Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. Cramer
Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. Cramer
Uploaded by
adiaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
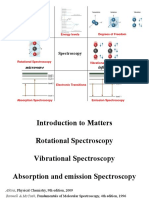
15 views5 pagesEnergy in molecules can be stored in electronic, translational, rotational, and vibrational forms. For diatomic molecules:
Rotational energy levels are determined by solving the rigid rotor Schrodinger equation. This provides equally spaced energy levels proportional to J(J+1) where J is the rotational quantum number.
Vibrational energy levels are modeled as a quantum harmonic oscillator. This provides equally spaced energy levels of hν(v+1/2) where ν is the vibrational frequency and v is the vibrational quantum number.
The dissociation energy (De) of a diatomic molecule is related to the electronic ground state energy and the zero-point vibrational energy of hν
Original Description:
Termo Videos
Original Title
ThermoVid_1_06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnergy in molecules can be stored in electronic, translational, rotational, and vibrational forms. For diatomic molecules:
Rotational energy levels are determined by solving the rigid rotor Schrodinger equation. This provides equally spaced energy levels proportional to J(J+1) where J is the rotational quantum number.
Vibrational energy levels are modeled as a quantum harmonic oscillator. This provides equally spaced energy levels of hν(v+1/2) where ν is the vibrational frequency and v is the vibrational quantum number.
The dissociation energy (De) of a diatomic molecule is related to the electronic ground state energy and the zero-point vibrational energy of hν
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. Cramer
Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. Cramer
Uploaded by
adiazEnergy in molecules can be stored in electronic, translational, rotational, and vibrational forms. For diatomic molecules:
Rotational energy levels are determined by solving the rigid rotor Schrodinger equation. This provides equally spaced energy levels proportional to J(J+1) where J is the rotational quantum number.
Vibrational energy levels are modeled as a quantum harmonic oscillator. This provides equally spaced energy levels of hν(v+1/2) where ν is the vibrational frequency and v is the vibrational quantum number.
The dissociation energy (De) of a diatomic molecule is related to the electronic ground state energy and the zero-point vibrational energy of hν
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Statistical Molecular
Thermodynamics
Christopher J. Cramer
Video 1.6
Diatomic Molecular Energy Levels
How is energy stored in a Molecule?
Electronic energy. Changes in the kinetic and
potential energy of one or more electrons associated
with the molecule. Same as many-electron atoms.
Kinetic Energy:
Translational energy. The molecule can move
(translate) in space. Same particle-in-a-box solutions
as for atoms.
Rotational energy. The entire molecule can rotate in
space. Schrdinger equation: Rigid-rotator.
Vibrational energy. The nuclei can move relative to
one another in space. Schrdinger equation:
Quantum-mechanical harmonic oscillator.
Rotational Energy LevelsDiatomics
moment of inertia: I = m1R12 + m 2 R22
The Schrdinger equation for the rigid
rotator provides energy levels:
h2
J = J ( J + 1)
2I
J = 0,1,2,K
The degeneracy of a given level, gJ, is:
g J = 2J +1
6h 2
3 =
I
3h 2
2 =
I
h2
1 =
I
0 = 0
J=4
J=3
J=2
J=1
J=0
rotational energy
10h 2
4 =
I
Vibrational Energy Levels
m1
m2
Vibrational motion is modeled as a harmonic oscillator, with
two masses attached by a spring
careful, nu and vee
R
Solving the Schrdinger equation for the QM
harmonic oscillator yields the energy levels:
v = h v +
2
v = 0,1,2, K
The levels are non-degenerate,
that is gv=1 for all values of v.
energy
The energy levels
v=4
v=3
v=2
v =1
v=0
Re
The energy levels are equally
spaced by h.
The energy of the lowest state
is NOT zero. The difference is
called zero-point energy.
1
R
0 = h
2
Bond Dissociation energy
m1
V(R)
Energy
The dissociation energy and the
electronic energy of a diatomic
molecule are related by the zero
point energy,
m2
negative of the ground-state electronic energy
D0
h
De = D0 +
2
De
dissociation energy
=0
De
For example, for H2(g):
R
Re
De = 458 kJ mol1
The zero-point vibrational energy: h/2
D0 = 432 kJ mol1
= 4401 cm1 = 52 kJ mol1
You might also like
- CHM2045 Chapter 9 Part 1Document3 pagesCHM2045 Chapter 9 Part 1Destiny Kit ManuelNo ratings yet
- Chul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModelDocument13 pagesChul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModellazharNo ratings yet
- Principles of Molecular SpectrosDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Molecular SpectrosShaheentariq_4No ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Rotational SpectrosDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy Rotational SpectrosMONERAH D ALOSAIMINo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document18 pagesLecture 3Balaraju BanothNo ratings yet
- HW1 PDFDocument2 pagesHW1 PDFesteban0paredes0auleNo ratings yet
- Principles of Molecular SpectrosDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Molecular SpectrosoomganapathiNo ratings yet
- 7 Statistical Thermodynamics-IIDocument30 pages7 Statistical Thermodynamics-IICahyarani ParamestiNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - Wikiversity PDFDocument36 pagesSpectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - Wikiversity PDFKishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDocument36 pagesSpectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityKishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDocument9 pagesSpectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDr. Gazi Jahirul ISlamNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Lecture Notes 2Document34 pagesBasic Chemistry Lecture Notes 2youngNo ratings yet
- StatisticalPhysics-Part1-Handout. 04 Febr 2021.Document27 pagesStatisticalPhysics-Part1-Handout. 04 Febr 2021.Muhammad Agustian AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2Document11 pagesTutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2JoserineNo ratings yet
- 2 V 1.36 x10 M 78 Amu V 3.05 x10: TransDocument4 pages2 V 1.36 x10 M 78 Amu V 3.05 x10: TransSa RaNo ratings yet
- Physics T3 Y10Document6 pagesPhysics T3 Y10Mohammed AbdulqareebNo ratings yet
- Microwave SpectrosDocument46 pagesMicrowave SpectrosMOHAMMED ABDUL HAINo ratings yet
- PH307 EndsemDocument2 pagesPH307 EndsemHarshita TripathiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesStatistical Thermodynamicsbits_who_am_iNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument66 pagesSpectrosVivek Earnest nathNo ratings yet
- Chem 310 CH 19 S18Document28 pagesChem 310 CH 19 S18Supreeth PrasadNo ratings yet
- EE138 Chapter 8 - Slides - Annotated 11-05Document29 pagesEE138 Chapter 8 - Slides - Annotated 11-05WenhaoShiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 ENERGY CONVERSIONDocument12 pagesModule 1 ENERGY CONVERSIONJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- The Born-Oppenheimer Approximation: Potential Energy SurfacesDocument18 pagesThe Born-Oppenheimer Approximation: Potential Energy SurfacesThảo HàNo ratings yet
- BIoenergetics BTOL Cramer 25 9 07Document58 pagesBIoenergetics BTOL Cramer 25 9 07subhoiitkgpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1A Spectroscopy.: Prof. Mike Ashfold (S305) (Mike - Ashfold@bris - Ac.uk)Document63 pagesChemistry 1A Spectroscopy.: Prof. Mike Ashfold (S305) (Mike - Ashfold@bris - Ac.uk)Abd El-Fattah Mohamed OufNo ratings yet
- QuantumTheory 1 SlidesDocument33 pagesQuantumTheory 1 SlidessamebalutNo ratings yet
- Chem 151 - PS 1Document2 pagesChem 151 - PS 1Alelie AyenNo ratings yet
- Type of SpectrumDocument5 pagesType of Spectrumfiza choudharyNo ratings yet
- 4 Molecular Orbital MethodsDocument40 pages4 Molecular Orbital MethodstudoorNo ratings yet
- From Atoms To Solids: Jeffrey C. GrossmanDocument44 pagesFrom Atoms To Solids: Jeffrey C. Grossmanchethugowda7No ratings yet
- CHM 217 3Q2016-17 - Final Exam PDFDocument2 pagesCHM 217 3Q2016-17 - Final Exam PDFcfmonarquiaNo ratings yet
- MT Exam 2022Document6 pagesMT Exam 2022ultrasonic.205No ratings yet
- MIT2 57S12 Lec Notes 2004 PDFDocument177 pagesMIT2 57S12 Lec Notes 2004 PDFGerman ToledoNo ratings yet
- Rotational-Vibrational SpectrosDocument13 pagesRotational-Vibrational Spectrosmarosh.marwa.slivaniNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry by Shriver & AtkinsDocument81 pagesInorganic Chemistry by Shriver & AtkinsSalma KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- MolecularEnergyLevelsNotes PDFDocument5 pagesMolecularEnergyLevelsNotes PDFLorena Monterrosas PérezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Density Functional Theory (2022)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Density Functional Theory (2022)APURI SIMON BNo ratings yet
- 2017 VT CHEM 579 Handout Section 3 (D2L)Document35 pages2017 VT CHEM 579 Handout Section 3 (D2L)Anonymous wPVGEORpjHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The AtomDocument64 pagesChapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The Atomvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 - Structure of AtomsDocument71 pagesChapter 2.1 - Structure of Atomsahmad yasinNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument42 pages1 IntroductionJustine CabuayNo ratings yet
- DR TMMP (Quantum)Document50 pagesDR TMMP (Quantum)Tmmp SmileNo ratings yet
- Chem 110, Chapter 7 PDFDocument62 pagesChem 110, Chapter 7 PDFنواف السلميNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure AMDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure AMShardaNo ratings yet
- Physics XIIDocument42 pagesPhysics XIIsudarshaneducation06No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - 2020 Spring - Part 5Document30 pagesChapter 9 - 2020 Spring - Part 5John FrankNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical ChemistryOke OluwafemiNo ratings yet
- PH503: Year 2015: Problem Set-IX Instructor: Subhradip GhoshDocument1 pagePH503: Year 2015: Problem Set-IX Instructor: Subhradip GhoshPrabhat RayNo ratings yet
- Elemental Quantum Mechanics: OutlineDocument21 pagesElemental Quantum Mechanics: OutlineBhuneshwar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Microwave Spectroscopy-1Document35 pagesMicrowave Spectroscopy-1surajjamal111No ratings yet
- 1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument6 pages1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeSagi IbiNo ratings yet
- 3.A. Electrochemistry: Topic 3: EnergyDocument67 pages3.A. Electrochemistry: Topic 3: EnergyJeam Russell AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 & AnswersDocument4 pagesExam 1 & AnswerspsychoxboyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument43 pagesQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomspussysweeperNo ratings yet
- 2 - Energy and Energy TransferDocument101 pages2 - Energy and Energy TransferJinit SanghviNo ratings yet
- Molecules in Electromagnetic Fields: From Ultracold Physics to Controlled ChemistryFrom EverandMolecules in Electromagnetic Fields: From Ultracold Physics to Controlled ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument8 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument4 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument8 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument8 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument5 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument5 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument8 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument5 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Practice Solutions - 05 - Chemical Equilibrium - Calculating The Equilibrium ConstantDocument2 pagesPractice Solutions - 05 - Chemical Equilibrium - Calculating The Equilibrium ConstantadiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument6 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- 1 3 BruteForceAlgorithmsDocument18 pages1 3 BruteForceAlgorithmsadiazNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument5 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- EE3BA3 - Final Exam: Wednesday, December 18, 2013 4:00pm IWC 1 (3) 3 HoursDocument3 pagesEE3BA3 - Final Exam: Wednesday, December 18, 2013 4:00pm IWC 1 (3) 3 HoursadiazNo ratings yet
- Kelvin FunctionsDocument2 pagesKelvin FunctionsJeremy DiazNo ratings yet
- ELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials (Fall 2013)Document1 pageELEC ENG 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials (Fall 2013)adiazNo ratings yet