Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copper Losses 2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper Losses 2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Uploaded by
abcd3511Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Copper Losses 2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper Losses 2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Uploaded by
abcd3511Copyright:
Available Formats
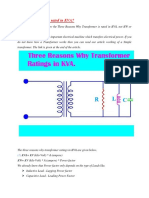
There are two type of losses in a transformer;
1. Copper Losses
2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper losses ( IR) depends on Current which passing through
transformer winding while Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation
Losses depends on Voltage.
So the Cu Losses depend on the rating current of the load so the load type will
determine the powerfactor P.F , Thats why the rating of Transformer in
kVA,Not in kW.
Designer doesnt know the actual consumer power factor while manufacturing
transformers and generators i.e. the P.F (Power factor) of Transformer and
Generator/Alternator depends on the nature of connected load such as resistive
load, capacitive load, and inductive load as Motors, etc.
But Motor has fixed Power factor, i.e. motor has defined power factor and the
rating has been mentioned in KW on Motor nameplate data table. Thats why we
are rated Motor in kW or HP (kilowatts/ Horsepower) instead of kVA.
In addition, Motor is a device which converts Electrical power into Mechanical
power. In this case, the load is not electrical, but mechanical (Motors Output)
and we take into the account only active power which has to be converted into
mechanical load. Moreover, the motor power factor does not depend on the load
and it works on any P.F because of its design
You might also like
- Caravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideFrom EverandCaravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Transformer Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesTransformer Interview QuestionsAnonymous sAmJfcV50% (4)
- Kva Rattings of TransformersDocument1 pageKva Rattings of TransformersFahad Yousaf KhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDanish AliNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument6 pagesENERGYTharindu PiyumalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions: Why Generator Is Rated in KVA and Motor in KW?Document2 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Questions: Why Generator Is Rated in KVA and Motor in KW?BIBI MOHANANNo ratings yet
- Lab Assingment Name: Umar Rahman Reg Nos: Fa18-Epe-015 Subject: Electric Machine Submitted T0: Sir Ali Muhammad DATE 4/10/2020Document13 pagesLab Assingment Name: Umar Rahman Reg Nos: Fa18-Epe-015 Subject: Electric Machine Submitted T0: Sir Ali Muhammad DATE 4/10/2020Maooz JanNo ratings yet
- Why Alternator and Generator Are Rated in KVA. Not in KW - 1Document2 pagesWhy Alternator and Generator Are Rated in KVA. Not in KW - 1scribd0% (1)
- Bee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyDocument8 pagesBee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyrasoolNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksDocument5 pagesEM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksAmarabalan NarasingamNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument17 pagesTransformerKULDEEP SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Application of CapacitorsDocument21 pagesApplication of CapacitorsMariam MugheesNo ratings yet
- Power FactorDocument27 pagesPower Factorapi-232121477No ratings yet
- Electricalprep Com Transformers More 5Document16 pagesElectricalprep Com Transformers More 5gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument22 pagesTransformerIF21 Minit ChitrodaNo ratings yet
- Losses and Efficiency of Induction MotorDocument5 pagesLosses and Efficiency of Induction MotorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- 22EE303 Electrical Machines I Unit-IiDocument8 pages22EE303 Electrical Machines I Unit-IiNANDHAKUMAR ANo ratings yet
- Important Question For EEE Viva Exam Prepared By: MD - Mynul Hasan (Prince)Document12 pagesImportant Question For EEE Viva Exam Prepared By: MD - Mynul Hasan (Prince)Mehedi Hasan HemelNo ratings yet
- Losses in Transformers and Efficiency in Transformers - Electrical Engineering InfoDocument16 pagesLosses in Transformers and Efficiency in Transformers - Electrical Engineering InfoSaravana Perumal KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor Controlling PanelDocument15 pagesAutomatic Power Factor Controlling PanelheruvalaNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewHakim Abdul Rahim100% (1)
- Capacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeDocument6 pagesCapacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeMukeshKumarMahtoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document31 pagesLecture 09khizeraftab1018No ratings yet
- HayuDocument5 pagesHayuHayu BayisaNo ratings yet
- 2 PFDocument51 pages2 PFAbdo EssaNo ratings yet
- Why We Can't Store AC in Batteries Instead of DC - or Can We Store AC in Batteries Instead of DC?Document5 pagesWhy We Can't Store AC in Batteries Instead of DC - or Can We Store AC in Batteries Instead of DC?Debabrata DasNo ratings yet
- Active and Reactive PowerDocument19 pagesActive and Reactive PowerGairik Chakraborty100% (2)
- Hysteresis Eddy Current Iron or Core Losses and Copper Loss in TransformerDocument8 pagesHysteresis Eddy Current Iron or Core Losses and Copper Loss in Transformersampath kumarNo ratings yet
- Losses in A DC Generator and DC MotorDocument2 pagesLosses in A DC Generator and DC MotorMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- TLCpaperLG1 PDFDocument28 pagesTLCpaperLG1 PDFAnonymous imiMwtNo ratings yet
- Dual Boost, Control, Current Control, ConclusionDocument6 pagesDual Boost, Control, Current Control, ConclusionHema LathaNo ratings yet
- EEE Unit 4Document7 pagesEEE Unit 4pradeepkumarsa980No ratings yet
- Topic 6 (Power Supply) : Name: Amelinda Azalia Savira Class: EK-3ADocument6 pagesTopic 6 (Power Supply) : Name: Amelinda Azalia Savira Class: EK-3Avira amelindaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Question and Answer 1690821024Document24 pagesElectrical Question and Answer 1690821024Meraj Alam100% (1)
- Assignment - Answered - Electrical MachinesDocument3 pagesAssignment - Answered - Electrical Machinesappiagyei nicholasNo ratings yet
- Eee NoteDocument4 pagesEee NoteNusaeb Ahmed FarhanNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument33 pagesDC MachineAnu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsDocument21 pagesElectrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsTariqNo ratings yet
- Designing of Distribution Transformer 1Document86 pagesDesigning of Distribution Transformer 1anilk9774No ratings yet
- 303 AdhamDocument5 pages303 Adhamaam5112002No ratings yet
- Intelligent Power Supply Design and Its DescriptionDocument45 pagesIntelligent Power Supply Design and Its Descriptionmilind kailaNo ratings yet
- The Induction Motor - A Short Circuited Rotating Transformer - A Comparative Analysis C1503021014Document5 pagesThe Induction Motor - A Short Circuited Rotating Transformer - A Comparative Analysis C1503021014mkdir911No ratings yet
- 19EE307 - ND2023 Unit - 1 & 2Document3 pages19EE307 - ND2023 Unit - 1 & 2Nanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Karam Abdo REPORT 1 PDFDocument8 pagesAhmed Karam Abdo REPORT 1 PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Pe Whole PDFDocument165 pagesPe Whole PDFHarshithaPuretiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Flyback Transformers - CoilcraftDocument5 pagesA Guide To Flyback Transformers - Coilcraftjit genesisNo ratings yet
- Potentail TransformerDocument16 pagesPotentail TransformerNOV DAVANNNo ratings yet
- Transformer Type & TutorialDocument106 pagesTransformer Type & TutorialHasan Basyaria100% (1)
- Ahmed Karam Abdo REPORT 22 PDFDocument7 pagesAhmed Karam Abdo REPORT 22 PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Power Supply FunctionDocument4 pagesPower Supply FunctiondunkinkunatNo ratings yet
- MotorEffic&PF CM5Document28 pagesMotorEffic&PF CM5Alaa RamadanNo ratings yet
- Transformer & MotorDocument92 pagesTransformer & MotorAshutosh RaiNo ratings yet
- Power Transformers - Definition, Types, and Applications - Electrical4UDocument5 pagesPower Transformers - Definition, Types, and Applications - Electrical4UHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Generator Operation Curve ExplainDocument10 pagesGenerator Operation Curve ExplainThar LayNo ratings yet
- Power Factor FundamentalsDocument28 pagesPower Factor FundamentalsSHARJEEL MUNAWAR100% (1)
- UNIT 1aaDocument164 pagesUNIT 1aaDr.K.Krishna VeniNo ratings yet
- Pe IntroductionDocument31 pagesPe IntroductionJunaxic MuxicNo ratings yet
- Cha 2Document72 pagesCha 2Yheyis Mitike FaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesDocument7 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesBricksoe NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesNo ratings yet
- InfraredDocument18 pagesInfraredabcd3511No ratings yet
- Syllabus First SemesterDocument32 pagesSyllabus First Semesterabcd3511No ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus Instrumentation EngineeringDocument5 pagesGATE Syllabus Instrumentation Engineeringabcd3511No ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Serial Communication - I Serial InterfaceDocument3 pagesLecture 11: Serial Communication - I Serial Interfaceabcd3511No ratings yet
- Kristin Ackerson, Virginia Tech EE Spring 2002Document29 pagesKristin Ackerson, Virginia Tech EE Spring 2002jit_72No ratings yet