Professional Documents
Culture Documents
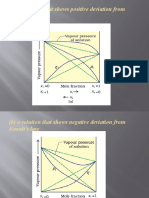
(B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's Law
(B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's Law
Uploaded by
PRAVIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pagesThis document discusses key concepts in vapor-liquid equilibrium including:
1) Dalton's law which states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual components.
2) Raoult's law which relates the vapor pressure of a component in a mixture to its mole fraction in the liquid phase.
3) Activity coefficients which are used to modify Raoult's law for non-ideal solutions showing positive or negative deviation from ideal behavior.
4) Various diagrams used to represent vapor-liquid equilibrium such as T-x-y, P-x-y diagrams.
Original Description:
vle-10
Original Title
vle-10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts in vapor-liquid equilibrium including:
1) Dalton's law which states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual components.
2) Raoult's law which relates the vapor pressure of a component in a mixture to its mole fraction in the liquid phase.
3) Activity coefficients which are used to modify Raoult's law for non-ideal solutions showing positive or negative deviation from ideal behavior.
4) Various diagrams used to represent vapor-liquid equilibrium such as T-x-y, P-x-y diagrams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pages(B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's Law
(B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's Law
Uploaded by
PRAVINThis document discusses key concepts in vapor-liquid equilibrium including:
1) Dalton's law which states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual components.
2) Raoult's law which relates the vapor pressure of a component in a mixture to its mole fraction in the liquid phase.
3) Activity coefficients which are used to modify Raoult's law for non-ideal solutions showing positive or negative deviation from ideal behavior.
4) Various diagrams used to represent vapor-liquid equilibrium such as T-x-y, P-x-y diagrams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
(b) a solution that shows negative deviation from
Raoult's law.
Daltons law
Ptotal = p1+ p2
Where,
Ptotal -Total pressure
p1 ,p2 -Partial pressure of component.
Composition of liquid phase :
x1= p1/ p10
= partial pressure of component /vapour pressure of pure component
Composition in gaseous phase :
y 1= p1/ P
= partial pressure of component /total pressure
Raoults law becomes
yiP=xiPisat (i=1,2,3..n)
Where:
yi = Vapor-phase mole fraction.
xi = Liquid-phase mole fraction.
Pi = Vapor pressure of pure species i at the T of the system.
yi P = Partial pressure of species i.
VLE by Modified Raoults Law
yi P = xi i Pisat ( i= 1,2,..,N)
Where
i = Activity coefficient.
T-x-y diagram/boiling point diagram
Effect of varying pressure on equilibrium
diagram
P-x-y Diagram
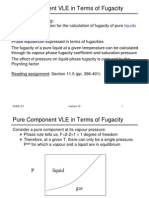
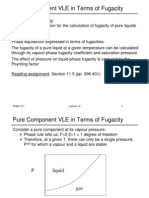
Fugacity: It is derived from Latin, expressed as
fleetness or escaping tendency. It is used
to study extensively phase and chemical reaction
equilibrium.
G = RT ln f +
- Is an constant depends on temperature and nature
of gas.
fugacity has same units as pressure for an ideal gas.
Activity coefficient equations
Wohls three suffix equation
Margules equation
Van laar equation
Wilson equation
Non random two liquid (NRTL)equation
Universal quasi chemical (UNIQUAC)equation
Universal functional activity coefficient (UNIFAC)
method
You might also like
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument11 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Law: Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument12 pagesDalton's Law: Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument15 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vle 9Document10 pagesVle 9PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vle 4Document15 pagesVle 4PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vap EquilibriumDocument14 pagesVap EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- What Is Equilibrium?Document12 pagesWhat Is Equilibrium?PRAVINNo ratings yet
- TFDXZDocument14 pagesTFDXZPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Composition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)Document8 pagesComposition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: LiquidsDocument8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: Liquidsahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics IIIIIIIIDocument14 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics IIIIIIIIDarnell HendersonNo ratings yet
- Chaoter 14 Phase EquilibriumDocument19 pagesChaoter 14 Phase EquilibriumHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1Document8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1scienziatoNo ratings yet
- UygfcDocument10 pagesUygfcPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Phases and SolutionDocument66 pagesChapter 3 - Phases and SolutionSYUHADAFAATAHNo ratings yet
- Review of Phase Equilibria - NEWDocument19 pagesReview of Phase Equilibria - NEWkarmawii taqatqaNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionDocument16 pagesPhase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Fe Chemical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Chemical EngineeringJudith LugoNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument28 pagesVapor Liquid EquilibriumKhloud MadihNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Introduction To Solution ThermodynamicsDocument26 pagesLecture 1. Introduction To Solution ThermodynamicsHan VendiolaNo ratings yet
- Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument9 pagesWhere, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Pert 11 - KESETIMBANGAN UAP-CAIR-PendahuluanDocument31 pagesPert 11 - KESETIMBANGAN UAP-CAIR-PendahuluanErlangga Aria PratamaNo ratings yet
- Ceic3001 NotesDocument3 pagesCeic3001 NotesZooy2012No ratings yet
- Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Chapter 9 - Introduction To Multicomponent SystemsDocument14 pagesIntroductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Chapter 9 - Introduction To Multicomponent SystemsHarshil TejaniNo ratings yet
- 1-Vle Part 1Document30 pages1-Vle Part 1Arfa Zulkifli01No ratings yet
- Vle For DummiesDocument8 pagesVle For Dummiesira_rancicNo ratings yet
- PokjhgvcDocument14 pagesPokjhgvcPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Flash CalculationDocument12 pagesFlash CalculationHamidreza HasaniNo ratings yet
- Liquid Vapor Equilibria - SOLN THERMO PDFDocument26 pagesLiquid Vapor Equilibria - SOLN THERMO PDFYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document42 pagesChapter 10JARVIS ASSITNo ratings yet
- Binary Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument7 pagesBinary Vapor Liquid EquilibriumBiain A SecasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Functions of SolutionsDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Functions of SolutionsBRENDA VIVIANA ARANDA JURADONo ratings yet
- Subscripts KEY: FIG. 25-1 NomenclatureDocument2 pagesSubscripts KEY: FIG. 25-1 NomenclatureGerardo MediavillaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Vle Part 1Document35 pagesWeek 2 - Vle Part 1dhanieemaNo ratings yet
- ثرمو محاضرة 3 مرحلة 3Document38 pagesثرمو محاضرة 3 مرحلة 3Al-Hassan NeimaNo ratings yet
- P, T-Flash CalculationDocument12 pagesP, T-Flash CalculationBennyNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent and Multiphase SystemsDocument15 pagesMulticomponent and Multiphase SystemsZain AliNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument19 pagesPhase DiagramsKaaya GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriaDocument47 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriaKent GardoseNo ratings yet
- LIGSflashpointDocument2 pagesLIGSflashpointjonabelNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent Systems, Partial Molar Quantities, and The Chemical PotentialDocument5 pagesMulticomponent Systems, Partial Molar Quantities, and The Chemical PotentialsgybleeNo ratings yet
- Flashing CalculationsDocument8 pagesFlashing CalculationsjcmarabouNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument39 pagesVapor Liquid EquilibriumyeenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- CH 5030 Transport PhenomenaDocument12 pagesCH 5030 Transport PhenomenaAlps AnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Thermodynamics and Equilibrium: D RTDLNFDocument2 pagesLecture 2: Thermodynamics and Equilibrium: D RTDLNFRinaldi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Phase EquilibriumDocument47 pagesLecture 7 Phase EquilibriumShivani ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- ثرمو2Document19 pagesثرمو2Al-Hassan NeimaNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument39 pagesVapor Liquid EquilibriumTouhid IslamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Vapor Liquid Equilibriumshiv007anshNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument39 pagesVapor Liquid EquilibriumJakeWilliam100% (1)
- Chapitre 4 - 543Document14 pagesChapitre 4 - 543Andrian SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Lec. 3 DR, MarwaDocument25 pagesLec. 3 DR, MarwaFathi ShokryNo ratings yet
- Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium: Mata Kuliah: Termodinamika IIDocument70 pagesVapor/Liquid Equilibrium: Mata Kuliah: Termodinamika IIputri wahyuniNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument2 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriumCornelius YudhaNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument3 pagesWhere, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Composition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)Document8 pagesComposition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Yip=Xiγip (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientDocument2 pagesYip=Xiγip (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientPRAVINNo ratings yet
- OIUHGFDXZDocument5 pagesOIUHGFDXZPRAVINNo ratings yet
- UygfcDocument10 pagesUygfcPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressureDocument7 pagesEffect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressurePRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument9 pagesWhere, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- TFDXZDocument14 pagesTFDXZPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Activity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityDocument4 pagesActivity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Activity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityDocument4 pagesActivity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityPRAVINNo ratings yet
- PokjhgvcDocument14 pagesPokjhgvcPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Law: Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument12 pagesDalton's Law: Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- (A) A Solution That Shows Positive Deviation From Raoult's LawDocument7 pages(A) A Solution That Shows Positive Deviation From Raoult's LawPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vap EquilibriumDocument14 pagesVap EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Yip=Xiγi P (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientDocument7 pagesYip=Xiγi P (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Activity (A) : A F/ F Activity CoefficientDocument3 pagesActivity (A) : A F/ F Activity CoefficientPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument11 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vle 9Document10 pagesVle 9PRAVINNo ratings yet
- What Is Equilibrium?Document12 pagesWhat Is Equilibrium?PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapour LiquidDocument5 pagesVapour LiquidPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument15 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vle 4Document15 pagesVle 4PRAVINNo ratings yet