Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 2 Hormones Worksheet
7 2 Hormones Worksheet
Uploaded by
api-309893409Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 2 Hormones Worksheet
7 2 Hormones Worksheet
Uploaded by
api-309893409Copyright:
Available Formats
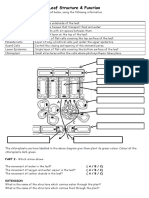
7.
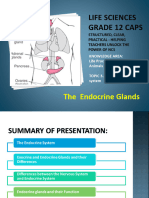
2 Hormones (The Endocrine system)
The endocrine system coordinates activities but in
a different way to the nervous system. There are
a number of organs in your body involved which
produce hormones and these are called endocrine
glands which include the adrenal glands and
pancreas.
Fill in the definition of a hormone using your
syllabus and highlight the key words.
Hormones:
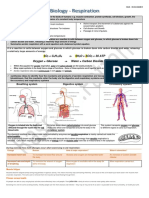
Effects of Adrenaline
Deeper, more rapid breathing
Dilation of airways so more air reaches alveoli in lungs for gas exchange
Liver cells to convert glycogen to glucose. Diffuses into blood and to muscles where it
is a source of energy for sudden contraction.
Heat rate increases- more oxygen and glucose transported to working muscles.
Blood diverted away from digestive system to muscles.
Vasodilation of blood vessels in brain and muscles so more glucose and oxygen
delivered to these organs.
SJI International
Science Department - March 16
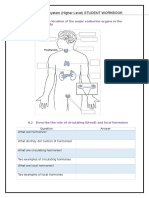
Comparing the Nervous System and the Hormonal System
Nervous System
Hormonal System
Structure
Forms of information
Pathway
Duration of response
Target area
Speed of reaction
Response
Summary Questions:
1. What are stimuli? Give an example
2. What are receptors? Give an example in humans.
3. What are effectors? Give an example in humans.
4. What is a response? Give an example
5. What two systems in the human body respond to stimuli?
6. Use the words to fill in the gaps showing the sequence of events in a coordinated
response.
->
Effector
SJI International
Response
->
Receptor
->
Coordination
Stimulus
->
Science Department - March 16
You might also like
- Leaf Structure WorksheetDocument1 pageLeaf Structure Worksheetapi-309893409100% (1)
- UNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Document7 pagesUNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- 8 0 The Endocrine SystemDocument11 pages8 0 The Endocrine Systemapi-343368893100% (7)
- Unit 3 Module 1Document6 pagesUnit 3 Module 1heide100% (1)
- H8a - A Bugs LifeDocument2 pagesH8a - A Bugs Lifeapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Tellingbiologyteachersguide HeatherwegenhartDocument6 pagesTellingbiologyteachersguide Heatherwegenhartapi-288654969No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument25 pagesHormonesapi-309893409No ratings yet
- 3.5.3 Responses in The Human Endocrine System1Document22 pages3.5.3 Responses in The Human Endocrine System1John Mark JuarezNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument13 pagesHormonesethankhoo2007No ratings yet
- Hormonal CoordinationDocument4 pagesHormonal Coordinationtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- ELS - Q2 - Week 5bDocument15 pagesELS - Q2 - Week 5bShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Diah Ayu Wulandari 2. Febi Tribawanti 3. Ivo Pramaysella 4. Werdini SapitriDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Diah Ayu Wulandari 2. Febi Tribawanti 3. Ivo Pramaysella 4. Werdini SapitriSabil fananiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 HormonesDocument9 pagesLesson 7 HormonesArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Fuj JobbyDocument15 pagesAnatomy Fuj JobbyObadah AbdulsattarNo ratings yet
- IntroductiontohumanphysiologyDocument325 pagesIntroductiontohumanphysiologyMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- How Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesDocument4 pagesHow Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination and Response Noteskavya.gulatiNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine SystemBonny writerNo ratings yet
- Coordination HormonesDocument32 pagesCoordination HormonesMohammed FahimNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantDocument21 pagesTransport in PlantIsheba WarrenNo ratings yet
- Chemical CoordinationDocument34 pagesChemical CoordinationThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 2Document31 pagesEndocrine System - Part 2Maryem NabawiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Animal SciDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Animal SciKylle BedisNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemTherese MaleriadoNo ratings yet
- Module 27Document14 pagesModule 27Jerico CastilloNo ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- TVBS Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesTVBS Nervous SystemAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemDocument73 pagesChapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemAbdullah AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in ELS For Week 5 and 6Document29 pagesActivity Sheet in ELS For Week 5 and 6RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 1 PDFDocument10 pagesEndocrine System 1 PDFDilNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument26 pagesSistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Course WorkDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Course Workgodfreymandela88No ratings yet
- Assignment 1-1692985000311Document7 pagesAssignment 1-1692985000311chandraket singhNo ratings yet
- HPA - Chapter 8Document6 pagesHPA - Chapter 8Amanda Marie Best OsbourneNo ratings yet
- Holy Child Colleges of ButuanDocument8 pagesHoly Child Colleges of ButuanJoseph Mark Ocampo ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 13: Coordination and ResponseDocument21 pagesUnit 13: Coordination and ResponseLưu ThiếuNo ratings yet
- Scie Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesScie Reviewer 3rd QuarteratienzanorrayneNo ratings yet
- Physio IntroDocument72 pagesPhysio IntroGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Internal Environment 2. The Control of Body TemperatureDocument14 pagesInternal Environment 2. The Control of Body TemperaturealexobamaNo ratings yet
- 4A Notes Coordination and ResponseDocument15 pages4A Notes Coordination and ResponsenatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Blue and Cream Vintage General ProposalDocument12 pagesBlue and Cream Vintage General ProposalKimberly Jane MitraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine System?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine System?JR MamelocoNo ratings yet
- 6O + C H O - 6H O + 6co + 38 ATP Oxygen + Glucose - Water + Carbon Dioxide + EnergyDocument2 pages6O + C H O - 6H O + 6co + 38 ATP Oxygen + Glucose - Water + Carbon Dioxide + EnergyRacha Abdel Fattah MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Practical Question PheDocument10 pagesPractical Question Pherishabh.kumar.0040No ratings yet
- PrintDocument5 pagesPrintArvind ManokarNo ratings yet
- Stress Handout For Revision - 02.10Document9 pagesStress Handout For Revision - 02.10Afifa AfrozNo ratings yet
- University of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandDocument11 pagesUniversity of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandAbhimanyu RanaNo ratings yet
- PP17 Human Endocrine System 1467827365Document131 pagesPP17 Human Endocrine System 1467827365fionamore009No ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument8 pagesBIOLOGYr14r3sh1No ratings yet
- 5.1 Communication and HomeostasisDocument7 pages5.1 Communication and HomeostasisbexNo ratings yet
- Citation NeededDocument5 pagesCitation NeededArvind ManokarNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument6 pagesHuman Physiologysubu231201No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document109 pagesChapter 3amala raviNo ratings yet
- Bodysystemspart 3Document18 pagesBodysystemspart 3api-230330590No ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Behavior ScribDocument12 pagesPhysiological Basis of Behavior ScribJJ WoodruffNo ratings yet
- Biomedicalcontrolsystems Unit5shortquestionsanswers 170421103554 PDFDocument4 pagesBiomedicalcontrolsystems Unit5shortquestionsanswers 170421103554 PDFNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Control Systems: Unit V - Biomedical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesBiomedical Control Systems: Unit V - Biomedical ApplicationsNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Coordination Question and answersDocument9 pagesCoordination Question and answersmbaliitumisoNo ratings yet
- 5 Homeostasis and Response ChecklistDocument5 pages5 Homeostasis and Response Checklistu19majli0No ratings yet
- Control NotesDocument11 pagesControl NotesRaman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Answer Key End of Chapter QuestionsDocument102 pagesAnswer Key End of Chapter QuestionsPhoebe Faye LyNo ratings yet
- Alimentary Canal ws1Document5 pagesAlimentary Canal ws1api-309893409No ratings yet
- CholeraDocument10 pagesCholeraapi-309893409No ratings yet
- LabourDocument8 pagesLabourapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Alimentary CanalDocument29 pagesAlimentary Canalapi-309893409100% (1)
- Respiration InvestigationDocument3 pagesRespiration Investigationapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Respirometer PPQDocument3 pagesRespirometer PPQapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Respiration HomeworkDocument8 pagesRespiration Homeworkapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument35 pagesAerobic Respirationapi-309893409100% (3)
- Circus WorksheetsDocument16 pagesCircus Worksheetsapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Reproduction WsDocument6 pagesReproduction Wsapi-309893409100% (1)
- A Sexual and Sexual Card SortDocument2 pagesA Sexual and Sexual Card Sortapi-309893409100% (1)
- Past Exam QuestionDocument1 pagePast Exam Questionapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Fertilisation and PregnancyDocument33 pagesFertilisation and Pregnancyapi-309893409No ratings yet
- 10 3 Tropic Response ppt2Document37 pages10 3 Tropic Response ppt2api-309893409No ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1Document1 pageInformation Sheet 1api-309893409No ratings yet
- Leaves and PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesLeaves and Photosynthesisapi-309893409100% (1)
- Dna Structure gp13Document3 pagesDna Structure gp13api-309893409No ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition RevisionDocument1 pagePlant Nutrition Revisionapi-3098934090% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Carbonate Practical Set UpDocument1 pageHydrogen Carbonate Practical Set Upapi-309893409No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryapi-309893409No ratings yet
- 1 Innate ImmunityDocument12 pages1 Innate Immunityapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Active ImmunityDocument17 pagesActive Immunityapi-309893409No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument17 pagesEnzymesapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Tropic Response QsDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Tropic Response Qsapi-309893409No ratings yet