Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics - Formulas and Tips
Mathematics - Formulas and Tips
Uploaded by
Rene RaynesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics - Formulas and Tips
Mathematics - Formulas and Tips
Uploaded by
Rene RaynesCopyright:
Available Formats
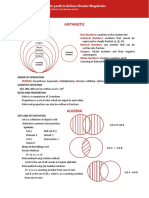
POLYNOMIALS
Synthetic Division
- Write down all coefficients ONLY (ignore sign) for each
power, leaving 0 for missing powers
- Bring down the first term to the bottom
- Multiply it by the coefficient youre dividing (zero of
the function) (e.g. x-4, +4..... x+4,-4)
- Put it below the next coefficient and add them down
- Multiply it by the coefficient youre dividing and
repeat
Factor Theorem
If you input the zero of a function into the equation
and its equal to zero, then that function is a factor of
that equation
Remainder Theorem
If you input the zero of the dividing function into the
divided equation and get a number, then that number
is the remainder of the quotient
BINOMIALS
Coefficient of next term:
C=
coefficient of previousexponent of previous x
exponent of previous y + 1
rth term of (x + y)n:
r th term=
n!
x n1+1 y r1
(nr +1)! (r1)!
Sum of coefficients of an expansion:
If = 0, roots are equal
If >1, roots are real & unequal
If <1, roots are imaginary
Properties of quadratic roots:
of Roots , x 1 + x2 =
Product of Roots , x 1 x 2=
Quadratic Formula:
B B24 AC
x=
2A
Discriminant and Properties:
2
B 4 AC
C
A
PARTIAL FRACTIONS
Breaking down a polynomials
- Put each equation as a denominator
- If powered, each power is a denominator (e.g.
(x+1)3 then (x+1)1, (x+1)2, (x+1)3 are separate
denominators)
- A variable goes in the numerator depending
on the number of roots in the denominator,
(e.g. (x+1)3 then A/(x+1)3, (x2+x+1)2 then (Ax
+ B)/ (x2+x+1)2)
- Equate the two sides then multiply by the originals
denominator (everything should cancel and leave the
variables multiplied the rest)
- To solve for a variable, isolate the term to the original
and plug in the zero of the terms respective zero
denominator
VARIATIONS
Direct Variation
x directly proportional to y,
x=ky
Inverse Variation
x is inversely proportional to
- Substitute 1 for each variable and equate
QUADRATIC FORMULA
B
A
y,
x=
k
y
Joint Variation
x is directly proportional to y
and inversely proportional to the square of z
x=k
y
x2
PROGRESSIONS
Arithmetic Progression
You might also like
- Calc 2 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCalc 2 Cheat Sheetvgc3491No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 & Trig Regent ReviewDocument16 pagesAlgebra 2 & Trig Regent ReviewCassieGrecoNo ratings yet
- Maths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesDocument18 pagesMaths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesamandaNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Functions Their GraphsDocument40 pagesPolynomial Functions Their GraphsMaria MagdalenaNo ratings yet
- 1 MathDocument7 pages1 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For E&BE (Rijksuniversiteit Groningen) Mathematics For E&BE (Rijksuniversiteit Groningen)Document8 pagesMathematics For E&BE (Rijksuniversiteit Groningen) Mathematics For E&BE (Rijksuniversiteit Groningen)Panagiotis ScordisNo ratings yet
- Types of Functions - TypesofFunctionsDocument9 pagesTypes of Functions - TypesofFunctionsZara MalikNo ratings yet
- Types of Functions: 1 PolynomialsDocument9 pagesTypes of Functions: 1 PolynomialsZara MalikNo ratings yet
- Cantey - Calculus Memory BookDocument18 pagesCantey - Calculus Memory BookscottswallowsNo ratings yet
- MHF4U Unit 1Document9 pagesMHF4U Unit 1Daniswara HafidzNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Linear EquationsDocument3 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Linear Equationsplea5ureNo ratings yet
- Formulas Calculo Integral (By Carrascal)Document4 pagesFormulas Calculo Integral (By Carrascal)IñakiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TDocument97 pagesMathematics TPh'ng Jiun YanNo ratings yet
- Vocab ListDocument5 pagesVocab Listapi-336254119No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Final GuideDocument4 pagesTrigonometry Final Guidegracekim111No ratings yet
- 6 2 Evaluating and Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument15 pages6 2 Evaluating and Graphing Polynomial Functionsapi-200092859No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Math OverviewDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Math OverviewmicjenNo ratings yet
- Definitions & Examples: Polynomial FunctionsDocument17 pagesDefinitions & Examples: Polynomial Functionsshiela valdemoroNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TDocument110 pagesMathematics TleeshanghaoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Function? How To Describe A Function Domain and RangeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Function? How To Describe A Function Domain and RangeVikashKumarNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument24 pagesPolynomialssmartyshubh choreographyNo ratings yet
- Topics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014Document5 pagesTopics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014YonYonNo ratings yet
- Different Types of FunctionsDocument68 pagesDifferent Types of FunctionsBohtyar KhanNo ratings yet
- Bab 1Document8 pagesBab 1jak92No ratings yet
- 2.2 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial FunctionsDocument30 pages2.2 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial FunctionsJo-Emmanuel P. PañeNo ratings yet
- g12m FunctionsDocument34 pagesg12m Functionsapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics - OdtDocument20 pagesDiscrete Mathematics - OdtAhmedbacha Abdelkader100% (1)
- Advanced Higher Mechanics Unit 3 Notes COMPLETEDocument5 pagesAdvanced Higher Mechanics Unit 3 Notes COMPLETERyan_Hoyle95No ratings yet
- DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS USING SYNTHETIC DIVISION Class ObservationDocument23 pagesDIVIDING POLYNOMIALS USING SYNTHETIC DIVISION Class ObservationReinabelle Marfil MarquezNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Quadratic Equations: Zero of The Function-A Value Where F (X) 0 and The Graph of The Function Intersects The X-AxisDocument18 pages4.5 Quadratic Equations: Zero of The Function-A Value Where F (X) 0 and The Graph of The Function Intersects The X-AxisAml AmlNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument78 pagesMathematicsJohneil Perea Asi100% (2)
- Mathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraDocument10 pagesMathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraJAY BHAVIN SHETH (B14EE014)No ratings yet
- Week (1) Summary For Calc001x: Pre-University CalculusDocument31 pagesWeek (1) Summary For Calc001x: Pre-University CalculusIbrahim OmarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Algebra: Lesson 9: Partial FractionsDocument7 pagesEngineering Algebra: Lesson 9: Partial FractionsMontes Arianne A.No ratings yet
- SsDocument3 pagesSscristinejoydalag3No ratings yet
- Polynomial FunctionsDocument6 pagesPolynomial FunctionsYUMITEEENo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Relations and FunctionsDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Relations and FunctionsAnthony BalatarNo ratings yet
- A) Graphs of Functions NotesDocument10 pagesA) Graphs of Functions NotesHaoyu WangNo ratings yet
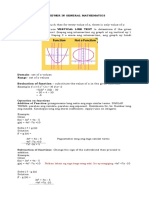
- Reviewer in General MathematicsDocument4 pagesReviewer in General MathematicsKristine Marie LaderaNo ratings yet
- PartfracDocument5 pagesPartfracgoxuNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Full PDFDocument276 pagesDifferential Calculus Full PDFIrah Mae Escaro CustodioNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer MathDocument10 pagesLET Reviewer MathJohn Carlo Telan Panganiban80% (5)
- Rational Function and Its GraphDocument7 pagesRational Function and Its Graphidris raineNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes PDFDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Notes PDFCharles GribbenNo ratings yet
- Dividing Polynomials Using Synthetic DivisionDocument29 pagesDividing Polynomials Using Synthetic DivisionReinabelle Marfil MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document11 pagesLesson 1michael.golendukhinNo ratings yet
- L1 Simplifying ExpressionsDocument5 pagesL1 Simplifying ExpressionsvivianNo ratings yet
- X and Y-InterceptDocument21 pagesX and Y-InterceptjudeNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 pagesICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Apex Institute100% (3)
- June 29Document22 pagesJune 29charlotawalaNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Class 9 Notes PDFDocument6 pagesPolynomials Class 9 Notes PDFFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term Math ReviewerDocument7 pages3rd Term Math ReviewerRaf FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Section 4.1 Exponential Functions An Exponential Function F (X) Is Defined byDocument15 pagesSection 4.1 Exponential Functions An Exponential Function F (X) Is Defined byAANo ratings yet
- Representation of Rational FunctionsDocument33 pagesRepresentation of Rational FunctionsAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Math 11 CORE Gen Math Q1 Week 6Document23 pagesMath 11 CORE Gen Math Q1 Week 6Celine Mary DamianNo ratings yet
- Finally: Partial FractionsDocument10 pagesFinally: Partial FractionsPrabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- 4 Housekeeping PDFDocument12 pages4 Housekeeping PDFRene RaynesNo ratings yet
- Area Ab Perimeter, P 2 (A+b) Diagonal, D A B: Solid Geometry Triangle Squares and RectanglesDocument1 pageArea Ab Perimeter, P 2 (A+b) Diagonal, D A B: Solid Geometry Triangle Squares and RectanglesRene RaynesNo ratings yet
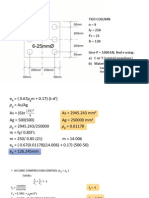
- WSD Column ExampleDocument8 pagesWSD Column ExampleRene RaynesNo ratings yet
- Materials Handling & StorageDocument13 pagesMaterials Handling & StorageRene Raynes100% (1)
- ACES Staff Application FormDocument1 pageACES Staff Application FormRene RaynesNo ratings yet
- Soil - Chapter 1 Summary and ReviewerDocument2 pagesSoil - Chapter 1 Summary and ReviewerRene RaynesNo ratings yet