Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
410 viewsForm 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Form 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Uploaded by
EeJun LeeAir pressure is caused by the constant motion and collisions of air particles exerting a force on surfaces. It acts equally in all directions and decreases with increasing altitude as there is less air above. Two factors that affect air pressure are volume and temperature - as the volume decreases or temperature increases, the particles move faster and collide with surfaces more, exerting a greater pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CHP 11-13 PDFDocument106 pagesCHP 11-13 PDFLittle-psyco :30% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 6Document2 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 6EeJun Lee40% (5)
- Form 2 Air PressureDocument8 pagesForm 2 Air PressureCeline YingNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressureDocument15 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressuredodoNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDocument2 pagesAir Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDeepa Ramiah Deepa RamiahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 5 PDFDocument52 pagesChemistry Chapter 5 PDFByron Adriano PullutasigNo ratings yet
- Air ColumnDocument2 pagesAir Columnsibi RajNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureDocument3 pages6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureNg AliceNo ratings yet
- Pressure 2Document21 pagesPressure 2Gabriel BacusNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Science - Form 2Document6 pagesAir Pressure: Science - Form 2BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 The Vertical Structure of The AtmosphereDocument8 pagesLecture 05 The Vertical Structure of The AtmosphereJess RadañaNo ratings yet
- Air PressureDocument1 pageAir PressureIslamic KidNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureDocument16 pages6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6Jaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDocument14 pagesUniversidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDelmer David RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureDocument34 pagesChapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureChuahSiewHoon100% (1)
- The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains The Behavior of Gases, Part IDocument6 pagesThe Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains The Behavior of Gases, Part I민머오No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5ricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureDocument17 pages6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureabdullmalikNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument19 pagesPressuregrantstuartwNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document11 pagesAtmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3REGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Only Depth Affects Pressure!!!Document2 pagesOnly Depth Affects Pressure!!!Kara SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDF MeteoDocument24 pagesChapter 2 PDF MeteosecretzNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper 3 (Wind Production On Earth) - SOTELODocument5 pagesConcept Paper 3 (Wind Production On Earth) - SOTELOPilsam, Jr. SoteloNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument14 pagesAtmosphereAmit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument6 pagesProperties of GasesclairowrightsNo ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is PressureJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure The AtomsDocument3 pagesAir Pressure The AtomsGowshikaNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure and WindsDocument38 pagesAir Pressure and WindsMerlpa May AlcardeNo ratings yet
- Y8 - Science - 6.5 - For StudentsDocument20 pagesY8 - Science - 6.5 - For StudentsNurulAinMatAronNo ratings yet
- + Text Only Site + Non-Flash Version + Contact Glenn: Property Viscosity and Compressibility AtmosphereDocument2 pages+ Text Only Site + Non-Flash Version + Contact Glenn: Property Viscosity and Compressibility AtmosphereRupak KumarNo ratings yet
- CHP: 13 PhysicsDocument32 pagesCHP: 13 PhysicsAbdul Rahman Mohammed MoezNo ratings yet
- Applied Is Perpendicular To The Surface of Objects Per Unit Area. The Basic Formula For Pressure Is F/A (Force Per Unit Area)Document5 pagesApplied Is Perpendicular To The Surface of Objects Per Unit Area. The Basic Formula For Pressure Is F/A (Force Per Unit Area)y_abutalebNo ratings yet
- Causes For Horizontal Variation of Atmospheric PressureDocument1 pageCauses For Horizontal Variation of Atmospheric Pressuresantanu40580No ratings yet
- WJEC GCSE Physics Revision - Kinetic TheoryDocument2 pagesWJEC GCSE Physics Revision - Kinetic TheoryMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Coursework - For Group BDocument11 pagesChemistry Coursework - For Group Bwilson chandigaNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesAir Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- L6 Air PressureDocument34 pagesL6 Air PressureVasuNo ratings yet
- Pressure and WindsDocument2 pagesPressure and WindsShehzad AliNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment (Latest)Document8 pagesPhysics Assignment (Latest)Apple MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 FORCES AND MOTIONDocument76 pagesChapter 8 FORCES AND MOTIONNorita JosephNo ratings yet
- Answer To Atmosphere QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswer To Atmosphere QuestionsR. BorresNo ratings yet
- WK 6 WIND A. Pressure Gradient B. Buys Ballot S LawDocument8 pagesWK 6 WIND A. Pressure Gradient B. Buys Ballot S Lawkimcristobal52No ratings yet
- ConChem Guide 4t QuarterDocument19 pagesConChem Guide 4t QuarterKiller KnightNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Fundamentals 7Document7 pagesAerodynamic Fundamentals 7Ernest Real ReaNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesTemperature, Pressure and WindssinanggipNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson 4 AssignmentDocument3 pagesGeography Lesson 4 AssignmentAnanya MagarNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument14 pagesAtmospheric PressureIsabel Filan100% (1)
- 1-The Earth's Atmosphere Structure:: Astronomy and Meteorology LectureDocument3 pages1-The Earth's Atmosphere Structure:: Astronomy and Meteorology Lectureparwezomar2002No ratings yet
- Kegy 210Document15 pagesKegy 210Soumyashree BeheraNo ratings yet
- atmospheric pressureDocument9 pagesatmospheric pressureFizza FatimaNo ratings yet
- MT Meteo1 Midterm Module 2A 2nd Sem 2022 2023Document9 pagesMT Meteo1 Midterm Module 2A 2nd Sem 2022 2023John Paul BarretoNo ratings yet
- Pressure As A Property of AirDocument3 pagesPressure As A Property of AirJinky P. RefurzadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure From Gravity or AccelerationDocument29 pagesFluid Pressure From Gravity or Accelerationfadillah mutiaNo ratings yet
- Global Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesGlobal Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fourair Pressure and WindDocument61 pagesChapter Fourair Pressure and Windwarkisa0No ratings yet
- Vacuum Technology 6 1Document43 pagesVacuum Technology 6 1Antonio SanchezNo ratings yet
- 6CHEM - HO - Air PressureDocument2 pages6CHEM - HO - Air PressureMaksuda HossainNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Atmosphere Around YouDocument4 pages2.1 The Atmosphere Around YouAnaNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Exam Tips 2019Document4 pagesPT3 Science Exam Tips 2019EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 6Document2 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 6EeJun Lee40% (5)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 10Document3 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 10EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Document24 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 5EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 4Document13 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 4EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 1 NotesDocument22 pagesForm 5 Chapter 1 NotesEeJun Lee50% (2)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
Form 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Form 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Uploaded by
EeJun Lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
410 views2 pagesAir pressure is caused by the constant motion and collisions of air particles exerting a force on surfaces. It acts equally in all directions and decreases with increasing altitude as there is less air above. Two factors that affect air pressure are volume and temperature - as the volume decreases or temperature increases, the particles move faster and collide with surfaces more, exerting a greater pressure.
Original Description:
Original Title
Form 2 Chapter 6 notes.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAir pressure is caused by the constant motion and collisions of air particles exerting a force on surfaces. It acts equally in all directions and decreases with increasing altitude as there is less air above. Two factors that affect air pressure are volume and temperature - as the volume decreases or temperature increases, the particles move faster and collide with surfaces more, exerting a greater pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
410 views2 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Form 2 Chapter 6 Notes
Uploaded by
EeJun LeeAir pressure is caused by the constant motion and collisions of air particles exerting a force on surfaces. It acts equally in all directions and decreases with increasing altitude as there is less air above. Two factors that affect air pressure are volume and temperature - as the volume decreases or temperature increases, the particles move faster and collide with surfaces more, exerting a greater pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
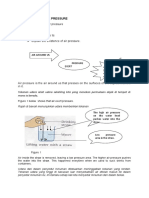
Form 2 Chapter 6: AIR PRESSURE
6.1 Air Pressure
6.1.1 Kinetic Theory of Gases
The kinetic theory of gases states that
Air or gases are matters that have particles that move
randomly in all directions.
Gas particles in a container collide with each other and
with the walls of the container all the time.
Gas particles exert a force on the wall of the container
This force produces a pressure
Air presses down on all things in the Earth's surface. The
pressure exerted by air particles on the surface on an object
is known as air pressure or atmospheric pressure.
The features of air pressure are :
Acts in all direction
Changes from one place to another
Decreases the higher we go above ground level. This is
due to at high place, the amount on air decreases. This
explains why the air pressure on the top of a mountain is
lower that at the foot of the mountain.
pg. 1
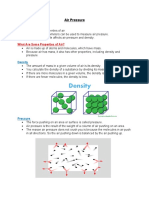
Form 2 Chapter 6: AIR PRESSURE
6.1.2 Factors Affecting Air Pressure
Air pressure is affected by volume and temperature of air.
Factor
Effect
Explanation
Volume
Air pressure
As the volume decreases, the
increases with
air particles move in a smaller
decreasing
space. As a result, more
volume of the
particles hit the wall of the
container and
container. Therefore, a higher
produces a
pressure acts on the wall of
larger force.
the container.
Temperat Air pressure
As the temperature increases,
ure
increases as
the air particles have more
the gas
kinetic energy. More particles
increases.
hit the wall of the container
with greater force. Therefore,
the pressure increases.
pg. 2
You might also like
- CHP 11-13 PDFDocument106 pagesCHP 11-13 PDFLittle-psyco :30% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 6Document2 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 6EeJun Lee40% (5)
- Form 2 Air PressureDocument8 pagesForm 2 Air PressureCeline YingNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressureDocument15 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressuredodoNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDocument2 pagesAir Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDeepa Ramiah Deepa RamiahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 5 PDFDocument52 pagesChemistry Chapter 5 PDFByron Adriano PullutasigNo ratings yet
- Air ColumnDocument2 pagesAir Columnsibi RajNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureDocument3 pages6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureNg AliceNo ratings yet
- Pressure 2Document21 pagesPressure 2Gabriel BacusNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Science - Form 2Document6 pagesAir Pressure: Science - Form 2BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 The Vertical Structure of The AtmosphereDocument8 pagesLecture 05 The Vertical Structure of The AtmosphereJess RadañaNo ratings yet
- Air PressureDocument1 pageAir PressureIslamic KidNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureDocument16 pages6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6Jaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDocument14 pagesUniversidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDelmer David RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureDocument34 pagesChapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureChuahSiewHoon100% (1)
- The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains The Behavior of Gases, Part IDocument6 pagesThe Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains The Behavior of Gases, Part I민머오No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5ricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureDocument17 pages6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureabdullmalikNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument19 pagesPressuregrantstuartwNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document11 pagesAtmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3REGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Only Depth Affects Pressure!!!Document2 pagesOnly Depth Affects Pressure!!!Kara SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDF MeteoDocument24 pagesChapter 2 PDF MeteosecretzNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper 3 (Wind Production On Earth) - SOTELODocument5 pagesConcept Paper 3 (Wind Production On Earth) - SOTELOPilsam, Jr. SoteloNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument14 pagesAtmosphereAmit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument6 pagesProperties of GasesclairowrightsNo ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is PressureJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure The AtomsDocument3 pagesAir Pressure The AtomsGowshikaNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure and WindsDocument38 pagesAir Pressure and WindsMerlpa May AlcardeNo ratings yet
- Y8 - Science - 6.5 - For StudentsDocument20 pagesY8 - Science - 6.5 - For StudentsNurulAinMatAronNo ratings yet
- + Text Only Site + Non-Flash Version + Contact Glenn: Property Viscosity and Compressibility AtmosphereDocument2 pages+ Text Only Site + Non-Flash Version + Contact Glenn: Property Viscosity and Compressibility AtmosphereRupak KumarNo ratings yet
- CHP: 13 PhysicsDocument32 pagesCHP: 13 PhysicsAbdul Rahman Mohammed MoezNo ratings yet
- Applied Is Perpendicular To The Surface of Objects Per Unit Area. The Basic Formula For Pressure Is F/A (Force Per Unit Area)Document5 pagesApplied Is Perpendicular To The Surface of Objects Per Unit Area. The Basic Formula For Pressure Is F/A (Force Per Unit Area)y_abutalebNo ratings yet
- Causes For Horizontal Variation of Atmospheric PressureDocument1 pageCauses For Horizontal Variation of Atmospheric Pressuresantanu40580No ratings yet
- WJEC GCSE Physics Revision - Kinetic TheoryDocument2 pagesWJEC GCSE Physics Revision - Kinetic TheoryMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Coursework - For Group BDocument11 pagesChemistry Coursework - For Group Bwilson chandigaNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesAir Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- L6 Air PressureDocument34 pagesL6 Air PressureVasuNo ratings yet
- Pressure and WindsDocument2 pagesPressure and WindsShehzad AliNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment (Latest)Document8 pagesPhysics Assignment (Latest)Apple MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 FORCES AND MOTIONDocument76 pagesChapter 8 FORCES AND MOTIONNorita JosephNo ratings yet
- Answer To Atmosphere QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswer To Atmosphere QuestionsR. BorresNo ratings yet
- WK 6 WIND A. Pressure Gradient B. Buys Ballot S LawDocument8 pagesWK 6 WIND A. Pressure Gradient B. Buys Ballot S Lawkimcristobal52No ratings yet
- ConChem Guide 4t QuarterDocument19 pagesConChem Guide 4t QuarterKiller KnightNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Fundamentals 7Document7 pagesAerodynamic Fundamentals 7Ernest Real ReaNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesTemperature, Pressure and WindssinanggipNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson 4 AssignmentDocument3 pagesGeography Lesson 4 AssignmentAnanya MagarNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument14 pagesAtmospheric PressureIsabel Filan100% (1)
- 1-The Earth's Atmosphere Structure:: Astronomy and Meteorology LectureDocument3 pages1-The Earth's Atmosphere Structure:: Astronomy and Meteorology Lectureparwezomar2002No ratings yet
- Kegy 210Document15 pagesKegy 210Soumyashree BeheraNo ratings yet
- atmospheric pressureDocument9 pagesatmospheric pressureFizza FatimaNo ratings yet
- MT Meteo1 Midterm Module 2A 2nd Sem 2022 2023Document9 pagesMT Meteo1 Midterm Module 2A 2nd Sem 2022 2023John Paul BarretoNo ratings yet
- Pressure As A Property of AirDocument3 pagesPressure As A Property of AirJinky P. RefurzadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure From Gravity or AccelerationDocument29 pagesFluid Pressure From Gravity or Accelerationfadillah mutiaNo ratings yet
- Global Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesGlobal Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fourair Pressure and WindDocument61 pagesChapter Fourair Pressure and Windwarkisa0No ratings yet
- Vacuum Technology 6 1Document43 pagesVacuum Technology 6 1Antonio SanchezNo ratings yet
- 6CHEM - HO - Air PressureDocument2 pages6CHEM - HO - Air PressureMaksuda HossainNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Atmosphere Around YouDocument4 pages2.1 The Atmosphere Around YouAnaNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Exam Tips 2019Document4 pagesPT3 Science Exam Tips 2019EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 6Document2 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 6EeJun Lee40% (5)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 10Document3 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 10EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Document24 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 5EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 4Document13 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 4EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 1 NotesDocument22 pagesForm 5 Chapter 1 NotesEeJun Lee50% (2)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet