Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macrophagecellsnadia
Macrophagecellsnadia
Uploaded by
api-2979451290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageMacrophage cells are a unique type of white blood cell found in the immune system that digest cancer cells and unwanted substances through a process called phagocytosis. Inside the macrophage cell, organelles help create protein and break down debris that is engulfed. A recent study on axolotls showed that macrophage cells play a key role in limb regeneration, as removing macrophages prevented regrowth, while some remaining allowed slower regrowth. Scientists believe macrophages are important to starting the limb regeneration process but are still determining their exact function, which could help enable human limb regrowth.
Original Description:
Original Title
macrophagecellsnadia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMacrophage cells are a unique type of white blood cell found in the immune system that digest cancer cells and unwanted substances through a process called phagocytosis. Inside the macrophage cell, organelles help create protein and break down debris that is engulfed. A recent study on axolotls showed that macrophage cells play a key role in limb regeneration, as removing macrophages prevented regrowth, while some remaining allowed slower regrowth. Scientists believe macrophages are important to starting the limb regeneration process but are still determining their exact function, which could help enable human limb regrowth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageMacrophagecellsnadia
Macrophagecellsnadia
Uploaded by
api-297945129Macrophage cells are a unique type of white blood cell found in the immune system that digest cancer cells and unwanted substances through a process called phagocytosis. Inside the macrophage cell, organelles help create protein and break down debris that is engulfed. A recent study on axolotls showed that macrophage cells play a key role in limb regeneration, as removing macrophages prevented regrowth, while some remaining allowed slower regrowth. Scientists believe macrophages are important to starting the limb regeneration process but are still determining their exact function, which could help enable human limb regrowth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
MacrophageCells
ByNadiaAlvarez
Cells make up literally every living thing you
could think of, plants, animals and humans.
There are about 200 different types of cells
found in human beings, but one you've
probablyneverheardofiscalledamacrophage
cell. A macrophage cell is a unique type of
white blood cell and is found in the immune
system digesting cancer cells, and unwanted
substances found in the body in a process
known as phagocytosis. Phagocytosis is when
a cell devours a particle to create a small
structure insidecalleda phagosometokeepthe
dead cell from harming thebody.Thecellalso
generates
both
inflammatory
and
antiinflammatory signals to the spot the host
may be injured by releasing cytokines. This is
because dead cells are able to activate a
proinflammatory response which can lead to
autoimmune disease. The organelles,ribosome
andlysosomefoundinsidethemacrophagecell
help it create protein and break down debris
thatthemacrophageengulfs.
These cells are not just found in humans, in
fact a recent study of the axolotl (aquatic
salamander) showed that macrophage cells
are akeyparttothebeginningprocessofwhy
they are able to regenerate their limbs. In the
experiment all macrophages are removed
from a salamander with an amputatedlegand
the result showed absolutely no regrowth.
Whereas the salamander with only some
macrophages removed is still able to regrow
its leg just not as quick as it would beableto
with its full macrophage count. Scientists
know that macrophages play a huge part in
the beginning of the limb regeneration
process but are not sure exactlywhattheyare
doing that results in a new limb growing.
They also believethishasbroughtusonestep
closer to being able to regrow limbs on
humans and will lead to the answer in the
nearfuture.
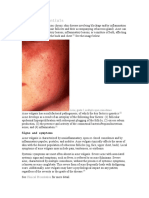
Left:
Axolotl
(aquaticsalamander)
Right:
Macrophagecells
You might also like
- Covid Protocol DetoxDocument20 pagesCovid Protocol DetoxAlfred Sambulan83% (6)
- 28 Important MCQS: Inflammation and RepairDocument30 pages28 Important MCQS: Inflammation and RepairAbhishek Ojha100% (11)
- Aaoms Position Paper Mronj 2022Document24 pagesAaoms Position Paper Mronj 2022Rodrigo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition Case Study-2Document5 pagesMalnutrition Case Study-2dakota100% (1)
- Chapter Overview: 9: ProtozoaDocument10 pagesChapter Overview: 9: ProtozoaBianca ElbrechtNo ratings yet
- Cuk Cell Biology 2020 (2nd Sem)Document10 pagesCuk Cell Biology 2020 (2nd Sem)Pokemon GoNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractgabisantana2400No ratings yet
- Macrophage ICDocument10 pagesMacrophage ICchristian lunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Overview: 8: FungiDocument17 pagesChapter Overview: 8: FungiBianca ElbrechtNo ratings yet
- Studying CellsDocument1 pageStudying CellsJSTN JRNNo ratings yet
- The Theme of Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function in CellsDocument8 pagesThe Theme of Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function in CellschrisNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Practical 3 PDFDocument11 pagesCell Biology Practical 3 PDFEswaran Singam100% (1)
- 32 Bacterialcell 2009Document5 pages32 Bacterialcell 2009ariffdrNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes MICROBIO SECOND YEARDocument12 pagesLecture Notes MICROBIO SECOND YEARBeatrix Adrianna PabulayanNo ratings yet
- Properties and Classification of Microorganisms: Background Background Background Background BackgroundDocument11 pagesProperties and Classification of Microorganisms: Background Background Background Background Backgroundshamarief10100% (1)
- Botany Lab Exercises 3 To 8 Group 7 2B7 PDFDocument7 pagesBotany Lab Exercises 3 To 8 Group 7 2B7 PDFRicky Justin NgoNo ratings yet
- Eu BacteriaDocument1 pageEu BacteriaFara MadihaNo ratings yet
- GenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2Document14 pagesGenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2jeknendoNo ratings yet
- NematodaDocument16 pagesNematodatapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesAsexual Reproductionshehzad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Micro 1st ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesMicro 1st ProkaryotesMatahari SempurnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document65 pagesChapter 2Rhon Paolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Spanish 210 TestDocument2 pagesSpanish 210 Testi dont know my nameNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Exercise 6Document3 pagesMicroPara Exercise 6hooNo ratings yet
- Booktext ID 104548024&PLACEBO IEDocument103 pagesBooktext ID 104548024&PLACEBO IEajaypatidar001No ratings yet
- Chap 9 - MicroorganismsDocument20 pagesChap 9 - Microorganismsdiamehta1512No ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista - Characteristics and Classification of ProtistDocument4 pagesKingdom Protista - Characteristics and Classification of Protistabdulmaliqopeyemi04No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells. BacteriaDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cells. BacteriaAndreea VrabieNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology and ImmunologyDocument12 pagesHuman Physiology and ImmunologyYash BansodNo ratings yet
- The Kingdom of Protists - 1st MeetingDocument39 pagesThe Kingdom of Protists - 1st Meetingsitimukholifah5575No ratings yet
- Macrophage, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMacrophage, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts in MicrobiologyHazelle RoxasNo ratings yet
- The Kingdom of ProtistsDocument67 pagesThe Kingdom of ProtistsNila FirmaliaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Lab Report MicDocument2 pagesIntroduction Lab Report Micainnur azwanaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell CultureDocument15 pagesAnimal Cell Cultureppareek16892No ratings yet
- Viruses, Protists Part III)Document49 pagesViruses, Protists Part III)kylevNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology - Chapter One The Bacterial Cell: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument139 pagesBacteriology - Chapter One The Bacterial Cell: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesKirsten Hazel MejiaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Bacteria and VirusesDocument51 pagesAP Biology Bacteria and VirusesMichael TsaiNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument9 pagesBiological ClassificationAdarsh Chobey0% (1)
- JOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesDocument9 pagesJOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesJOHN-AHL MATIASNo ratings yet
- Immunity Virus 2Document10 pagesImmunity Virus 2Aditya Mohan GuptaNo ratings yet
- By Vojo Deretic and Daniel J. Klionsky: BiologyDocument8 pagesBy Vojo Deretic and Daniel J. Klionsky: BiologyJonathanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Organelles in CellDocument23 pagesFunctions of Organelles in CellZahid ShehzarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument122 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsAdithya NanuvalaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument8 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsMarcy BoralNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Amino AcidDocument5 pagesVocabulary Amino AcidbenjaminNo ratings yet
- BIO - 320 - Lab Report - 2Document12 pagesBIO - 320 - Lab Report - 2Hazwan Hamim100% (1)
- Different Types of CellsDocument25 pagesDifferent Types of CellsHakdog LaparoNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document6 pagesLab 3mkder571No ratings yet
- Macro PhagesDocument10 pagesMacro PhagesZahid ShehzarNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious Disease: PathogensDocument5 pages6.3 Defence Against Infectious Disease: PathogensantonioolufNo ratings yet
- A5 Innate ImmunityDocument18 pagesA5 Innate ImmunityRizkia Milladina HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument8 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and Ontogeny of Immune SystemDocument5 pagesPhylogeny and Ontogeny of Immune SystemGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Leukocytes: (White Blood Cells)Document41 pagesLeukocytes: (White Blood Cells)syed nomanshahNo ratings yet
- Microbiology (Laden Saleh) FinalDocument240 pagesMicrobiology (Laden Saleh) FinalLaden SalehNo ratings yet
- Activities With in CellDocument10 pagesActivities With in CellTiwaan02No ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument16 pagesImmunologyimvikrantranjanNo ratings yet
- BSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Document4 pagesBSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- Science News Article BiologyDocument2 pagesScience News Article BiologyImiejen AltheaNo ratings yet
- 5 Marks (Human Health and Disease)Document6 pages5 Marks (Human Health and Disease)niharikak208No ratings yet
- Practice Essentials AcneDocument6 pagesPractice Essentials AcneaigoooNo ratings yet
- EULAR Points To Consider For The Management of Difficult To Treat Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument14 pagesEULAR Points To Consider For The Management of Difficult To Treat Rheumatoid ArthritisseleneNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument70 pagesInflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Pathology Book - Chapter 2 - Inflammation - HKDocument12 pagesPathology Book - Chapter 2 - Inflammation - HKagar agarNo ratings yet
- Enzyme 20pagesDocument20 pagesEnzyme 20pagesEddie Optin100% (2)
- Review of The Oral Disease-Systemic Disease Link. Part I: Heart Disease, DiabetesDocument10 pagesReview of The Oral Disease-Systemic Disease Link. Part I: Heart Disease, DiabetesAristya Julianto SidhartaNo ratings yet
- History Taking Orthopaedics CompleteDocument6 pagesHistory Taking Orthopaedics CompletenorisahnirishNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory ResponseDocument7 pagesInflammatory Responseᵇᵅᵇᵞ Anden GonzagaNo ratings yet
- 15+cancer Fighting+Foods+That+Enhance+Detox+&+Rejuvenation+Document17 pages15+cancer Fighting+Foods+That+Enhance+Detox+&+Rejuvenation+Mirta Brajkovic KurkutovicNo ratings yet
- HelminthDocument13 pagesHelminthAmanda Powers100% (1)
- PhotodermatitisDocument7 pagesPhotodermatitisPrakMBBSNo ratings yet
- A New Attempt in Comparison Between 3 Racial Groups in India-Based On Lip Prints (Cheiloscopy)Document5 pagesA New Attempt in Comparison Between 3 Racial Groups in India-Based On Lip Prints (Cheiloscopy)irfanadil2006No ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress in ImmunotoxicityDocument6 pagesOxidative Stress in ImmunotoxicityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Shock - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument11 pagesShock - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional Editionazaria zhafirahNo ratings yet
- Gut Dysbiosis, Leaky Gut, and Intestinal Epithelial Proliferation in Neurological Disorders Towards The Development of A New Therapeutic Using Amino Acids, Prebiotics, Probiotics, and PostbioticsDocument23 pagesGut Dysbiosis, Leaky Gut, and Intestinal Epithelial Proliferation in Neurological Disorders Towards The Development of A New Therapeutic Using Amino Acids, Prebiotics, Probiotics, and PostbioticsLevente BalázsNo ratings yet
- LT - Regular Cumulative - 04.05.2021Document22 pagesLT - Regular Cumulative - 04.05.2021Pranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument70 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesAdebisi OluwatomiwaNo ratings yet
- Burn & ScaldDocument35 pagesBurn & ScaldMAHFUZ ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Surgical Infection PDFDocument20 pagesSurgical Infection PDFosaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pruritus A ReviewDocument11 pagesChronic Pruritus A Reviewjolu2beNo ratings yet
- IL1 AntagonistaDocument13 pagesIL1 AntagonistaZitlal-lin VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Sisa SlideDocument53 pagesSisa SlideUmiyanti AzizahNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Pathway: Dedi Susila, Dr. Span. KMNDocument27 pagesPain Management Pathway: Dedi Susila, Dr. Span. KMNNadya Wiratami NurrakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- 2019 2 6 - enDocument4 pages2019 2 6 - enmisulica2010No ratings yet
- 15 Health Benefits of GarlicDocument4 pages15 Health Benefits of GarlichiteshNo ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)