Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 viewsRegr I Ration
Regr I Ration
Uploaded by
Francisco ServignaThe document summarizes the ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It lists the common assumptions made in analyzing the cycle including constant pressure processes in the evaporator and condenser, saturated vapor at the evaporator outlet and saturated liquid at the condenser outlet. The analysis section defines the thermodynamic processes that occur in the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. Equations are provided for the coefficient of performance and compressor isentropic efficiency. The document concludes with a sample question asking to determine values like refrigerant mass flow rate and compressor power input given conditions for a refrigeration plant operating between specified pressure limits and using a compressor with a known isentropic efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- MEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked RefrigerationDocument25 pagesMEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked Refrigerationsayabudakcomey75% (12)
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument44 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration CycleJohnlloyd Barreto100% (2)
- Lecture 2Document45 pagesLecture 2Dominic Padua Paningbatan100% (1)
- Practice Test CH 4Document4 pagesPractice Test CH 4Umair Nadeem100% (1)
- UC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolDocument4 pagesUC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolgambitNo ratings yet
- MM311 LAB 3 FinalDocument7 pagesMM311 LAB 3 FinaldipanshilNo ratings yet
- L29 - Vapor Compression RefrigerationDocument21 pagesL29 - Vapor Compression RefrigerationSrivatsan SampathNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument3 pagesRefrigerationKartik PardhiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Comp. LinkedDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Comp. LinkedDin TescoNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFDocument6 pagesLS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFdildin01No ratings yet
- 06 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Frigo) 1 PDFDocument44 pages06 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Frigo) 1 PDFAntonio Di FioreNo ratings yet
- PP Chapter 5 Refrigeration Cycle Sem 2 2011-2012Document19 pagesPP Chapter 5 Refrigeration Cycle Sem 2 2011-2012Amuthan ShanmugumNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument10 pagesSampledebojit.dasNo ratings yet
- Termodinamika Ii Semester Genap TA 2007/2008Document20 pagesTermodinamika Ii Semester Genap TA 2007/2008Fikri Sarwo GpsNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument19 pagesME 403 Refrigeration and Air Conditioninghamza awanNo ratings yet
- Ideal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument9 pagesIdeal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump DiagramDocument17 pagesHeat Pump DiagramAhmed SabryNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 11: Refrigeration CyclesDocument37 pagesChapter No. 11: Refrigeration CyclesKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument64 pagesRefrigerationHeat.MotionNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On RefrigerationDocument7 pagesStudy Notes On Refrigerationram kumarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Performance of Vapour Compression System PDFDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Performance of Vapour Compression System PDFakhudaiwalaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFDocument94 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFYash ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesDocument14 pagesChapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Syllabus92 DFSFSFDocument10 pagesRefrigeration Syllabus92 DFSFSFMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document3 pagesExp 2megfwfdkjNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: Chap 11 Section 11.1 - 11.4Document39 pagesRefrigeration: Chap 11 Section 11.1 - 11.4SYED WAIZ SHAHNo ratings yet
- Duyuru2018 Refrigeration CycleDocument4 pagesDuyuru2018 Refrigeration CycleGaurav KeshriNo ratings yet
- Rankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFDocument9 pagesRankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFthienNo ratings yet
- Thermal Sizing of A S&T ExchangerDocument67 pagesThermal Sizing of A S&T Exchangerraja raniNo ratings yet
- Rac 1-5 Week Lecture SlidesDocument215 pagesRac 1-5 Week Lecture Slidesmfnzk1980No ratings yet
- Standard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument11 pagesStandard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CyclejjNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument26 pagesRefrigeration Systemwandee2393No ratings yet
- Experiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument30 pagesExperiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Rey Experiment No. 5 Ref Training UnitDocument13 pagesRey Experiment No. 5 Ref Training UnitrickybobbyNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle PDFDocument41 pagesRankine Cycle PDFAlmeghalawy83% (12)
- 2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TDocument4 pages2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TAman RedhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg Thermodynamics Lab ManualDocument32 pagesChemical Engg Thermodynamics Lab ManualGee DevilleNo ratings yet
- 4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterDocument11 pages4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterRiky IkhwanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants On Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System With Dedicated Mechanical SubcoolinDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants On Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System With Dedicated Mechanical SubcoolinDr. Akhilesh AroraNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump CycleDocument25 pagesHeat Pump CycleDario Rajmanovich100% (1)
- Carnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramDocument6 pagesCarnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramdhruvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - RefrigerationDocument43 pagesChapter 4 - RefrigerationMatthew ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System PDFDocument39 pagesRefrigeration System PDFSiti Hajar Shamsul Kamar86% (7)
- Rankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDocument6 pagesRankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDofrt SlimobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Refrigeration Cycles 11.1 Refrigeration and Heat Pump Coefficient of PerformanceDocument5 pagesChapter 11: Refrigeration Cycles 11.1 Refrigeration and Heat Pump Coefficient of PerformanceHussamNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression CycleDocument18 pagesVapor Compression CycledaanNo ratings yet
- 4 Air Standared Cycles PDFDocument75 pages4 Air Standared Cycles PDFAli ZameerNo ratings yet
- HVAC (Heat - Ventilation - Air-Conditioning) : - Refrigeration - PsychrometricsDocument9 pagesHVAC (Heat - Ventilation - Air-Conditioning) : - Refrigeration - Psychrometricsmarjan 01No ratings yet
- Refrigeration Cycle Diagram Explained - RefrigeraDocument1 pageRefrigeration Cycle Diagram Explained - Refrigerabrbjprx7q5No ratings yet
- IEEE Photonics Journal Paper Template Example SubmissionDocument3 pagesIEEE Photonics Journal Paper Template Example Submissiondebojit.dasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EBMV3103Document13 pagesLab Manual EBMV3103VOON KIN ONNNo ratings yet
- Gas Steam and Combined CyclesDocument84 pagesGas Steam and Combined CyclesJane Smith100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123No ratings yet
- Lab 02 RACDocument6 pagesLab 02 RACSaad mubeenNo ratings yet
- J. Gas CyclesDocument8 pagesJ. Gas CyclesdaphcosiNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration System UnfinishedDocument12 pagesBasic Refrigeration System UnfinishedClinton FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Refrigeration TutorDocument11 pagesExperiment On Refrigeration TutorGgNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Heat Pump and Heat Engine Systems: Theory And PracticeFrom EverandGeothermal Heat Pump and Heat Engine Systems: Theory And PracticeNo ratings yet
- Ocr 33987 PP 09 Jan L Gce 2816 01Document12 pagesOcr 33987 PP 09 Jan L Gce 2816 01Philip_830No ratings yet
- EXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument12 pagesEXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesLowEnd GamerNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics AND Department of Applied ScienceDocument3 pagesDepartment of Physics AND Department of Applied ScienceTKK-TEXTILE PSG CTNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculations For A 5 Story BuildingDocument14 pagesSample Design Calculations For A 5 Story BuildinglonerstarNo ratings yet
- Material Katalis Dan Fotokatalis (MKF) 1Document27 pagesMaterial Katalis Dan Fotokatalis (MKF) 1Hanoum RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- FYBSc Physical & Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesFYBSc Physical & Organic ChemistryManali SawantNo ratings yet
- Study The Methods of Balancing of Multi-Cylinder Engine Like In-Line Engine, Radial Engine, V-EngineDocument28 pagesStudy The Methods of Balancing of Multi-Cylinder Engine Like In-Line Engine, Radial Engine, V-EngineSiddhant BrahmbhattNo ratings yet
- Effect of PbO Percent On Mechanical Prop PDFDocument6 pagesEffect of PbO Percent On Mechanical Prop PDFFocuNo ratings yet
- An Instrumented Tractor For Use in Motion Behaviour Studies On Sloping GroundDocument6 pagesAn Instrumented Tractor For Use in Motion Behaviour Studies On Sloping GroundSergey ZlenkoNo ratings yet
- 2.structure of Matter and Principles of AdhesionDocument4 pages2.structure of Matter and Principles of Adhesioncdfg ghjy100% (1)
- A Poor Man's Derivation of Scaling Laws For The Kondo ProblemDocument7 pagesA Poor Man's Derivation of Scaling Laws For The Kondo ProblemTianhaoRenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionDocument8 pagesLecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionKowser mahmudNo ratings yet
- Api 1104 1999-9Document1 pageApi 1104 1999-9Rohit KambleNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Diffusion of Hydrogen in Pure Metals and AlloysDocument10 pagesSolubility and Diffusion of Hydrogen in Pure Metals and AlloysBalló NorbertNo ratings yet
- CHAMANI e RAJARATNAM 1994Document6 pagesCHAMANI e RAJARATNAM 1994Valter AlbinoNo ratings yet
- PT DetailingDocument52 pagesPT Detailingcuongnguyen100% (4)
- 3 Echoes in The Quantum SymphonyDocument2 pages3 Echoes in The Quantum SymphonyMarsuki HardjoNo ratings yet
- Quantum ExamplesDocument26 pagesQuantum ExamplesAbdalmoedAlaiashyNo ratings yet
- Asphalt EnesDocument5 pagesAsphalt EnesvermavermapoojaNo ratings yet
- Topografi + GeodeticDocument11 pagesTopografi + GeodeticShinta Aritonang100% (1)
- MMJ1153-B - Review of 1D Problems - Part1Document43 pagesMMJ1153-B - Review of 1D Problems - Part1'Rafiq De Mil SellosNo ratings yet
- PalmgrenDocument12 pagesPalmgrenGomathi SankarNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 Q4 MELC 5 Week-3bDocument8 pagesGenChem2 Q4 MELC 5 Week-3bBSED FIL 1- Ashley Romarie A. LactaotaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Vibration and WaveDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Vibration and WavePrakash DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ExerciseDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Exerciseحسن كميت hassankomeit lNo ratings yet
- MicromeriticsDocument109 pagesMicromeriticsSan GalNo ratings yet
- Nikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)Document2 pagesNikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)yasir127No ratings yet
- Geophysics ProjectDocument9 pagesGeophysics ProjectYoobsan Asaffaa FufaaNo ratings yet
Regr I Ration
Regr I Ration
Uploaded by
Francisco Servigna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It lists the common assumptions made in analyzing the cycle including constant pressure processes in the evaporator and condenser, saturated vapor at the evaporator outlet and saturated liquid at the condenser outlet. The analysis section defines the thermodynamic processes that occur in the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. Equations are provided for the coefficient of performance and compressor isentropic efficiency. The document concludes with a sample question asking to determine values like refrigerant mass flow rate and compressor power input given conditions for a refrigeration plant operating between specified pressure limits and using a compressor with a known isentropic efficiency.
Original Description:
great
Original Title
Regr i Ration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It lists the common assumptions made in analyzing the cycle including constant pressure processes in the evaporator and condenser, saturated vapor at the evaporator outlet and saturated liquid at the condenser outlet. The analysis section defines the thermodynamic processes that occur in the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. Equations are provided for the coefficient of performance and compressor isentropic efficiency. The document concludes with a sample question asking to determine values like refrigerant mass flow rate and compressor power input given conditions for a refrigeration plant operating between specified pressure limits and using a compressor with a known isentropic efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views2 pagesRegr I Ration
Regr I Ration
Uploaded by
Francisco ServignaThe document summarizes the ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It lists the common assumptions made in analyzing the cycle including constant pressure processes in the evaporator and condenser, saturated vapor at the evaporator outlet and saturated liquid at the condenser outlet. The analysis section defines the thermodynamic processes that occur in the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. Equations are provided for the coefficient of performance and compressor isentropic efficiency. The document concludes with a sample question asking to determine values like refrigerant mass flow rate and compressor power input given conditions for a refrigeration plant operating between specified pressure limits and using a compressor with a known isentropic efficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Week 6
V-P Refrigeration Cycle
ME 354 Tutorial
Summary
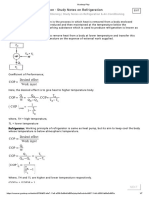
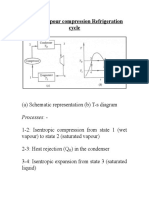
The ideal Refrigeration cycle schematic and T-s diagram:
Common Assumptions:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
Evaporator and Condenser are constant pressure devices (P4=P1 & P3=P2)
Saturated vapour at the evaporator outlet (state 1)
Saturated liquid at the condenser outlet (state 3)
Steady operating conditions
ke, pe = 0
Adiabatic process in expansion valve (h3=h4)
For Ideal Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle: Isentropic compression
(s2=s1)
Analysis:
Compressor win = h2 h1
Condenser q Ht = h2 h3
Expansion Valve h3 = h4
Evaporator qL = h1 h4
Coefficient of Performance (COPR ):
COPR =
Benefit q L h1 h4
=
=
Cost
win h2 h1
Compressor Isentropic Efficiency:
c =
ws h2 s h1
=
wa h2 a h1
Page 1 of 2
Week 6
V-P Refrigeration Cycle
ME 354 Tutorial
Question
A large refrigeration plant is to be maintained at -15oC, and it requires refrigeration at a
rate of 100 kW. The condenser of the plant is to be cooled by liquid water, which
experiences a temperature rise of 8oC as it flows over the coils of the condenser. The
plant uses refrigerant-134a between the pressure limits of 120 kPa and 700 kPa.
Assuming the compressor has an isentropic efficiency of 75%, determine:
a) The mass flow rate of the refrigerant
b) The power input to the compressor
c) The mass flow rate of the cooling water
d) The rate of exergy destruction associated with the compression process (assume
T0=25oC)
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- MEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked RefrigerationDocument25 pagesMEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked Refrigerationsayabudakcomey75% (12)
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument44 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration CycleJohnlloyd Barreto100% (2)
- Lecture 2Document45 pagesLecture 2Dominic Padua Paningbatan100% (1)
- Practice Test CH 4Document4 pagesPractice Test CH 4Umair Nadeem100% (1)
- UC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolDocument4 pagesUC Davis ENG 103 Midterm 2010 SolgambitNo ratings yet
- MM311 LAB 3 FinalDocument7 pagesMM311 LAB 3 FinaldipanshilNo ratings yet
- L29 - Vapor Compression RefrigerationDocument21 pagesL29 - Vapor Compression RefrigerationSrivatsan SampathNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument3 pagesRefrigerationKartik PardhiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Comp. LinkedDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Comp. LinkedDin TescoNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFDocument6 pagesLS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFdildin01No ratings yet
- 06 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Frigo) 1 PDFDocument44 pages06 - Thermodynamic - Cycles - (Frigo) 1 PDFAntonio Di FioreNo ratings yet
- PP Chapter 5 Refrigeration Cycle Sem 2 2011-2012Document19 pagesPP Chapter 5 Refrigeration Cycle Sem 2 2011-2012Amuthan ShanmugumNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument10 pagesSampledebojit.dasNo ratings yet
- Termodinamika Ii Semester Genap TA 2007/2008Document20 pagesTermodinamika Ii Semester Genap TA 2007/2008Fikri Sarwo GpsNo ratings yet
- ME 403 Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument19 pagesME 403 Refrigeration and Air Conditioninghamza awanNo ratings yet
- Ideal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument9 pagesIdeal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump DiagramDocument17 pagesHeat Pump DiagramAhmed SabryNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 11: Refrigeration CyclesDocument37 pagesChapter No. 11: Refrigeration CyclesKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument64 pagesRefrigerationHeat.MotionNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On RefrigerationDocument7 pagesStudy Notes On Refrigerationram kumarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Performance of Vapour Compression System PDFDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Performance of Vapour Compression System PDFakhudaiwalaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFDocument94 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFYash ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesDocument14 pagesChapter 10: Refrigeration CyclesGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Syllabus92 DFSFSFDocument10 pagesRefrigeration Syllabus92 DFSFSFMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document3 pagesExp 2megfwfdkjNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: Chap 11 Section 11.1 - 11.4Document39 pagesRefrigeration: Chap 11 Section 11.1 - 11.4SYED WAIZ SHAHNo ratings yet
- Duyuru2018 Refrigeration CycleDocument4 pagesDuyuru2018 Refrigeration CycleGaurav KeshriNo ratings yet
- Rankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFDocument9 pagesRankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFthienNo ratings yet
- Thermal Sizing of A S&T ExchangerDocument67 pagesThermal Sizing of A S&T Exchangerraja raniNo ratings yet
- Rac 1-5 Week Lecture SlidesDocument215 pagesRac 1-5 Week Lecture Slidesmfnzk1980No ratings yet
- Standard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument11 pagesStandard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CyclejjNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument26 pagesRefrigeration Systemwandee2393No ratings yet
- Experiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument30 pagesExperiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Rey Experiment No. 5 Ref Training UnitDocument13 pagesRey Experiment No. 5 Ref Training UnitrickybobbyNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle PDFDocument41 pagesRankine Cycle PDFAlmeghalawy83% (12)
- 2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TDocument4 pages2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TAman RedhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg Thermodynamics Lab ManualDocument32 pagesChemical Engg Thermodynamics Lab ManualGee DevilleNo ratings yet
- 4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterDocument11 pages4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterRiky IkhwanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants On Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System With Dedicated Mechanical SubcoolinDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants On Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System With Dedicated Mechanical SubcoolinDr. Akhilesh AroraNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump CycleDocument25 pagesHeat Pump CycleDario Rajmanovich100% (1)
- Carnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramDocument6 pagesCarnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramdhruvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - RefrigerationDocument43 pagesChapter 4 - RefrigerationMatthew ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System PDFDocument39 pagesRefrigeration System PDFSiti Hajar Shamsul Kamar86% (7)
- Rankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDocument6 pagesRankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDofrt SlimobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Refrigeration Cycles 11.1 Refrigeration and Heat Pump Coefficient of PerformanceDocument5 pagesChapter 11: Refrigeration Cycles 11.1 Refrigeration and Heat Pump Coefficient of PerformanceHussamNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression CycleDocument18 pagesVapor Compression CycledaanNo ratings yet
- 4 Air Standared Cycles PDFDocument75 pages4 Air Standared Cycles PDFAli ZameerNo ratings yet
- HVAC (Heat - Ventilation - Air-Conditioning) : - Refrigeration - PsychrometricsDocument9 pagesHVAC (Heat - Ventilation - Air-Conditioning) : - Refrigeration - Psychrometricsmarjan 01No ratings yet
- Refrigeration Cycle Diagram Explained - RefrigeraDocument1 pageRefrigeration Cycle Diagram Explained - Refrigerabrbjprx7q5No ratings yet
- IEEE Photonics Journal Paper Template Example SubmissionDocument3 pagesIEEE Photonics Journal Paper Template Example Submissiondebojit.dasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EBMV3103Document13 pagesLab Manual EBMV3103VOON KIN ONNNo ratings yet
- Gas Steam and Combined CyclesDocument84 pagesGas Steam and Combined CyclesJane Smith100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123No ratings yet
- Lab 02 RACDocument6 pagesLab 02 RACSaad mubeenNo ratings yet
- J. Gas CyclesDocument8 pagesJ. Gas CyclesdaphcosiNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration System UnfinishedDocument12 pagesBasic Refrigeration System UnfinishedClinton FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Refrigeration TutorDocument11 pagesExperiment On Refrigeration TutorGgNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Heat Pump and Heat Engine Systems: Theory And PracticeFrom EverandGeothermal Heat Pump and Heat Engine Systems: Theory And PracticeNo ratings yet
- Ocr 33987 PP 09 Jan L Gce 2816 01Document12 pagesOcr 33987 PP 09 Jan L Gce 2816 01Philip_830No ratings yet
- EXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument12 pagesEXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesLowEnd GamerNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics AND Department of Applied ScienceDocument3 pagesDepartment of Physics AND Department of Applied ScienceTKK-TEXTILE PSG CTNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculations For A 5 Story BuildingDocument14 pagesSample Design Calculations For A 5 Story BuildinglonerstarNo ratings yet
- Material Katalis Dan Fotokatalis (MKF) 1Document27 pagesMaterial Katalis Dan Fotokatalis (MKF) 1Hanoum RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- FYBSc Physical & Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesFYBSc Physical & Organic ChemistryManali SawantNo ratings yet
- Study The Methods of Balancing of Multi-Cylinder Engine Like In-Line Engine, Radial Engine, V-EngineDocument28 pagesStudy The Methods of Balancing of Multi-Cylinder Engine Like In-Line Engine, Radial Engine, V-EngineSiddhant BrahmbhattNo ratings yet
- Effect of PbO Percent On Mechanical Prop PDFDocument6 pagesEffect of PbO Percent On Mechanical Prop PDFFocuNo ratings yet
- An Instrumented Tractor For Use in Motion Behaviour Studies On Sloping GroundDocument6 pagesAn Instrumented Tractor For Use in Motion Behaviour Studies On Sloping GroundSergey ZlenkoNo ratings yet
- 2.structure of Matter and Principles of AdhesionDocument4 pages2.structure of Matter and Principles of Adhesioncdfg ghjy100% (1)
- A Poor Man's Derivation of Scaling Laws For The Kondo ProblemDocument7 pagesA Poor Man's Derivation of Scaling Laws For The Kondo ProblemTianhaoRenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionDocument8 pagesLecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionKowser mahmudNo ratings yet
- Api 1104 1999-9Document1 pageApi 1104 1999-9Rohit KambleNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Diffusion of Hydrogen in Pure Metals and AlloysDocument10 pagesSolubility and Diffusion of Hydrogen in Pure Metals and AlloysBalló NorbertNo ratings yet
- CHAMANI e RAJARATNAM 1994Document6 pagesCHAMANI e RAJARATNAM 1994Valter AlbinoNo ratings yet
- PT DetailingDocument52 pagesPT Detailingcuongnguyen100% (4)
- 3 Echoes in The Quantum SymphonyDocument2 pages3 Echoes in The Quantum SymphonyMarsuki HardjoNo ratings yet
- Quantum ExamplesDocument26 pagesQuantum ExamplesAbdalmoedAlaiashyNo ratings yet
- Asphalt EnesDocument5 pagesAsphalt EnesvermavermapoojaNo ratings yet
- Topografi + GeodeticDocument11 pagesTopografi + GeodeticShinta Aritonang100% (1)
- MMJ1153-B - Review of 1D Problems - Part1Document43 pagesMMJ1153-B - Review of 1D Problems - Part1'Rafiq De Mil SellosNo ratings yet
- PalmgrenDocument12 pagesPalmgrenGomathi SankarNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 Q4 MELC 5 Week-3bDocument8 pagesGenChem2 Q4 MELC 5 Week-3bBSED FIL 1- Ashley Romarie A. LactaotaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Vibration and WaveDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Vibration and WavePrakash DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ExerciseDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Exerciseحسن كميت hassankomeit lNo ratings yet
- MicromeriticsDocument109 pagesMicromeriticsSan GalNo ratings yet
- Nikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)Document2 pagesNikrothal LX: (Resistance Heating Wire and Resistance Wire)yasir127No ratings yet
- Geophysics ProjectDocument9 pagesGeophysics ProjectYoobsan Asaffaa FufaaNo ratings yet