Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsCommon Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Common Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Uploaded by
MiloševićZoranThe document provides an overview of five common English tenses: present simple, past simple, future simple, present perfect, and present continuous. It describes when to use each tense, examples of words that signal their use, how each tense is formed grammatically, and the helping verbs associated with each one.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSignal Wordsbethsde92% (12)
- Tenses NotesDocument21 pagesTenses NotesTheebaaRamasamyNo ratings yet
- Hortatory ExpositionDocument15 pagesHortatory ExpositionAvito ShafaNo ratings yet
- Time ExpressionsDocument1 pageTime ExpressionsMatteo CianforliniNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument9 pagesSimple Present TenseTJRNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Present TenseMeto FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Interview TensesDocument9 pagesInterview Tensesdaniel21805No ratings yet
- How To Teach The Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesHow To Teach The Present Continuouschalonniaa100% (1)
- TENSES (Present Tenses)Document38 pagesTENSES (Present Tenses)Mauries Irenia PutriNo ratings yet
- Universitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIDocument19 pagesUniversitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIRiandy LiuNo ratings yet
- 123Document15 pages123Ngọc MaiNo ratings yet
- English Tense Timeline QuerformatDocument3 pagesEnglish Tense Timeline QuerformatqkhaiproNo ratings yet
- General EnglishDocument142 pagesGeneral Englishmanyfid0% (1)
- Independent Work: ThemeDocument12 pagesIndependent Work: ThemeHacer BullaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Limbii EnglezeDocument15 pagesGramatica Limbii Englezeaadypmp2004No ratings yet
- The Present Progressive TenseDocument18 pagesThe Present Progressive Tenseapi-213942189No ratings yet
- Time LinesDocument5 pagesTime LinesEmily De LeónNo ratings yet
- Pre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2Document44 pagesPre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2daniel madrigalNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses - Adjective OrderDocument13 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses - Adjective OrderMihaiMereNo ratings yet
- Sw9 Verb TensesDocument25 pagesSw9 Verb TensesInês castaNo ratings yet
- Tenses (Notes) : Chart-Active Verb TensesDocument2 pagesTenses (Notes) : Chart-Active Verb TensesNana KawaiiNo ratings yet
- For My LoveDocument3 pagesFor My LoveDoung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Mythily A/P Manimaran Kasthuri A/P Krishnan Thamaiyanthi A/P RatnamDocument23 pagesMythily A/P Manimaran Kasthuri A/P Krishnan Thamaiyanthi A/P RatnamThämäíyänthí RätnämNo ratings yet
- Tenses English ClubDocument46 pagesTenses English ClubShah AkNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Continuous TenselepromNo ratings yet
- PP O PP ContinuousDocument5 pagesPP O PP Continuousveronicamadrid126No ratings yet
- Verb Tense and Aspect 2020Document3 pagesVerb Tense and Aspect 2020Helan NowsheraNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument38 pagesTenses Reviewmasro apriwanNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument82 pagesTENSESimami rahayuNo ratings yet
- Pet Grammar PointsDocument69 pagesPet Grammar PointsTatiana ZaraNo ratings yet
- Verbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesDocument22 pagesVerbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesangeloNo ratings yet
- Option Modules: TenseDocument22 pagesOption Modules: TenseTrinh ThụcNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument11 pagesGrammarPedro MarsiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Grammar TensesDocument2 pagesTeaching Grammar TensesAndrea CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Best English Grammar Notes by Top IAS CoDocument54 pagesBest English Grammar Notes by Top IAS Coana mNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses: Present Perfect TenseKatarina Perčobić100% (1)
- English TaskDocument21 pagesEnglish TaskKarina Sahla GafurNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuos TenseDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect Continuos TenseZAHRANo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument6 pagesPresent TenseHanina Na NaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument14 pagesTensessurveys4yougovNo ratings yet
- Best English Notes by Top IAS Coaching CenterDocument54 pagesBest English Notes by Top IAS Coaching CenterSunil rathiNo ratings yet
- Study StuffDocument33 pagesStudy StuffJEEVANMECHATRONICSNo ratings yet
- Summary GrammarDocument19 pagesSummary Grammarmarin.creative88No ratings yet
- English Verb Tense ReviewDocument46 pagesEnglish Verb Tense ReviewKashishShNo ratings yet
- English Tenses ReviewDocument6 pagesEnglish Tenses ReviewJulie KolaříkováNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byDocument75 pagesMuhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byNo HikariNo ratings yet
- Ammar 1 - PRESENT PROGRESSIVEDocument3 pagesAmmar 1 - PRESENT PROGRESSIVEAdithyan NairNo ratings yet
- Tugas Persentase Kelompok 5 Intermediate GrammarDocument10 pagesTugas Persentase Kelompok 5 Intermediate GrammarDelphiboddeNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument25 pagesGrammarPedro MarsiNo ratings yet
- Using The Future Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesUsing The Future Continuous TenseTRACY NGU HUI SIENo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument49 pagesVerb TensesHazel GaylanNo ratings yet
- GrammerDocument250 pagesGrammerSobharaj Tk100% (1)
- Simple TenseDocument13 pagesSimple TenseChad HayesNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument48 pagesVerbsRyla TangahuNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Meeting 8Document13 pagesMeeting 8Fitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Tenses - BeginnersDocument116 pagesOverview of Tenses - BeginnersSai AmruthaNo ratings yet
- Everyday TensesDocument28 pagesEveryday TensesdrsbishnoiNo ratings yet
Common Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Common Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Uploaded by
MiloševićZoran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe document provides an overview of five common English tenses: present simple, past simple, future simple, present perfect, and present continuous. It describes when to use each tense, examples of words that signal their use, how each tense is formed grammatically, and the helping verbs associated with each one.
Original Description:
Common tenses
Original Title
Common Tenses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of five common English tenses: present simple, past simple, future simple, present perfect, and present continuous. It describes when to use each tense, examples of words that signal their use, how each tense is formed grammatically, and the helping verbs associated with each one.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageCommon Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Common Tenses: An Overview of The FIVE Most Important Tenses in The English Language
Uploaded by
MiloševićZoranThe document provides an overview of five common English tenses: present simple, past simple, future simple, present perfect, and present continuous. It describes when to use each tense, examples of words that signal their use, how each tense is formed grammatically, and the helping verbs associated with each one.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
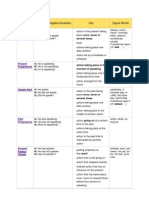
COMMON TENSES
An overview of the FIVE most important tenses in the English language
Present Simple
(I go)
Past Simple
(I went)
Future Simple
(I will go)
Present Perfect
(I have gone)
Present Continuous
(I am going)
When do I use this
tense?
Used for present facts
and repeated actions.
Used for completed
actions in the past.
Used for future actions,
even if they are only a
few seconds in the
future.
Used for actions which
started in the past and
are still true now.
Used for temporary
actions going on now.
Words that signal
use of the tense:
every (day, week, month,
year, etc.), always,
usually, often,
sometimes, etc.
Yesterday, last (week,
month, year, etc.), when I
was a child, this morning
(if it is no longer
morning), etc.
Tomorrow, next (week,
month, year, etc.), in the
future, when I retire,
when I get home, etc.
Since, for, ever (with
questions), up to now,
how long (with
questions), etc.
Now, at the moment,
today, this week,
presently, etc.
How do I make the
tense?
The first form of the verb
is used to make the
Present Simple.
The second form of the
verb is used for the Past
Simple.
However, when making
questions and negatives
in the Past Simple, we
use the helping verb
"did" and leave the main
verb in its infinitive form
(1st form).
The Future Simple is
formed with the helping
verb will and the first
form of the verb.
The Present Perfect is
formed with the helping
verb have (or: has) and
the third form of the verb.
The Present Continuous
is formed with the helping
verb to be (am, are, is)
and the "-ing" form of the
verb.
did
will
have / has
to be (am, are, is)
For questions and
negatives the helping
verb (do / does) is used
with the first form of the
verb.
An important rule with
the Present Simple is:
Dont forget the "s" with
he, she & it!
Which helping verb
do I use?
do / does
You might also like
- Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSignal Wordsbethsde92% (12)
- Tenses NotesDocument21 pagesTenses NotesTheebaaRamasamyNo ratings yet
- Hortatory ExpositionDocument15 pagesHortatory ExpositionAvito ShafaNo ratings yet
- Time ExpressionsDocument1 pageTime ExpressionsMatteo CianforliniNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument9 pagesSimple Present TenseTJRNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Present TenseMeto FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Interview TensesDocument9 pagesInterview Tensesdaniel21805No ratings yet
- How To Teach The Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesHow To Teach The Present Continuouschalonniaa100% (1)
- TENSES (Present Tenses)Document38 pagesTENSES (Present Tenses)Mauries Irenia PutriNo ratings yet
- Universitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIDocument19 pagesUniversitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIRiandy LiuNo ratings yet
- 123Document15 pages123Ngọc MaiNo ratings yet
- English Tense Timeline QuerformatDocument3 pagesEnglish Tense Timeline QuerformatqkhaiproNo ratings yet
- General EnglishDocument142 pagesGeneral Englishmanyfid0% (1)
- Independent Work: ThemeDocument12 pagesIndependent Work: ThemeHacer BullaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Limbii EnglezeDocument15 pagesGramatica Limbii Englezeaadypmp2004No ratings yet
- The Present Progressive TenseDocument18 pagesThe Present Progressive Tenseapi-213942189No ratings yet
- Time LinesDocument5 pagesTime LinesEmily De LeónNo ratings yet
- Pre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2Document44 pagesPre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2daniel madrigalNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses - Adjective OrderDocument13 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses - Adjective OrderMihaiMereNo ratings yet
- Sw9 Verb TensesDocument25 pagesSw9 Verb TensesInês castaNo ratings yet
- Tenses (Notes) : Chart-Active Verb TensesDocument2 pagesTenses (Notes) : Chart-Active Verb TensesNana KawaiiNo ratings yet
- For My LoveDocument3 pagesFor My LoveDoung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Mythily A/P Manimaran Kasthuri A/P Krishnan Thamaiyanthi A/P RatnamDocument23 pagesMythily A/P Manimaran Kasthuri A/P Krishnan Thamaiyanthi A/P RatnamThämäíyänthí RätnämNo ratings yet
- Tenses English ClubDocument46 pagesTenses English ClubShah AkNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Continuous TenselepromNo ratings yet
- PP O PP ContinuousDocument5 pagesPP O PP Continuousveronicamadrid126No ratings yet
- Verb Tense and Aspect 2020Document3 pagesVerb Tense and Aspect 2020Helan NowsheraNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument38 pagesTenses Reviewmasro apriwanNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument82 pagesTENSESimami rahayuNo ratings yet
- Pet Grammar PointsDocument69 pagesPet Grammar PointsTatiana ZaraNo ratings yet
- Verbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesDocument22 pagesVerbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesangeloNo ratings yet
- Option Modules: TenseDocument22 pagesOption Modules: TenseTrinh ThụcNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument11 pagesGrammarPedro MarsiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Grammar TensesDocument2 pagesTeaching Grammar TensesAndrea CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Best English Grammar Notes by Top IAS CoDocument54 pagesBest English Grammar Notes by Top IAS Coana mNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses: Present Perfect TenseKatarina Perčobić100% (1)
- English TaskDocument21 pagesEnglish TaskKarina Sahla GafurNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuos TenseDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect Continuos TenseZAHRANo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument6 pagesPresent TenseHanina Na NaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument14 pagesTensessurveys4yougovNo ratings yet
- Best English Notes by Top IAS Coaching CenterDocument54 pagesBest English Notes by Top IAS Coaching CenterSunil rathiNo ratings yet
- Study StuffDocument33 pagesStudy StuffJEEVANMECHATRONICSNo ratings yet
- Summary GrammarDocument19 pagesSummary Grammarmarin.creative88No ratings yet
- English Verb Tense ReviewDocument46 pagesEnglish Verb Tense ReviewKashishShNo ratings yet
- English Tenses ReviewDocument6 pagesEnglish Tenses ReviewJulie KolaříkováNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byDocument75 pagesMuhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byNo HikariNo ratings yet
- Ammar 1 - PRESENT PROGRESSIVEDocument3 pagesAmmar 1 - PRESENT PROGRESSIVEAdithyan NairNo ratings yet
- Tugas Persentase Kelompok 5 Intermediate GrammarDocument10 pagesTugas Persentase Kelompok 5 Intermediate GrammarDelphiboddeNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument25 pagesGrammarPedro MarsiNo ratings yet
- Using The Future Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesUsing The Future Continuous TenseTRACY NGU HUI SIENo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument49 pagesVerb TensesHazel GaylanNo ratings yet
- GrammerDocument250 pagesGrammerSobharaj Tk100% (1)
- Simple TenseDocument13 pagesSimple TenseChad HayesNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument48 pagesVerbsRyla TangahuNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Meeting 8Document13 pagesMeeting 8Fitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Tenses - BeginnersDocument116 pagesOverview of Tenses - BeginnersSai AmruthaNo ratings yet
- Everyday TensesDocument28 pagesEveryday TensesdrsbishnoiNo ratings yet