Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon Compound Form 4
Carbon Compound Form 4
Uploaded by
Ct Sophie PheaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Food Additives PresentationDocument8 pagesFood Additives PresentationCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Acid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Document9 pagesAcid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Mod 7 - Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesSet 1 Mod 7 - Organic ChemistryquinlanyiuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesZaina ImamNo ratings yet
- Week 6 January 9-13-2023 LESSONDocument47 pagesWeek 6 January 9-13-2023 LESSONSam MauricioNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument15 pagesBasic ChemistryjuliusromatolentinoNo ratings yet
- Part 1 HCDocument22 pagesPart 1 HCGerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentDocument40 pagesSample DocumentJohn Joseph YeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.5 To EndDocument25 pagesChapter 5.5 To EndSofia LyonNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter 2019Document44 pagesChanges in Matter 2019api-423980580No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IgcseDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry Igcsenkoan12No ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundsDocument71 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundsJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Organic Chemistry ConceptsDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Organic Chemistry Conceptsnorlene narita macedaNo ratings yet
- Covid ClassDocument36 pagesCovid ClassErica Nicole C. LabialNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument35 pagesCarbon CompoundErica NatividadNo ratings yet
- Chapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01Document65 pagesChapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01VinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Branch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon MoleculesDocument31 pagesBranch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon Moleculesedgardo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic CompoundsemilyNo ratings yet
- Versatile Nature of CarbonDocument26 pagesVersatile Nature of CarbonAashish MenghaniNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Organic CompoundsDocument42 pagesCH 8 Organic CompoundsHeidi VagueNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesOrganic ChemistryAlyssa EridioNo ratings yet
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon CompoundDocument32 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon Compoundnur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Igcse Coordinated Sciences (Chemistry)Document10 pagesIgcse Coordinated Sciences (Chemistry)ratna gamidiNo ratings yet
- CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS MDocument31 pagesCARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS MAPARAJITHA N CNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistryc21fw.csyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Finals ReviewerDocument131 pagesGeneral Chemistry Finals ReviewerRc Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Carbon & Its Compounds: Chemistry Class XDocument31 pagesCh-4 Carbon & Its Compounds: Chemistry Class XSakshi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Document33 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Sarfraz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Section B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsDocument111 pagesSection B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsLeevan BarrattNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Functional GroupsDocument4 pages2.1 Functional GroupsBasti SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: 1. Physical StateDocument2 pagesAlkenes: 1. Physical State1101900No ratings yet
- Acquaintance With Covalent MoleculesDocument11 pagesAcquaintance With Covalent MoleculesAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument19 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFjacobNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument45 pagesOrganic Chemistrynicole.levy.ctcNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument33 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundslamliamqxzz01No ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Test For HydrocarbonsdhonaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Organic ChemistryDocument37 pagesOrganic ChemistryNjabulo Ah AhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Complete NotesDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistry Complete NotesAhmad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Reaction - Mechanism of AlkanesDocument39 pagesReaction - Mechanism of AlkanesGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Carbon CompoundDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Carbon CompoundSeddartth SanmugamNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 6 Periodic TableDocument27 pagesScience Chapter 6 Periodic TableAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Full Org ChemDocument13 pagesFull Org ChemSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundsDocument30 pagesCarbon CompoundsMimie Yasmin KamalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesAzib ZararNo ratings yet
- 1 RX Senyawa OrganikDocument25 pages1 RX Senyawa OrganikKelinci NgunutNo ratings yet
- L4-Q2-W4-Carbon AtomDocument48 pagesL4-Q2-W4-Carbon AtomColleen SerilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDahyun KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemistry of CellsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Chemistry of Cellsalvinlarano11No ratings yet
- Aromatic HCsDocument20 pagesAromatic HCsHasnaa EssamNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDocument23 pagesFunctional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDaniel D. RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Fuels, AlkanesDocument19 pagesIntroduction, Fuels, Alkanesjustinau22No ratings yet
- Freeradicals 171225065343Document58 pagesFreeradicals 171225065343Jawad HussainNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 NotesDocument9 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Characteristics of RadicalsDocument54 pagesCharacteristics of RadicalsdesyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument6 pagesChapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesJERVINLIM100% (1)
- Hand Out 7Document8 pagesHand Out 7Shela Mae LibandoNo ratings yet
- هيكلة الثاني عشر متقدمDocument42 pagesهيكلة الثاني عشر متقدمgorgeadams82No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound - YTDocument87 pagesCarbon and Its Compound - YTANIKA PRASHANTKUMAR JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Plant ReproductionDocument6 pagesPlant ReproductionCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Chromosome: Events That Occur in Each Stage of MitosisDocument3 pagesProphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Chromosome: Events That Occur in Each Stage of MitosisCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
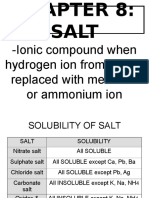
- SPM Form 5 Chemistry SaltDocument6 pagesSPM Form 5 Chemistry SaltCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
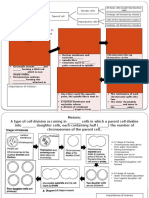
- Mitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsDocument2 pagesMitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
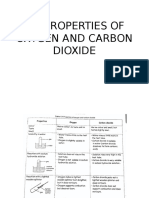
- 5.2 Properties of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideDocument5 pages5.2 Properties of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument13 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleDocument22 pages4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 5 - GrowthDocument2 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 5 - GrowthCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Form 4Document14 pagesElectrochemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
Carbon Compound Form 4
Carbon Compound Form 4
Uploaded by
Ct Sophie PheaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbon Compound Form 4
Carbon Compound Form 4
Uploaded by
Ct Sophie PheaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 2: CARBON COMPOUND
CARBON COMPOUND:
ORGANIC COMPOUND:
INORGANIC COMPOUND:
Isomerism: phenomenon where 2/more compound have SAME
.. but DIFFERENT
Isomers: compounds of SAME but DIFFERENT
..(same chemical properties & different physical
properties)
HYDROCARBON
A type of organic compound contain carbon & hydrogen only
Saturated hydrocarbon
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Contain only single covalent
bonds
Contain maximum possible no
of hydrogen atoms per carbon
Contain double or triple bonds
Contain fewer hydrogen
atoms per carbon atom
compared to a saturated
N OF ALKANE
ION REACTION
TION/BROMINATION)
ON OF ALKENE
HYDROGENATION
HALOGENATION
HYDRATION
CONDITION
EQUATION
OBSERVATION
Excess O2: complete
combustion
Limited O2: incomplete
combustion
Alkane+O2CO2+H2O
(complete)
Alkane + O2 CO +
H2O
(incomplete)
Presence of sunlight or
ultraviolet
Burn with more sooty
flame due to high % of
C atoms but than
alkane
flammable: large
molecule
Excess O2: complete
combustion
Limited O2: incomplete
combustion
Alkene+O2CO2+H2O
(complete)
Alkenes + O2 CO +
H2O (incomplete)
Burn with more sooty
flame due to high % of
C atoms
flammable: large
molecule
Catalyst:
platinum/nickel
temperature: 180C
Room condition
Use Cl2: chlorination
process
Use Br2: bromination
process
Catalyst: phosphoric
acid
Tempt: 300C,
Pressure: 600 a.t.p
Alkenes + H2 Alkane
Alkenes + chlorine
dichloroalkane
Alkenes + bromine
dibromoalkane
Alkenes + steam
Alcohol
Brown colour of Br
decolourised bcoz
alkenes is unsaturated,
addition reaction occur
wen Br H2O added to
alkenes
FATS
NATURAL ESTERS FOUND IN ANIMALS(SOLID) AND
PLANTS(LIQUID)
CONTAIN C, H, O
MADE UP OF 3 MOLECULES OF FATTY ACIDS & A MOLECULE
OF GLYCEROL
TYPE OF BOND
PHYSICAL STATE
AT ROOM
SATURATED
FATS
UNSATURATED
FATS
Single bond b/w
carbons atoms
At least a
double bond
b/w carbons
atoms
Solid
Liquid
You might also like
- Food Additives PresentationDocument8 pagesFood Additives PresentationCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Acid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Document9 pagesAcid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Mod 7 - Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesSet 1 Mod 7 - Organic ChemistryquinlanyiuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesZaina ImamNo ratings yet
- Week 6 January 9-13-2023 LESSONDocument47 pagesWeek 6 January 9-13-2023 LESSONSam MauricioNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument15 pagesBasic ChemistryjuliusromatolentinoNo ratings yet
- Part 1 HCDocument22 pagesPart 1 HCGerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentDocument40 pagesSample DocumentJohn Joseph YeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.5 To EndDocument25 pagesChapter 5.5 To EndSofia LyonNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter 2019Document44 pagesChanges in Matter 2019api-423980580No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IgcseDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry Igcsenkoan12No ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundsDocument71 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundsJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Organic Chemistry ConceptsDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Organic Chemistry Conceptsnorlene narita macedaNo ratings yet
- Covid ClassDocument36 pagesCovid ClassErica Nicole C. LabialNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument35 pagesCarbon CompoundErica NatividadNo ratings yet
- Chapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01Document65 pagesChapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01VinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Branch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon MoleculesDocument31 pagesBranch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon Moleculesedgardo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic CompoundsemilyNo ratings yet
- Versatile Nature of CarbonDocument26 pagesVersatile Nature of CarbonAashish MenghaniNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Organic CompoundsDocument42 pagesCH 8 Organic CompoundsHeidi VagueNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesOrganic ChemistryAlyssa EridioNo ratings yet
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon CompoundDocument32 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon Compoundnur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Igcse Coordinated Sciences (Chemistry)Document10 pagesIgcse Coordinated Sciences (Chemistry)ratna gamidiNo ratings yet
- CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS MDocument31 pagesCARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS MAPARAJITHA N CNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistryc21fw.csyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Finals ReviewerDocument131 pagesGeneral Chemistry Finals ReviewerRc Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Carbon & Its Compounds: Chemistry Class XDocument31 pagesCh-4 Carbon & Its Compounds: Chemistry Class XSakshi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Document33 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Sarfraz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Section B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsDocument111 pagesSection B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsLeevan BarrattNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Functional GroupsDocument4 pages2.1 Functional GroupsBasti SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: 1. Physical StateDocument2 pagesAlkenes: 1. Physical State1101900No ratings yet
- Acquaintance With Covalent MoleculesDocument11 pagesAcquaintance With Covalent MoleculesAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument19 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFjacobNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument45 pagesOrganic Chemistrynicole.levy.ctcNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument33 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundslamliamqxzz01No ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Test For HydrocarbonsdhonaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Organic ChemistryDocument37 pagesOrganic ChemistryNjabulo Ah AhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Complete NotesDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistry Complete NotesAhmad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Reaction - Mechanism of AlkanesDocument39 pagesReaction - Mechanism of AlkanesGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Carbon CompoundDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Carbon CompoundSeddartth SanmugamNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 6 Periodic TableDocument27 pagesScience Chapter 6 Periodic TableAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Full Org ChemDocument13 pagesFull Org ChemSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundsDocument30 pagesCarbon CompoundsMimie Yasmin KamalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesAzib ZararNo ratings yet
- 1 RX Senyawa OrganikDocument25 pages1 RX Senyawa OrganikKelinci NgunutNo ratings yet
- L4-Q2-W4-Carbon AtomDocument48 pagesL4-Q2-W4-Carbon AtomColleen SerilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDahyun KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemistry of CellsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Chemistry of Cellsalvinlarano11No ratings yet
- Aromatic HCsDocument20 pagesAromatic HCsHasnaa EssamNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDocument23 pagesFunctional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDaniel D. RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Fuels, AlkanesDocument19 pagesIntroduction, Fuels, Alkanesjustinau22No ratings yet
- Freeradicals 171225065343Document58 pagesFreeradicals 171225065343Jawad HussainNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 NotesDocument9 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Characteristics of RadicalsDocument54 pagesCharacteristics of RadicalsdesyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument6 pagesChapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesJERVINLIM100% (1)
- Hand Out 7Document8 pagesHand Out 7Shela Mae LibandoNo ratings yet
- هيكلة الثاني عشر متقدمDocument42 pagesهيكلة الثاني عشر متقدمgorgeadams82No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound - YTDocument87 pagesCarbon and Its Compound - YTANIKA PRASHANTKUMAR JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Plant ReproductionDocument6 pagesPlant ReproductionCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Chromosome: Events That Occur in Each Stage of MitosisDocument3 pagesProphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Chromosome: Events That Occur in Each Stage of MitosisCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 5 Chemistry SaltDocument6 pagesSPM Form 5 Chemistry SaltCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsDocument2 pagesMitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Properties of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideDocument5 pages5.2 Properties of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument13 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleDocument22 pages4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 5 - GrowthDocument2 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 5 - GrowthCt Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Form 4Document14 pagesElectrochemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet