Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsOhm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Uploaded by
Abdul AddaharyOhm's law describes the mathematical relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The formula I=V/R shows that for a given resistance, if the voltage is doubled then the current will double, and if the voltage is halved then the current will also be halved. Manipulating the equations leads to expressions for calculating voltage and resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Discussion - Ohm - S LawDocument2 pagesDiscussion - Ohm - S LawChrisEmilsonHernaez50% (4)
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document4 pagesExp 2Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and ResistanceDocument1 pageOhm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and ResistanceqilahmazlanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Ohm - S LawDocument23 pagesOhm - S LawEngr Abdul Samad MalikNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Charges and Ohm LawDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Charges and Ohm Lawعلي محمودNo ratings yet
- Resistors and Resistor CircuitsDocument4 pagesResistors and Resistor CircuitsBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law 2017Document10 pagesOhms Law 2017drakeNo ratings yet
- Here We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterDocument2 pagesHere We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterRoy Axel HabocNo ratings yet
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ohms LawDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ohms LawJoshteKunNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument20 pagesOhms LawWilfredo Ijan, JrNo ratings yet
- 8 and 9. Simple Elctric Circuit & Ohms LawDocument13 pages8 and 9. Simple Elctric Circuit & Ohms LawJose Navarro100% (1)
- Ohm's LawDocument24 pagesOhm's LawIrish de LeonNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 LabDocument3 pagesChapter 17 LabOMGPIKAJEWNo ratings yet
- Pages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedDocument13 pagesPages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedsoniNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngDocument12 pagesOhm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngViana Celina AngNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law and PowerDocument32 pagesOhms Law and PowerGilbert TamayoNo ratings yet
- To Analyze The OhmDocument2 pagesTo Analyze The OhmHana VvnaNo ratings yet
- Cekit Electronics BookDocument3 pagesCekit Electronics BookScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 4.2.7 ResistanceDocument2 pages4.2.7 ResistanceIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- Methodology ExperimentDocument1 pageMethodology ExperimentJuju ManullangNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel CircuitDocument13 pagesSeries Parallel Circuitelvis mendezNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectronic CircuitsAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science CAT Lab ReportDocument5 pagesYear 9 Science CAT Lab ReportKaitlyn CarrNo ratings yet
- Resistance FormulaDocument14 pagesResistance FormulaCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Principles: Electricity and MatterDocument11 pagesBasic Electrical Principles: Electricity and MatterEberson LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Ohms-Law WattDocument31 pagesOhms-Law WattCatherineNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawMuhammad Tayyab MadniNo ratings yet
- The Practical Benefits in Ohms Law Is Determining The Barriers Can Replacement of Each Circuit, Radios Ad TVDocument2 pagesThe Practical Benefits in Ohms Law Is Determining The Barriers Can Replacement of Each Circuit, Radios Ad TVJuju ManullangNo ratings yet
- (Week 2) Lecture 3 and 4 Objectives: Learning Objectives of This Lecture AreDocument11 pages(Week 2) Lecture 3 and 4 Objectives: Learning Objectives of This Lecture Arekainat malikNo ratings yet
- OHM'S LAW Report 101Document32 pagesOHM'S LAW Report 101Cezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Ohmic and Non-OhmicDocument4 pagesOhmic and Non-Ohmicjustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's Lawsyedshehzd_9No ratings yet
- Module in Science II-1Document8 pagesModule in Science II-1Gladzkee Cabello GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsDocument4 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MatterDocument10 pagesElectricity and MatterJefferson EscobarNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Worksheet RPHDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Worksheet RPHcamiscoolyuNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms Lawceller101No ratings yet
- Lecture On Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesLecture On Ohm's LawJanxi Carlisle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Hysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10Document15 pagesHysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10raosamhith1No ratings yet
- The Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltageDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltagechristiankenthusaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage ResistanceDocument2 pagesPotential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage Resistanceschauhan12No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Parallel CircuitDocument2 pagesOhm's Law: Parallel Circuitnhie_quh29No ratings yet
- Document 43Document20 pagesDocument 43bumbadiyaviralNo ratings yet
- Dhruv Khurana Grade 10 Ruby Shanghai Singapore International School Word Count: 1,000Document6 pagesDhruv Khurana Grade 10 Ruby Shanghai Singapore International School Word Count: 1,000Dhruv KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's LawAdrielNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument11 pagesOhm's LawMarifer RamirezNo ratings yet
- Physics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)Document6 pagesPhysics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)naNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesOhms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDarius Dave CruzNo ratings yet
- Computation and Relations of VariablesDocument2 pagesComputation and Relations of Variablesrurucj08No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument31 pagesOhms LawMike Jacson BautistaNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Tutorial 1: Introduction To MarketingDocument2 pagesTutorial 1: Introduction To MarketingAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Part 1Document2 pagesTutorial 2-Part 1Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- WBB10202 Innovation Management Lecturer: Suhaiza Ngah Topic 1: Perspectives On InnovationDocument16 pagesWBB10202 Innovation Management Lecturer: Suhaiza Ngah Topic 1: Perspectives On InnovationAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Theory: P P or P PDocument4 pagesTheory: P P or P PAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Checklist PMDocument3 pagesChecklist PMAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Checklist PMDocument4 pagesChecklist PMAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Z =R− J X Z=R+Jx Z=R+Jx: = 1 2 Πfc = 2 Πfl = −Document2 pagesZ =R− J X Z=R+Jx Z=R+Jx: = 1 2 Πfc = 2 Πfl = −Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Efp 80 C Sample Diesel: ResultDocument3 pagesEfp 80 C Sample Diesel: ResultAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Overview of Solid Processing Technologies For Palm Oil BiomassDocument3 pagesFigure 1: Overview of Solid Processing Technologies For Palm Oil BiomassAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Conclusions PilotplantDocument4 pagesConclusions PilotplantAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument3 pagesTransportAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Resultndiscussion 151126101738 Lva1 App6891Document2 pagesResultndiscussion 151126101738 Lva1 App6891Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Level Measurement Discussion ImDocument5 pagesLevel Measurement Discussion ImAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Anticline ImpermeableDocument4 pagesAnticline ImpermeableAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Refrence and ConclusionDocument2 pagesRefrence and ConclusionAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Exp1 ElecDocument22 pagesExp1 ElecAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Results: Table 1: Density Measurement (Water, Heater OFF)Document2 pagesResults: Table 1: Density Measurement (Water, Heater OFF)Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Energy and PowerDocument2 pagesEnergy and PowerAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- ConclusionconDocument1 pageConclusionconAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- HOW TO DO A LAB REPORT? Nur Aneesa S Groupmates : ObjectivesDocument2 pagesHOW TO DO A LAB REPORT? Nur Aneesa S Groupmates : ObjectivesAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Report OshaDocument6 pagesReport OshaAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Uploaded by
Abdul Addahary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOhm's law describes the mathematical relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The formula I=V/R shows that for a given resistance, if the voltage is doubled then the current will double, and if the voltage is halved then the current will also be halved. Manipulating the equations leads to expressions for calculating voltage and resistance.
Original Description:
s
Original Title
OHM_s law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOhm's law describes the mathematical relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The formula I=V/R shows that for a given resistance, if the voltage is doubled then the current will double, and if the voltage is halved then the current will also be halved. Manipulating the equations leads to expressions for calculating voltage and resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOhm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and Resistance
Uploaded by
Abdul AddaharyOhm's law describes the mathematical relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The formula I=V/R shows that for a given resistance, if the voltage is doubled then the current will double, and if the voltage is halved then the current will also be halved. Manipulating the equations leads to expressions for calculating voltage and resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
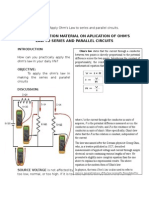
OHMS LAW THE RELATIONSHIP OF CURRENT, VOLTAGE AND
RESISTANCE
Ohms law describes mathematically how voltage, current and
resistance in a circuit are related.
Experimentally, if voltage across a resistor is increased, the current
through the resistor will also increase.
Voltage decreased the current decreased.
If the voltage is doubled, the current will double. If the voltage is
halved, the current will also be halved.
Ohm also determined that if the voltage is held constant, less
resistance results in more current, more resistance result in less
current.
For example, if the resistance is halved, the current doubles, resistance
doubled, the current is halved.
Ohms law state that current is directly proportional to voltage and
inversely proportional to resistance. Given the formula :
I
V
R
Where I is current in amperes (A), V is for voltage (V) and R is
resistance in ohm ().
For a constant value of R, I increased/decreased V will also
increased/decreased.
If V is constant R increased/decreased I will decreased/increased.
By manipulating the above equations, the expression for voltage and
resistance can be obtained :
V IR
V
R
I
You might also like
- Discussion - Ohm - S LawDocument2 pagesDiscussion - Ohm - S LawChrisEmilsonHernaez50% (4)
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document4 pagesExp 2Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and ResistanceDocument1 pageOhm'S Law - The Relationship of Current, Voltage and ResistanceqilahmazlanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Ohm - S LawDocument23 pagesOhm - S LawEngr Abdul Samad MalikNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Charges and Ohm LawDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Charges and Ohm Lawعلي محمودNo ratings yet
- Resistors and Resistor CircuitsDocument4 pagesResistors and Resistor CircuitsBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law 2017Document10 pagesOhms Law 2017drakeNo ratings yet
- Here We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterDocument2 pagesHere We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterRoy Axel HabocNo ratings yet
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ohms LawDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ohms LawJoshteKunNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument20 pagesOhms LawWilfredo Ijan, JrNo ratings yet
- 8 and 9. Simple Elctric Circuit & Ohms LawDocument13 pages8 and 9. Simple Elctric Circuit & Ohms LawJose Navarro100% (1)
- Ohm's LawDocument24 pagesOhm's LawIrish de LeonNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 LabDocument3 pagesChapter 17 LabOMGPIKAJEWNo ratings yet
- Pages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedDocument13 pagesPages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedsoniNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngDocument12 pagesOhm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngViana Celina AngNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law and PowerDocument32 pagesOhms Law and PowerGilbert TamayoNo ratings yet
- To Analyze The OhmDocument2 pagesTo Analyze The OhmHana VvnaNo ratings yet
- Cekit Electronics BookDocument3 pagesCekit Electronics BookScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 4.2.7 ResistanceDocument2 pages4.2.7 ResistanceIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- Methodology ExperimentDocument1 pageMethodology ExperimentJuju ManullangNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel CircuitDocument13 pagesSeries Parallel Circuitelvis mendezNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectronic CircuitsAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science CAT Lab ReportDocument5 pagesYear 9 Science CAT Lab ReportKaitlyn CarrNo ratings yet
- Resistance FormulaDocument14 pagesResistance FormulaCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Principles: Electricity and MatterDocument11 pagesBasic Electrical Principles: Electricity and MatterEberson LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Ohms-Law WattDocument31 pagesOhms-Law WattCatherineNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawMuhammad Tayyab MadniNo ratings yet
- The Practical Benefits in Ohms Law Is Determining The Barriers Can Replacement of Each Circuit, Radios Ad TVDocument2 pagesThe Practical Benefits in Ohms Law Is Determining The Barriers Can Replacement of Each Circuit, Radios Ad TVJuju ManullangNo ratings yet
- (Week 2) Lecture 3 and 4 Objectives: Learning Objectives of This Lecture AreDocument11 pages(Week 2) Lecture 3 and 4 Objectives: Learning Objectives of This Lecture Arekainat malikNo ratings yet
- OHM'S LAW Report 101Document32 pagesOHM'S LAW Report 101Cezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Ohmic and Non-OhmicDocument4 pagesOhmic and Non-Ohmicjustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's Lawsyedshehzd_9No ratings yet
- Module in Science II-1Document8 pagesModule in Science II-1Gladzkee Cabello GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsDocument4 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MatterDocument10 pagesElectricity and MatterJefferson EscobarNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Worksheet RPHDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Worksheet RPHcamiscoolyuNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms Lawceller101No ratings yet
- Lecture On Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesLecture On Ohm's LawJanxi Carlisle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Hysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10Document15 pagesHysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10raosamhith1No ratings yet
- The Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltageDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltagechristiankenthusaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage ResistanceDocument2 pagesPotential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage Resistanceschauhan12No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Parallel CircuitDocument2 pagesOhm's Law: Parallel Circuitnhie_quh29No ratings yet
- Document 43Document20 pagesDocument 43bumbadiyaviralNo ratings yet
- Dhruv Khurana Grade 10 Ruby Shanghai Singapore International School Word Count: 1,000Document6 pagesDhruv Khurana Grade 10 Ruby Shanghai Singapore International School Word Count: 1,000Dhruv KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's LawAdrielNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument11 pagesOhm's LawMarifer RamirezNo ratings yet
- Physics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)Document6 pagesPhysics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)naNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesOhms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDarius Dave CruzNo ratings yet
- Computation and Relations of VariablesDocument2 pagesComputation and Relations of Variablesrurucj08No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument31 pagesOhms LawMike Jacson BautistaNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Tutorial 1: Introduction To MarketingDocument2 pagesTutorial 1: Introduction To MarketingAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Part 1Document2 pagesTutorial 2-Part 1Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- WBB10202 Innovation Management Lecturer: Suhaiza Ngah Topic 1: Perspectives On InnovationDocument16 pagesWBB10202 Innovation Management Lecturer: Suhaiza Ngah Topic 1: Perspectives On InnovationAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Theory: P P or P PDocument4 pagesTheory: P P or P PAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Checklist PMDocument3 pagesChecklist PMAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Checklist PMDocument4 pagesChecklist PMAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Z =R− J X Z=R+Jx Z=R+Jx: = 1 2 Πfc = 2 Πfl = −Document2 pagesZ =R− J X Z=R+Jx Z=R+Jx: = 1 2 Πfc = 2 Πfl = −Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Efp 80 C Sample Diesel: ResultDocument3 pagesEfp 80 C Sample Diesel: ResultAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Overview of Solid Processing Technologies For Palm Oil BiomassDocument3 pagesFigure 1: Overview of Solid Processing Technologies For Palm Oil BiomassAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Conclusions PilotplantDocument4 pagesConclusions PilotplantAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument3 pagesTransportAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Resultndiscussion 151126101738 Lva1 App6891Document2 pagesResultndiscussion 151126101738 Lva1 App6891Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Level Measurement Discussion ImDocument5 pagesLevel Measurement Discussion ImAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Anticline ImpermeableDocument4 pagesAnticline ImpermeableAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Refrence and ConclusionDocument2 pagesRefrence and ConclusionAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Exp1 ElecDocument22 pagesExp1 ElecAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Results: Table 1: Density Measurement (Water, Heater OFF)Document2 pagesResults: Table 1: Density Measurement (Water, Heater OFF)Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Energy and PowerDocument2 pagesEnergy and PowerAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- ConclusionconDocument1 pageConclusionconAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- HOW TO DO A LAB REPORT? Nur Aneesa S Groupmates : ObjectivesDocument2 pagesHOW TO DO A LAB REPORT? Nur Aneesa S Groupmates : ObjectivesAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Report OshaDocument6 pagesReport OshaAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet