Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSD 211 Affricates
CSD 211 Affricates
Uploaded by
api-311020466Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CSD 211 Affricates
CSD 211 Affricates
Uploaded by
api-311020466Copyright:
Available Formats
Wednesday, September 16, 2015
CSD 211
Affricates
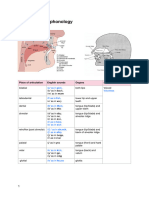
- Stop-plosive releasing to a fricative, in one movement
- Not simply a combination of the two manners (i.e., /ts/)
- Complete closure (not just constriction) between active and passive articulators, velum
raised to build pressure, but the air is slowly released (like a fricative) rather than
exploded (like a stop-plosive)
/tt/ - /dt/
Closure occurs a bit further back for the /t/ and /d/ to allow for the constriction portion
/tt/ = voiceless coronal-alveolar stop-plosive phase followed by a voiceless coronal
postalveolar fricative portion
/dt/ = voiced coronal-alveolar stop-plosive phase followed by a voiceless coronal
postalveolar fricative portion
Approximants
- Articulators approximate each other, but not so close to cause a constriction, so there is
a broader, smooth passage of air
- Glides: /w/, /j/
- Liquids: /l/, /r/
// - /w/
Lips round, tongue tip low, tongue body raised toward velum, which is raised
// = voiceless labio-velar fricative
/w/ = voiced labio-velar approximate or glide
/j/
Tongue body flat and middle tongue is raised toward midsection of hard palate, velum
is raised
/j/ = voiced mediodorsal-mediopalatal approximant
/l/
Tongue tip and alveolar ridge, tongue edges flat allow lateral airflow, velum raised
/l/ = voiced apico-alveolar lateral approximant
Wednesday, September 16, 2015
/r/
Bunched: middle tongue raised toward middle hard palate, tongue tip low, tongue is
retracted
-Voiced mediodorsal-medioplatal central approximant
Tongue-tip: tongue tip elevated toward alveolar ridge
-Voiced apico-postalveolar central approximant
Retroflex: tongue body is hollowed and bent backwards, with tongue tip curling toward
front of hard palate, lip rounding possible
Voiced apico-prepalatal central approximant
You might also like
- Phonetics: The Sounds of LanguageDocument42 pagesPhonetics: The Sounds of LanguageZahwa Khotrunnada JannahNo ratings yet
- Gramatyka Opisowa - Articulatory PhoneticsDocument4 pagesGramatyka Opisowa - Articulatory PhoneticspaulaNo ratings yet
- Booklet Term 2 Oral 1Document4 pagesBooklet Term 2 Oral 1Karen CamposNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: Four: Introduction To ConsonantsDocument3 pagesPhonetics: Four: Introduction To ConsonantsMaamar REDAOUIANo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument8 pagesConsonantshoangtrinhnguyen48No ratings yet
- Ma III Sem G 3012 DR Bulbul Gupta 17-07-2020 Consonants Anner of ArticulationDocument17 pagesMa III Sem G 3012 DR Bulbul Gupta 17-07-2020 Consonants Anner of Articulationسالم سیروانNo ratings yet
- Phono C&VDocument5 pagesPhono C&VLara SchummerNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Sounds of Languag EDocument35 pagesPhonetics: The Sounds of Languag Edini khanafiNo ratings yet
- 5 - English Consonants (Part 2)Document23 pages5 - English Consonants (Part 2)Faradill asyifaNo ratings yet
- Consonants - Manner of ArticulationDocument14 pagesConsonants - Manner of ArticulationSYIFA FADHILAH HAMIDNo ratings yet
- English Consonant Sounds (Point & Manner of Articulation, Voicing)Document2 pagesEnglish Consonant Sounds (Point & Manner of Articulation, Voicing)Jazmin SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Consonants ClassificationDocument17 pagesConsonants ClassificationJuan Carlos Núñez DuarteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Consonants1Document8 pagesLesson 4 Consonants1Lounis MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 3Document11 pagesTutorial Week 3Why BeNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument14 pagesSpeech OrgansYoga PermanaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 (Consonants Plosives)Document21 pagesSession 3 (Consonants Plosives)Đặng Lê Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Phonetics 2Document22 pagesMeeting 2 Phonetics 2estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Consonant SoundsDocument38 pagesHandout 2 - Consonant SoundsMINH HẠNH MC0% (1)
- Unit 6 Consonants and Their Classification: 1. What Is A Consonant?Document3 pagesUnit 6 Consonants and Their Classification: 1. What Is A Consonant?tho270704No ratings yet
- MCA Lab ManualDocument5 pagesMCA Lab ManualV SATYA KISHORENo ratings yet
- NHA1 - Consonants PlosivesDocument15 pagesNHA1 - Consonants Plosives08AV2DNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument7 pagesManner of ArticulationAlishaNo ratings yet
- Consonant Chart For English: StopsDocument4 pagesConsonant Chart For English: StopsamirzetzNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation Group 3Document11 pagesManner of Articulation Group 3safiramaharani324No ratings yet
- Bilabial PlosivesDocument3 pagesBilabial PlosivesliehokgieNo ratings yet
- PH&PH ArticulationDocument3 pagesPH&PH ArticulationmartynakocNo ratings yet
- NG Âm 1Document9 pagesNG Âm 1Thoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9 - CONSONANTS-part3Document23 pagesLESSON 9 - CONSONANTS-part3rosi mirandaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Slides - SVDocument239 pagesPhonetics Slides - SVhaibinhnguyen36No ratings yet
- Class Notes-6 English Consonant Sound DescriptionDocument3 pagesClass Notes-6 English Consonant Sound DescriptionMd. Rezaul Karim 1821421015No ratings yet
- Nama: Yudha Septa Dias P NIM: 12203193120 Mata Kuliah: English Phonology Kelas: Tbi 1BDocument9 pagesNama: Yudha Septa Dias P NIM: 12203193120 Mata Kuliah: English Phonology Kelas: Tbi 1BInayah RizkyNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 1 - Consonant SoundsDocument30 pagesPhonetics 1 - Consonant SoundsPriyanshu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation: Bilabial BilabialDocument3 pagesManner of Articulation: Bilabial BilabialWaleed MohammadNo ratings yet
- إلى هنا قد انتهت مسيرتنا مع الصوتياتDocument12 pagesإلى هنا قد انتهت مسيرتنا مع الصوتياتIsra SayedNo ratings yet
- Resume PhoneticsDocument4 pagesResume PhoneticsKhorinNo ratings yet
- Voicing and ConsonantsDocument52 pagesVoicing and ConsonantsLinh HaNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation (Nasals and Lateral) : BY, Yustina Navamalar Stephanie Kiew Praveen NaiduDocument7 pagesManner of Articulation (Nasals and Lateral) : BY, Yustina Navamalar Stephanie Kiew Praveen NaiduPraveenNaiduNo ratings yet
- Affricates: Designed by Glasmiry BelloDocument10 pagesAffricates: Designed by Glasmiry BelloAndy Williams ParryNo ratings yet
- TableofconsonantphonemesDocument3 pagesTableofconsonantphonemesdilarasc2121No ratings yet
- AssimilationDocument16 pagesAssimilationméto KouaNo ratings yet
- AffricateDocument3 pagesAffricateHuyen ThuongNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument4 pagesManner of ArticulationAsim KhanNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument11 pagesManner of ArticulationshettyNo ratings yet
- On Tap Thi Cuoi Ki DDocument33 pagesOn Tap Thi Cuoi Ki DTrang Nguyễn Ngọc BảoNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation MakDocument5 pagesManner of Articulation MakAtiQa100% (2)
- Stop Plosive csd211Document1 pageStop Plosive csd211api-311020466No ratings yet
- English ConsonantsDocument5 pagesEnglish ConsonantsJaz VidalNo ratings yet
- Plosive ConsonantsDocument3 pagesPlosive ConsonantsjazminNo ratings yet
- Expanations of PhonemeDocument2 pagesExpanations of PhonemeCristiano VladmakerNo ratings yet
- Sounds ClassificationDocument4 pagesSounds ClassificationSantiago Etcheverry FeelyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Consonants (Reading)Document13 pagesUnit 3 Consonants (Reading)Phước LêNo ratings yet
- Ceklist Pemeliharaan Instalasi Air BersihDocument3 pagesCeklist Pemeliharaan Instalasi Air BersihAthanasius HerdiriyonoNo ratings yet
- Additional ConsonantDocument14 pagesAdditional ConsonantFarhanis KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Allophonic Variants FlashcardsDocument17 pagesAllophonic Variants FlashcardsFlor EspinacoNo ratings yet
- Lý thuyết tiếng tổng hợpDocument12 pagesLý thuyết tiếng tổng hợpAnh Âu PhươngNo ratings yet
- Allo PhonesDocument2 pagesAllo PhonesCamo BritesNo ratings yet
- Materi 1-4 Pronunciation 2019Document7 pagesMateri 1-4 Pronunciation 2019kinantipuspa 2507No ratings yet
- MAnner of ArticulationDocument1 pageMAnner of Articulationnasreenkousar053No ratings yet
- SoundsDocument12 pagesSoundsNazia SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Pipes of the Church Organ - A Selection of Classic Articles on Organ Design and ConstructionFrom EverandPipes of the Church Organ - A Selection of Classic Articles on Organ Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Slide Show 1-PolDocument8 pagesSlide Show 1-Polapi-311020466No ratings yet
- Stop Plosive csd211Document1 pageStop Plosive csd211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Speech Production CSD 211Document6 pagesSpeech Production CSD 211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Review Midterm csd211Document2 pagesReview Midterm csd211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Ipa csd211Document4 pagesIpa csd211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Monophthongs csd211Document2 pagesMonophthongs csd211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Introduction CSD 211Document2 pagesIntroduction CSD 211api-311020466No ratings yet
- Graphemes CSD 211Document1 pageGraphemes CSD 211api-311020466No ratings yet