Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test 1 Brevet
Test 1 Brevet
Uploaded by
caroline_amideast8101Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 1 Brevet
Test 1 Brevet
Uploaded by
caroline_amideast8101Copyright:
Available Formats
A.
Consider the polynomials:
E (x ) 4x 2 9 (2x 3) 2 (3 2x )( x 5)
F (x ) (2x 3)(x 1)
1. Factorize E (x ), using first degree factors.
2. Solve the equation E (x ) 2x 3
E (x )
3. Let A (x )
F (x )
Solve the equation A (x ) 2
B.
Two real numbers a and b are given so that:
ab 2 3 and a b 2 2 3
Calculate the following:
1. a 2b ab 2
2.(a 2)(b 2)
3. a 2 b 2
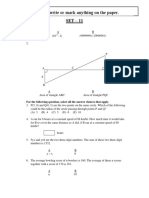
C. O is the intersection of two perpendicular lines (D) and (D’). (S) is a circle with center O and
radius 4cm. (S) intersects (D) at A and B, and (D’) at E and F.
M is a point of (S) distinct from A. (AM) intersects (D’) at N.
a) Make a figure.
b) Prove that the triangles AON and AMB are similar.
c) Calculate AM x AN.
D. Sami wants to rent a car. He receives two offers A and B.
Deposit Charge per km
Offer A 65 000 L.P 500 L.P
Offer B 55 000 L.P 540 L.P
Let x km be the distance traveled by Sami.
a) Find in terms of x the amount that Sami must pay for each of the two offers.
b) What should the traveled distance for the amount paid in A to be equal to that paid in
B?
c) Determine x so that offer A is cheaper than offer B.
d) Interpret graphically the preceding results.
E. A statistical series is given in the table below where a, b, c are integers and d is a decimal
number.
Values 14 15 16 Total
Frequencies 8 a b 32
Relative 25 d 31.25 c
frequencies in %
1. Calculate the numerical value of each of the numbers a, b, c and d.
2. Calculate the mean of this series.
You might also like
- NMTC 9-10Document26 pagesNMTC 9-10Arpan Das100% (2)
- GCHP 12Document11 pagesGCHP 12caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- 3D GeometryDocument11 pages3D Geometrycaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Amc 10 2000Document7 pagesAmc 10 2000Madhu Mohan ChandranNo ratings yet
- Form IV Mathematics SeriesDocument12 pagesForm IV Mathematics SeriesEmmanuel R. Siwila100% (1)
- Longman - Grammar Practice For Elementary (Longman)Document5 pagesLongman - Grammar Practice For Elementary (Longman)Sơn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Math 2 8Document3 pagesMath 2 8Prem GomesNo ratings yet
- Hypatia Combined ContestDocument17 pagesHypatia Combined ContestΘανάσης ΔρούγαςNo ratings yet
- 2001 AMC 12 ProblemsDocument5 pages2001 AMC 12 ProblemsjabagaweeNo ratings yet
- Revised Math Set11 QuetionsDocument6 pagesRevised Math Set11 QuetionsRajNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 1Document5 pagesPhysics Form 1Sand FossohNo ratings yet
- Top Model Paper-2 - ProtectedDocument3 pagesTop Model Paper-2 - ProtectedmaheshNo ratings yet
- Al Mansoura School Math. Final Exam. Date: / / Grade: ADocument3 pagesAl Mansoura School Math. Final Exam. Date: / / Grade: ASaid AdelNo ratings yet
- 2001 AMC 12/AHSME: Contributors: Silverfalcon, RrusczykDocument6 pages2001 AMC 12/AHSME: Contributors: Silverfalcon, Rrusczykjinghe zhangNo ratings yet
- Math IIDocument3 pagesMath IIJitendra Mohan BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 2021 MathsMC MockDocument14 pages2021 MathsMC MockSally YuNo ratings yet
- BStat BMath UGA 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesBStat BMath UGA 2019 PDFDHIRAJ DILLEP S NAIRNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 9 Remedial ActivityDocument5 pagesQuarter 2 Week 9 Remedial Activitymk25vf5jffNo ratings yet
- Value of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseDocument11 pagesValue of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- 8th Final 2012Document2 pages8th Final 2012api-253679034No ratings yet
- Maths Class To Special Paper 1Document7 pagesMaths Class To Special Paper 1manga addictNo ratings yet
- NMTC - 9 - 10 CKM Stage 1 JRDocument27 pagesNMTC - 9 - 10 CKM Stage 1 JRPuja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- S3 Maths Final Exam 2019-2020Document12 pagesS3 Maths Final Exam 2019-2020Yannie SoonNo ratings yet
- Section A: 456/1 Mathematics 2hrs 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesSection A: 456/1 Mathematics 2hrs 30 MinutesAthiyo Martin100% (1)
- SMO 2009 Junior QuestionDocument10 pagesSMO 2009 Junior QuestionwmdsgNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument169 pagesUntitledok bruhNo ratings yet
- Revision of Form 4 Add MathsDocument9 pagesRevision of Form 4 Add MathsnixleonNo ratings yet
- JuniorFinal2015 PDFDocument3 pagesJuniorFinal2015 PDFEko Pramesti SumartoNo ratings yet
- Ahsme 1995 PDFDocument7 pagesAhsme 1995 PDFQFDqNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 November 2005Document10 pagesMaths Paper 2 November 2005sandieletasNo ratings yet
- Memory Based GRE Question6janDocument17 pagesMemory Based GRE Question6janMrulay MistryNo ratings yet
- Test #1 AMATYC Student Mathematics League October/November 2010Document2 pagesTest #1 AMATYC Student Mathematics League October/November 2010สฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Test #1 AMATYC Student Mathematics League October/November 2010Document2 pagesTest #1 AMATYC Student Mathematics League October/November 2010สฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Bstat Bmath Uga 2017Document8 pagesBstat Bmath Uga 2017gautamNo ratings yet
- Test 2007 Final VersionDocument12 pagesTest 2007 Final Versionau auNo ratings yet
- Edexcel June 1999 Paper 6Document3 pagesEdexcel June 1999 Paper 6Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Ahsme 1956 PDFDocument6 pagesAhsme 1956 PDFQFDqNo ratings yet
- NMTC 11-12Document25 pagesNMTC 11-12ADITYA THAKURNo ratings yet
- Final Examination 2008-2009 Mathematics: C A B A B A C A A BDocument8 pagesFinal Examination 2008-2009 Mathematics: C A B A B A C A A BJackson WongNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9th Maths Mid Term Sample Paper (DAV) 2019-20Document4 pagesCBSE Class 9th Maths Mid Term Sample Paper (DAV) 2019-20Sandya100% (9)
- Sample Aptitude Test QuestionsDocument12 pagesSample Aptitude Test QuestionsPra SadNo ratings yet
- Kvpy-2011 QDocument11 pagesKvpy-2011 QikeaNo ratings yet
- ViewpdfDocument8 pagesViewpdfkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- 7 MathsDocument3 pages7 MathsMuraliNo ratings yet
- Wogmc8 2023Document4 pagesWogmc8 2023Minh BuiNo ratings yet
- Ahsme 1955 PDFDocument7 pagesAhsme 1955 PDFQFDqNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Grade 9 Mathematics FOR PRINTDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test Grade 9 Mathematics FOR PRINTArjean Kris LiwatNo ratings yet
- 2014 Maths Entrance ExamDocument11 pages2014 Maths Entrance ExammonyNo ratings yet
- Single Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Document7 pagesSingle Answer Type Vectors & 3D: A, B, C A 3, B 4, C 5Celestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- Aps Class 10 Standard Pre Board 2Document5 pagesAps Class 10 Standard Pre Board 2SumitNo ratings yet
- Eton - KS - MathsBPaper - 2010Document4 pagesEton - KS - MathsBPaper - 2010kabirNo ratings yet
- Maths 9Document3 pagesMaths 9Dev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 Question PaperDocument8 pages2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 Question PaperPascal NgNo ratings yet
- CLass 7 Math Annual-02-CQDocument2 pagesCLass 7 Math Annual-02-CQCNS CAABNo ratings yet
- MathDocument8 pagesMathcomedy houseNo ratings yet
- 2017 IMAS - Junior - 1127Document6 pages2017 IMAS - Junior - 1127hoangtranquoc2008No ratings yet
- AMTI (NMTC) - 2004: Ramanujan Contest - Inter LevelDocument25 pagesAMTI (NMTC) - 2004: Ramanujan Contest - Inter Levelasha jalan100% (1)
- Math - Ix QP Set-1Document6 pagesMath - Ix QP Set-1Madhav ManjulalNo ratings yet
- Contributors: Worthawholebean, Redcomet46, Djmathman, RrusczykDocument12 pagesContributors: Worthawholebean, Redcomet46, Djmathman, RrusczykKarl Henry DahaoNo ratings yet
- 9th MATHS ENGDocument5 pages9th MATHS ENGnishmitharodrigues02No ratings yet
- Topographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsFrom EverandTopographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsNo ratings yet
- Exam Revision NAME: - 2 BimesterDocument8 pagesExam Revision NAME: - 2 Bimestercaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Exponents Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesExponents Review Worksheetcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Diploma Program Group 4: Experimental Sciences Biology CourseDocument16 pagesEnzymes: Diploma Program Group 4: Experimental Sciences Biology Coursecaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Worksheet LogDocument6 pagesWorksheet Logcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Currency ConversionDocument3 pagesCurrency Conversioncaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Worksheet QuintoDocument4 pagesWorksheet Quintocaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Lesson 9-2: Prisms and PyramidsDocument6 pagesLesson 9-2: Prisms and Pyramidscaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Financial MathDocument8 pagesWorksheet 1 Financial Mathcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Worksheet Arithmetic SeqDocument4 pagesWorksheet Arithmetic Seqcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Activity ExcelDocument9 pagesActivity Excelcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- HW Exam Number2Document1 pageHW Exam Number2caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- The Following Diagram Is A Box and Whisker Plot For A Set of DataDocument1 pageThe Following Diagram Is A Box and Whisker Plot For A Set of Datacaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Arithmetic Seq and SeriesDocument6 pagesArithmetic Seq and Seriescaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Project 2Document2 pagesProject 2caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Arithmetic SequencesDocument8 pagesArithmetic Sequencescaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Project 2Document2 pagesProject 2caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Mensuration: 3D GeometryDocument13 pagesMensuration: 3D Geometrycaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- HW 22Document2 pagesHW 22caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- HW 1Document1 pageHW 1caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- ProjectsDocument3 pagesProjectscaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet