Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force Weight On Earth Density: Work Done Power
Force Weight On Earth Density: Work Done Power
Uploaded by
jordi17100 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 pageThis document contains formulas from physics relating to force, motion, energy, electricity, waves, and sound. Key formulas include: force equals mass times acceleration, density equals mass divided by volume, work done equals force times distance, kinetic energy equals half mass times velocity squared, resistance equals potential difference divided by current, resistors in parallel have the same voltage but total current equals the sum of individual currents. It also includes the speed-time, velocity-time, and displacement-time equations of motion and formulas for transformers, reflection, refraction, wavelength, frequency, and echo time.
Original Description:
Formule Quimico
Original Title
Formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains formulas from physics relating to force, motion, energy, electricity, waves, and sound. Key formulas include: force equals mass times acceleration, density equals mass divided by volume, work done equals force times distance, kinetic energy equals half mass times velocity squared, resistance equals potential difference divided by current, resistors in parallel have the same voltage but total current equals the sum of individual currents. It also includes the speed-time, velocity-time, and displacement-time equations of motion and formulas for transformers, reflection, refraction, wavelength, frequency, and echo time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 pageForce Weight On Earth Density: Work Done Power
Force Weight On Earth Density: Work Done Power
Uploaded by
jordi1710This document contains formulas from physics relating to force, motion, energy, electricity, waves, and sound. Key formulas include: force equals mass times acceleration, density equals mass divided by volume, work done equals force times distance, kinetic energy equals half mass times velocity squared, resistance equals potential difference divided by current, resistors in parallel have the same voltage but total current equals the sum of individual currents. It also includes the speed-time, velocity-time, and displacement-time equations of motion and formulas for transformers, reflection, refraction, wavelength, frequency, and echo time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
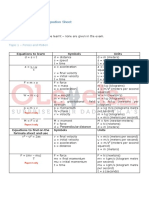
FORMULAS
Force (N) = Mass (kg) x Acceleration (m/s2)
Weight on Earth (N) = Mass (kg) x Acceleration due to Gravity (10 m/s2)
Density (kg/m3 g/cm3) =
Mass (kg) (g)
Volume (m3) (cm3)
Moment of a Force (Nm) = Force (N) x Perpendicular Distance (m)
Equilibrium total clockwise moment = total anticlockwise moment
Work Done (Joules) = Force (N) x Distance Moved (m)
Power (watts) = Work Done (Joules)
Time Taken (sec)
Gravitat. Pot. Energy (Joules) = Mass (kg) x Acceleration due to gravity (10 m/s2) x Height Moved (m)
Elastic Pot. Energy (Joules) = Force (N) x Distance moved (m)
Kinetic Energy (Joules) = x Mass (kg) x Speed2 ( (m/s)2 )
Speed or Velocity (m/s) = Distance Travelled (m)
Time Taken (sec)
distance travelled = area under a speed/time graph
Acceleration (m/s2) = Change in Velocity (m/s)
Time Taken (sec)
Equations of Motion
v=u+at
v2 = u2 + 2 a s
s = u t + a t2
Ammeter Connected in series
s = (u + v) t
2
Voltmeter Connected in parallel
Resistance (Ohms ()) = Potential Difference (P.d.) (Volts)
Current (I) (Amperes)
Resistors in
SERIES
I is the same through every resistor
VT = V1 + V2
RT = R 1 + R 2
PARALLEL
IT = I1 + I2
V is the same through every resistor
1 = 1 + 1
RT R1
R2
Electrical Power
P=VxI
P = I2 x R
Energy Transferred (Joules) = Power (watts) x Time (sec)
P = V2 / R
Transformer Primary Volt (V1) x Primary Current (I1) = Secondary Volt (V2) x Secondary Current (I2)
Frequency (Hz) = N of Oscillations or cycles
Time Taken (sec)
* Reflection inc = reflecRefraction inc > refrac
* Pitch Frequency
Loudness Amplitud
* echo time = 2 x distance(m)
speed (m/sec)
Speed of Wave (m/s) = Frequency (Hz) x Wavelenght () (m)
Quality Wave form
You might also like
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasRichie Harvy82% (17)
- Ultimate Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesUltimate Physics Cheat SheetNehal VoraNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics Exam Cheat SheetJib Bros100% (4)
- High School Physics Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesHigh School Physics Cheat SheetM J Rhoades50% (4)
- Physics Final Cheat Sheet With Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Final Cheat Sheet With Problems PDFEnriqueMinhazNo ratings yet
- Science Formula SheetDocument2 pagesScience Formula Sheetrhemaksha78% (9)
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionCamille67% (3)
- Csec Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesCsec Physics Formula SheetPURAN SUBRAMANIE50% (6)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Must To Know Formulas (NMAT) - TanDocument3 pagesMust To Know Formulas (NMAT) - TanAlanis abian100% (6)
- Physics FormulasDocument7 pagesPhysics FormulasaarzujoshipuraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Formula BookletDocument4 pagesIGCSE Formula BookletNisalNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Physics Igcse All Imp FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Igcse All Imp FormulasDhruvil Desai100% (1)
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionYusuf100% (3)
- Physics Formulas IGCSEDocument27 pagesPhysics Formulas IGCSEMichael KapoorNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasTerrence WalkerNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsbells tharayilNo ratings yet
- Physics Equations Ez Clap ScienceDocument4 pagesPhysics Equations Ez Clap ScienceNguyen Quan HaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae: Formula in Words Formula in Symbols UnitsDocument2 pagesPhysics Formulae: Formula in Words Formula in Symbols UnitsjzdoogNo ratings yet
- O-Level Formula List - OriginalDocument4 pagesO-Level Formula List - Originalbloober blooberNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Physics 1A A F L Angular Momentum (KG - M N PDocument1 pageFormulas For Physics 1A A F L Angular Momentum (KG - M N PLouiela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy II FormDocument17 pagesMatter and Energy II FormPaulNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: V V U M MDocument5 pagesPhysics Formulas: V V U M MEXa Krad NoitatpmetNo ratings yet
- Must To Know Formulas (NMAT)Document2 pagesMust To Know Formulas (NMAT)CatNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Formula Sheet - 240306 - 174340Document3 pagesCsec Physics Formula Sheet - 240306 - 174340bad653559No ratings yet
- Energy EquationsDocument2 pagesEnergy EquationsSandtanglo ToyerNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Formula Booklet - PhysicsDocument1 pageIGCSE Formula Booklet - PhysicsgauthamNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 - 4 Notes PreliminaryDocument7 pagesMod 1 - 4 Notes PreliminaryjajaichachaNo ratings yet
- Physics (5054) - Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics (5054) - Formula SheetAzka GilaniNo ratings yet
- Length and Time: SI UNITS: Systeme International D'unites (Modern Version of The Metric System)Document4 pagesLength and Time: SI UNITS: Systeme International D'unites (Modern Version of The Metric System)Ajitha Rajakantham DNo ratings yet
- Physics GlossaryDocument30 pagesPhysics Glossarywhiskey13No ratings yet
- Equations in PhysicsDocument2 pagesEquations in PhysicsDhruti MysoreNo ratings yet
- Bee6a674 Edexcel Igcse Physics Formula Sheet - WMDocument5 pagesBee6a674 Edexcel Igcse Physics Formula Sheet - WMcreepy carlieNo ratings yet
- GCE NA Level FormulasDocument4 pagesGCE NA Level FormulasNannookky EkkNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitDocument14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutoring Summary Sheet 101112Document6 pagesPhysics Tutoring Summary Sheet 101112pfredaNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Sag KabelDocument6 pagesPerhitungan Sag KabelDwi Hermawan100% (2)
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetAlan LancasterNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949100% (1)
- Final-01PE Units, Dimensions and Errors in Measurement - DocDocument10 pagesFinal-01PE Units, Dimensions and Errors in Measurement - Docnavidnazar12028No ratings yet
- Formulae - 2Document35 pagesFormulae - 2A.BensonNo ratings yet
- Category: Physics FormulasDocument24 pagesCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- AP Physics 1 - Simple Harmonic Motion ReviewDocument1 pageAP Physics 1 - Simple Harmonic Motion ReviewloncharnettCR100% (1)
- Engineering Formula SheetDocument10 pagesEngineering Formula SheetAdarsh Kumar Ang100% (1)
- Motion Short QuestionDocument2 pagesMotion Short QuestionBlue Eye'sNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- Exam Possible Questions: Velocity at HDocument31 pagesExam Possible Questions: Velocity at HJake FryNo ratings yet
- Symbols in Physics WorksheetDocument4 pagesSymbols in Physics WorksheetHugh Fox IIINo ratings yet
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDocument43 pagesVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae F2Document4 pagesPhysics Formulae F2EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument7 pagesPhysics RevisionFurret MasterNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet