being damaged. Highly ductile materials are useful
for stretching into wires. Malleability describes the property of a metals
ability to be deformed under compression. Highly malleable materials can
be readily rolled or hammered into sheets. While these properties are
similar, different materials react differently in these circumstances. Gold or
copper for example, are both highly ductile and malleable
You might also like
- LeamanDocument33 pagesLeamanJojo HohoNo ratings yet
- Ductility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability andDocument2 pagesDuctility and Malleability - The Difference Between Malleability andRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Ductility and MalleabilityDocument2 pagesDuctility and MalleabilityRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- DuctilityDocument3 pagesDuctilityCarlo CastorNo ratings yet
- Ductility: Almgsi AlloyDocument2 pagesDuctility: Almgsi AlloyzidaaanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleWajahat RasoolNo ratings yet
- Ductility Is When A Solid Material Stretches Under: Tensile Wire Malleability CompressiveDocument1 pageDuctility Is When A Solid Material Stretches Under: Tensile Wire Malleability Compressiveaditya singhNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Metal: Group 1 Members: Reymark M.laureanoDocument6 pagesThe Mechanical Properties of Metal: Group 1 Members: Reymark M.laureanoNinfa LansangNo ratings yet
- Welding Course 1Document79 pagesWelding Course 1Orueta ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Professional WeldingDocument213 pagesFundamentals of Professional Weldingapi-3856939No ratings yet
- Welding FundametalsDocument55 pagesWelding Fundametalsyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Toughness: Types of Stresses On Loads Imposed On WeldmentsDocument7 pagesToughness: Types of Stresses On Loads Imposed On WeldmentsWilly UioNo ratings yet
- E BookDocument287 pagesE BookNithin SubrmaniiNo ratings yet
- Special Properties of MatterDocument17 pagesSpecial Properties of MatterLizanne GauranaNo ratings yet
- Pointers - EngineDocument3 pagesPointers - EngineIvan QuidlatNo ratings yet
- Duct IlityDocument14 pagesDuct IlityMehman NasibovNo ratings yet
- Final PresentationDocument24 pagesFinal PresentationJoy DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their Properties (Report)Document48 pagesMetals and Their Properties (Report)Emmanuel BlancaverNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument10 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialsosama raufNo ratings yet
- Study Materials For Mechanical EngineersDocument63 pagesStudy Materials For Mechanical EngineersOmprakash ManharNo ratings yet
- EmmDocument18 pagesEmmrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- PRT 203 - Metal Forming and FabricationDocument130 pagesPRT 203 - Metal Forming and FabricationNiyonase OlivierNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of A Metal: DuctilityDocument6 pagesMechanical Properties of A Metal: DuctilityNinfa LansangNo ratings yet
- PR2 Malleability-Of-Metals 12eDocument20 pagesPR2 Malleability-Of-Metals 12eJAY NACIONNo ratings yet
- DuctilityDocument4 pagesDuctilitycelsolcruzNo ratings yet
- (Sibolinao) Midterm Assignment 1Document4 pages(Sibolinao) Midterm Assignment 1John Benedict SibolinaoNo ratings yet
- Materials of EngineeringDocument10 pagesMaterials of EngineeringVer MeoNo ratings yet
- Materials Science TensileDocument3 pagesMaterials Science Tensileaditya2053No ratings yet
- 18 Mechanical Properties of MaterialDocument4 pages18 Mechanical Properties of MaterialmosisaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsKailash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 2 Mechanical PropertiesDocument2 pages2 Mechanical Propertiesashu_adbnelNo ratings yet
- Concrete Steel: ElasticityDocument2 pagesConcrete Steel: ElasticityRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- Workshop AnswersDocument10 pagesWorkshop AnswerscollegememotagorebhawanNo ratings yet
- Dental Casting Alloys PDFDocument53 pagesDental Casting Alloys PDFamrsheblks100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials: (Chapter 2)Document8 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials: (Chapter 2)Kris OiraNo ratings yet
- Metals and Plastics: Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesMetals and Plastics: Chapter Learning ObjectivesTodd HembreeNo ratings yet
- Ferrous MetalDocument26 pagesFerrous MetalEdbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- Drilling Operations l3 NotesDocument21 pagesDrilling Operations l3 Notesishimwe kwizera willyNo ratings yet
- Metal Finishing and Properties Full PDFDocument18 pagesMetal Finishing and Properties Full PDFSarah Mae AjonNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structural MaterialsDocument72 pagesAircraft Structural MaterialsLION KINGNo ratings yet
- How Does Rust FormDocument5 pagesHow Does Rust FormRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers 3Document34 pagesChemistry For Engineers 3Audrey VicenteNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsSasaleleNo ratings yet
- Elasticity SAQDocument2 pagesElasticity SAQRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- Metallic MaterialDocument5 pagesMetallic MaterialSujan DebnathNo ratings yet
- Metal FormingDocument12 pagesMetal FormingSantoshNo ratings yet
- Ductility / Malleability: ToughnessDocument3 pagesDuctility / Malleability: ToughnessEyob EyobNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1V.Nagaraju 19O17-M-O5ONo ratings yet
- موادmatalic هندسيه PDFDocument10 pagesموادmatalic هندسيه PDFMustafam98No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsBoykeNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Document9 pagesAircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Jan Patrick VelosoNo ratings yet
- L1 - OPD 2 - Properties of Dental MaterialsDocument3 pagesL1 - OPD 2 - Properties of Dental MaterialsFatima Nurjanna AwaliNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsMuhangi ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"No ratings yet
- Tool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforFrom EverandTool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforNo ratings yet
- High-Speed Steel - The Development, Nature, Treatment, and use of High-Speed Steels, Together with Some Suggestions as to the Problems Involved in their UseFrom EverandHigh-Speed Steel - The Development, Nature, Treatment, and use of High-Speed Steels, Together with Some Suggestions as to the Problems Involved in their UseNo ratings yet
- Ironwork - Part II - Being a Continuation of the First Handbook, and Comprising from the Close of the Mediaeval Period to the End of the Eighteenth Century, Excluding English WorkFrom EverandIronwork - Part II - Being a Continuation of the First Handbook, and Comprising from the Close of the Mediaeval Period to the End of the Eighteenth Century, Excluding English WorkNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941From EverandTechnical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941No ratings yet
- Bis PDFDocument18 pagesBis PDFRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- H 1.5T+T D 1.5T OR 2T: RELIEF:-W 2T D Bend Radius +T Flange W 4T+Bend Radius BackDocument4 pagesH 1.5T+T D 1.5T OR 2T: RELIEF:-W 2T D Bend Radius +T Flange W 4T+Bend Radius BackRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- SuspensionDocument14 pagesSuspensionRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Rolling Circumference Can Be Defined As The Distance A Tire Travels in One Revolution. Due ToDocument6 pagesRolling Circumference Can Be Defined As The Distance A Tire Travels in One Revolution. Due ToRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Project Detailed Briefing SheetDocument4 pagesProject Detailed Briefing SheetRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- FT 675Document1 pageFT 675Ravi TarunNo ratings yet
- Column1 Fender Assembly Raditor Shell 3 Point Linkage Mounting BKTDocument1 pageColumn1 Fender Assembly Raditor Shell 3 Point Linkage Mounting BKTRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- InsertsDocument2 pagesInsertsRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Column1 Fender Assembly Lock Mounting BKT Assem Air Tank Mounting BKT Bonet HingeDocument1 pageColumn1 Fender Assembly Lock Mounting BKT Assem Air Tank Mounting BKT Bonet HingeRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Biw PDFDocument8 pagesBiw PDFRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- BossesDocument1 pageBossesRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Sheetmetal: - CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesSheetmetal: - CharacteristicsRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- New Ressume Spandan MohantyDocument3 pagesNew Ressume Spandan MohantyRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Sikagrout 215 M Pds 2Document2 pagesSikagrout 215 M Pds 2Dimas MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Miracle in Lexical ConcordanceDocument6 pagesMathematical Miracle in Lexical Concordanceapi-3700570No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 q1 w7Document56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 q1 w7NicoleNo ratings yet
- Preparation of CatalystsDocument44 pagesPreparation of CatalystslsueyinNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document32 pagesCH 2HFNo ratings yet
- Orifice PlateDocument6 pagesOrifice PlateArbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- TENSACCIAI - Rock and Soil AnchorsDocument0 pagesTENSACCIAI - Rock and Soil Anchorsnovakno1No ratings yet
- Technical DrawingDocument38 pagesTechnical DrawingKinfe MehariNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document3 pagesExp 1Mani MaNo ratings yet
- G. Paul, Et Al., A Simplified Predictive Model For Micellar-Polymer Flooding PDFDocument20 pagesG. Paul, Et Al., A Simplified Predictive Model For Micellar-Polymer Flooding PDFRaemora Zaith IthinNo ratings yet
- Peter Ciorau, Lou Pullia, Trek Hazelton, Wence Daks OPG-IMS, Pickering, CanadaDocument8 pagesPeter Ciorau, Lou Pullia, Trek Hazelton, Wence Daks OPG-IMS, Pickering, CanadaMalolan VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Line Transmission Technical ParametersDocument3 pagesLine Transmission Technical ParametersRianNo ratings yet
- Land Surveying Chapter 4 EDM and TheodoliteDocument13 pagesLand Surveying Chapter 4 EDM and TheodoliteAzrul ZulwaliNo ratings yet
- FT 15 LV 14Document15 pagesFT 15 LV 14jadungNo ratings yet
- Moving Air For Comfort - ASHRAE JournalDocument12 pagesMoving Air For Comfort - ASHRAE JournalJoel TorresNo ratings yet
- Problem Rankine CycleDocument3 pagesProblem Rankine CycleErwin SutionoNo ratings yet
- Springer Ebooks PDFDocument21 pagesSpringer Ebooks PDFMed HilalismeNo ratings yet
- ENGG10041 Assessment Term2 March 2018Document4 pagesENGG10041 Assessment Term2 March 2018Margarita TomadakhNo ratings yet
- TRUSSES Detailed DRGDocument3 pagesTRUSSES Detailed DRGprabhu81No ratings yet
- Paper 1 3-D Analysis of Building Frame Using Staad-ProDocument2 pagesPaper 1 3-D Analysis of Building Frame Using Staad-ProAnonymous CaemA1No ratings yet
- Polynomials Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument21 pagesPolynomials Linear Equations in Two VariablesthinkiitNo ratings yet
- As 1289.6.7.3-1999 Methods of Testing Soils For Engineering Purposes Soil Strength and Consolidation TestsDocument2 pagesAs 1289.6.7.3-1999 Methods of Testing Soils For Engineering Purposes Soil Strength and Consolidation TestsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- 1 Input Data: Profis Anchor 2.7.1Document6 pages1 Input Data: Profis Anchor 2.7.1Shafeeq KTNo ratings yet
- Towards The Ultimate Conservative Difference Scheme. II. Monotonicity and Conservation Combined in A Second-Order SchemeDocument10 pagesTowards The Ultimate Conservative Difference Scheme. II. Monotonicity and Conservation Combined in A Second-Order Schemejiangzhh19990% (1)
- Manual de Usuario Holiday PcwiDocument12 pagesManual de Usuario Holiday PcwijerrymcflyNo ratings yet
- Design of Thermal Systems - Stoecker 3rd EditionDocument568 pagesDesign of Thermal Systems - Stoecker 3rd EditionDeep Narula92% (13)
- Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument41 pagesPrestressed Concrete StructuresAmar WadoodNo ratings yet
- BEAMCOL13Document9 pagesBEAMCOL13NEONo ratings yet
- Circuitos Electroneumaticos NewDocument29 pagesCircuitos Electroneumaticos NewDaniel PantojaNo ratings yet