Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2: GSM and GPRS: Part 1: GSM Network Coverage Planning and Traffic Dimensioning
Tutorial 2: GSM and GPRS: Part 1: GSM Network Coverage Planning and Traffic Dimensioning
Uploaded by
syedazamshahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2: GSM and GPRS: Part 1: GSM Network Coverage Planning and Traffic Dimensioning
Tutorial 2: GSM and GPRS: Part 1: GSM Network Coverage Planning and Traffic Dimensioning
Uploaded by
syedazamshahCopyright:
Available Formats
Wireless Network Technologies
Tutorial 2: GSM and GPRS
Part 1: GSM Network Coverage Planning and Traffic Dimensioning
1. A telecom company aims to set up a GSM network in a small city and ask
you to carry out the network planning and dimensioning process.
All parameters related to the system are summarised below:
-
Total coverage area: 10,000 km2
Average active subscribers during busy hour: 4 users/km2 (assume
uniformly distributed)
Average call duration 110s during busy hour
Maximum Tx Power: 20W
Receiver sensitivity: -103 dBm
Pathloss (L) is given by:
L = 119+ 31.8 log(dkm)
Fading margin: 5dB
Others loss : 5 dB
Transmit antenna gain: 15dBi
Thermal noise: -108dBm
Minimum GoS guarantee during busy hour: 0.02
Control channels per cell: 2 timeslots
4.1 Compute the number of GSM cells to cover the city.
4.2 Compute the number of TRXs required in each cell.
Wireless Network Technologies
Part 2: GPRS Network Dimensioning
The telecom company has decided to extend GSM network to support GPRS
whose users requirements are given in Table below.
Packet Switched Traffic during GPRS Peak Hour
(Assume 85% channel occupancy for GPRS channels)
Mean data
rate (kbps)
Average
session/ hour
Online radio
32
0.1
Average
duration per
session (s)
300
Video
128
0.1
320
4096
Web browsing
64
0.2
450
5760
Total
Amount of
Data/h
(kbits)
960
10.8Mbits
20% of GSM users subscribe GPRS services. During the GPRS peak hour, 25%
of GPRS users and 50% of GSM users are active, respectively.
2.1 Determine if the existing network configuration (i.e. number of TRXs per
cell) is sufficient to support additional GPRS requirements as shown in Table
above.
2.2 Determine the maximum packet switched traffic in kbps that the existing
network configuration can support during GSM busy hour.
2.3 The GSM busy hour and GPRS peak hour in a cell in this GSM/GPRS
network occur at the same time. Prove if this requirement is achievable based
on the existing configuration. Provide suggestions for network upgrade if
applicable.
d) Determine the number of timeslots that are available for GPRS traffic
using information in table below.
Wireless Network Technologies
Appendix:
Erlang Table and Worked Examples
Erlang B Table
Wireless Network Technologies
#Channels
(TRX,
timeslots)
Erlang formula needs two of
these parameters as the inputs
Erlang
(Erl.)
xErlangs =
(calls per hour )(averageconversationtime)
3600 Seconds
Blocking
probability
(%)
Wireless Network Technologies
You might also like
- 4G LteDocument226 pages4G LteGagan100% (3)
- Irat HoDocument33 pagesIrat HoserafettinbNo ratings yet
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Anointing For Greatness TEXT: Ps 89:20-23 Acts 13:21-22Document1 pageAnointing For Greatness TEXT: Ps 89:20-23 Acts 13:21-22Wale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Build Up Your Chess 1 Exceprt PDFDocument13 pagesBuild Up Your Chess 1 Exceprt PDFguestuser19930% (1)
- Chess Tactics Scratch ExcerptDocument14 pagesChess Tactics Scratch ExcerptWale Ogunniran80% (5)
- First Fruits Bible Study: The Basic Concept: A Backyard AnalogyDocument4 pagesFirst Fruits Bible Study: The Basic Concept: A Backyard AnalogyWale Ogunniran100% (1)
- Eastar SpecificationsDocument2 pagesEastar SpecificationsUmar ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- 3G TechnologyDocument13 pages3G TechnologyRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewDocument72 pagesEnhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewPrashant SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Huawei 3G Introduction PDFDocument64 pagesHuawei 3G Introduction PDFZola BenNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning, Configuration and Deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture 2.1: Voice in GSMDocument7 pagesDimensioning, Configuration and Deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture 2.1: Voice in GSMSaow AphakNo ratings yet
- 3G Network SynchronisationDocument4 pages3G Network SynchronisationVikas KhantwalNo ratings yet
- What Is 3GDocument15 pagesWhat Is 3GShampad AyanNo ratings yet
- Technical Fundamentals of UMTSDocument100 pagesTechnical Fundamentals of UMTSgohiljsNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Link Budget 384 DataDocument27 pagesWCDMA Link Budget 384 DataAnjit RajkarnikarNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Advantages and A Comparison To TD-CDMADocument17 pagesWCDMA Advantages and A Comparison To TD-CDMAyurdumNo ratings yet
- GSM System EssentialsDocument45 pagesGSM System EssentialsDavidDavidNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is ADocument8 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is AAjay AryaNo ratings yet
- Basic CDMA Spectrum PlanningDocument18 pagesBasic CDMA Spectrum PlanningkadsandeepNo ratings yet
- BROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Document31 pagesBROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Apeksha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument8 pagesInterview QuestionVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit V Ststem Examples & Design IssuesDocument104 pagesUnit V Ststem Examples & Design IssuesK Sasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- The Next Generation Challenge For Software Defined RadioDocument12 pagesThe Next Generation Challenge For Software Defined Radiomdzakir_hussainNo ratings yet
- Module3 WCCDocument49 pagesModule3 WCCamruthajs05No ratings yet
- Interview Question On GSM Cdma WcdmaDocument17 pagesInterview Question On GSM Cdma WcdmaAnimesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- HSPA For Improved Data TransferDocument21 pagesHSPA For Improved Data TransferAmine InpticNo ratings yet
- Evolution From 3G To 4GDocument44 pagesEvolution From 3G To 4GKhalid ParkarNo ratings yet
- WCDMADocument2 pagesWCDMAshayan_2005No ratings yet
- GPRS&EDGE Network Planning and Optimization-Chapter 5 Network Planning-20040527-A-1.0Document48 pagesGPRS&EDGE Network Planning and Optimization-Chapter 5 Network Planning-20040527-A-1.0AmrAhmedAbdelFattahNo ratings yet
- Interference WCDMA and PCS 1900Document4 pagesInterference WCDMA and PCS 1900ali963852No ratings yet
- EA-452 Chap9Document135 pagesEA-452 Chap9ganeshuitNo ratings yet
- WCC Module-3 Notes PDFDocument57 pagesWCC Module-3 Notes PDFBRUNDA R VNo ratings yet
- Network Planning LteDocument16 pagesNetwork Planning LteRadhey S Sarda0% (1)
- Simple Capacity Estimations in Wimax/802.16 System: Loutfi Nuaymi, Ziad NounDocument5 pagesSimple Capacity Estimations in Wimax/802.16 System: Loutfi Nuaymi, Ziad NounMuharry HabibNo ratings yet
- Wireless Module3Document71 pagesWireless Module3kesebas6exNo ratings yet
- Assignement1 (Mobile&Satellite)Document22 pagesAssignement1 (Mobile&Satellite)Nur Faiqah100% (1)
- Evolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En TanDocument19 pagesEvolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En Tanszi1979No ratings yet
- Welcome To The 3rd GenerationDocument26 pagesWelcome To The 3rd GenerationRock DolphinNo ratings yet
- Wimax - Presentation - Case StudyDocument22 pagesWimax - Presentation - Case StudyOcira OyaroNo ratings yet
- Practical Tips On Cdma2000 1xEV-DO Forward-Link Movement: Cell MasterDocument12 pagesPractical Tips On Cdma2000 1xEV-DO Forward-Link Movement: Cell MasterMiguel Hugo PintosNo ratings yet
- Wireless AssignmentDocument38 pagesWireless AssignmentWendimu NigusieNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Radio PlanningDocument20 pagesWCDMA Radio PlanningAhmed MoniemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Modern Wireless Communication SystemsDocument58 pagesOverview of Modern Wireless Communication SystemsMani SandhuNo ratings yet
- A Mobile & Cellular Communication Assignment On: Opic No: 46Document16 pagesA Mobile & Cellular Communication Assignment On: Opic No: 46Gulshan PrakashNo ratings yet
- Soft Handover in UmtsDocument15 pagesSoft Handover in UmtsSaranyaNo ratings yet
- Justin Champion Room C208 - Tel: 3273: WWW - Staffs.ac - Uk/personal/engineering - and - Technology/jjc1Document33 pagesJustin Champion Room C208 - Tel: 3273: WWW - Staffs.ac - Uk/personal/engineering - and - Technology/jjc1bryanferrer07151986No ratings yet
- Edge EvolutionDocument4 pagesEdge EvolutionTsietsi Jeffrey LeokaokeNo ratings yet
- 02 Tm2110eu01tm 0004 GprsDocument62 pages02 Tm2110eu01tm 0004 GprsSajid SaleemNo ratings yet
- Ac RE56 41 GSM Data SecondDocument7 pagesAc RE56 41 GSM Data SecondCedrik PendjiNo ratings yet
- 3g CdmsDocument6 pages3g CdmshtrungNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The GSM SystemDocument32 pagesAn Overview of The GSM System0796105632No ratings yet
- Application Note: The Synchronization of 3G UMTS NetworksDocument0 pagesApplication Note: The Synchronization of 3G UMTS NetworksShejin RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Very Important - CDMADocument11 pagesWhitepaper Very Important - CDMAAbdur Razzaq sirajNo ratings yet
- White Paper: CDMA Network Technologies: A Decade of Advances and ChallengesDocument11 pagesWhite Paper: CDMA Network Technologies: A Decade of Advances and ChallengesGuruh EnbeNo ratings yet
- NOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Document10 pagesNOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Ramesh MattaparthiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GFrom EverandFundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GNo ratings yet
- Faculty Sets/Reset QuestionsDocument2 pagesFaculty Sets/Reset QuestionsWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Ranks 11Th With High Rate of TuberculosisDocument1 pageNigeria Ranks 11Th With High Rate of TuberculosisWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Substance AbuseDocument2 pagesSubstance AbuseWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Answers To QuestionsDocument20 pagesAnswers To Questionselmerc_207575No ratings yet
- Title: Eye Defect Date: 24/02/2015 Three Out of Five People Are Diagnosed of Eye Defects Daily-Eye ExpertDocument2 pagesTitle: Eye Defect Date: 24/02/2015 Three Out of Five People Are Diagnosed of Eye Defects Daily-Eye ExpertWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- CQI Basics PDFDocument8 pagesCQI Basics PDFWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Catalog PDFDocument31 pagesCatalog PDFWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Love Confession PDFDocument3 pagesLove Confession PDFWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Huawei AgissonDocument50 pagesHuawei Agissonluongtran50% (2)
- Huawei AgissonDocument50 pagesHuawei Agissonluongtran50% (2)
- Dual Band Networks: Parameters and OptimizationDocument93 pagesDual Band Networks: Parameters and OptimizationlephamtuananhNo ratings yet
- Dual Band Networks: Parameters and OptimizationDocument93 pagesDual Band Networks: Parameters and OptimizationlephamtuananhNo ratings yet
- KPIsDocument15 pagesKPIsbiswaksennayakNo ratings yet
- TPP Steel PlantDocument25 pagesTPP Steel PlantPRASANTHNo ratings yet
- Geostr C: Engineering and Testing ServicesDocument2 pagesGeostr C: Engineering and Testing ServicesTechnical Priyanka GroupNo ratings yet
- 1001076002-HT8911 Datasheet - V1.1Document13 pages1001076002-HT8911 Datasheet - V1.1Zhang EthanNo ratings yet
- Total DataDocument984 pagesTotal DataajayNo ratings yet
- Jetblue Airways: A New BeginningDocument25 pagesJetblue Airways: A New BeginningHesty Tri BudihartiNo ratings yet
- Newsela - A New Boredom Study Is Anything But BoringDocument3 pagesNewsela - A New Boredom Study Is Anything But Boringafolden91683No ratings yet
- Appositives and AdjectiveDocument2 pagesAppositives and AdjectiveRinda RiztyaNo ratings yet
- CE441 Class Lecture 01Document9 pagesCE441 Class Lecture 01ASHJAEE MANSIB CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Item Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostDocument1 pageItem Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostRockyNo ratings yet
- Frampton AntithesispedagogyDocument2 pagesFrampton AntithesispedagogyJohann WieseNo ratings yet
- Module 5 in Eed 114: ReviewDocument6 pagesModule 5 in Eed 114: ReviewYvi BenrayNo ratings yet
- Revised Copy of Wartsila 18V220SG ProjectDocument3 pagesRevised Copy of Wartsila 18V220SG ProjectZohaib AlamNo ratings yet
- Application of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONDocument19 pagesApplication of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Shree Vijaya Engineering and Construction PVT LTD: Ehs Risk AnalysisDocument8 pagesShree Vijaya Engineering and Construction PVT LTD: Ehs Risk AnalysisReda MashalNo ratings yet
- Chebyshev Filter: Linear Analog Electronic FiltersDocument10 pagesChebyshev Filter: Linear Analog Electronic FiltersSri Jai PriyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Activity On Expenditure Cycles - To Be ContinuedDocument3 pagesAssignment Activity On Expenditure Cycles - To Be ContinuedRico, Jalaica B.No ratings yet
- SCIETECHNODocument19 pagesSCIETECHNOChini ChanNo ratings yet
- Problem PipingDocument79 pagesProblem PipingSiddhi MhatreNo ratings yet
- Ril Sa71m15017693 R00Document5 pagesRil Sa71m15017693 R00Android100% (1)
- TRA2 - User ManualDocument40 pagesTRA2 - User ManualvaultedroomNo ratings yet
- Commercial Negotiations NotesDocument14 pagesCommercial Negotiations NotesJoan Foster100% (1)
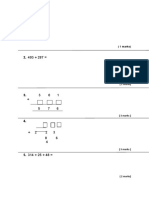
- Solve The Problems: (1 Marks)Document7 pagesSolve The Problems: (1 Marks)Govin RocketzNo ratings yet
- Anggaran ElektronikaDocument12 pagesAnggaran ElektronikaSeptian IswanjayaNo ratings yet
- ChitraDocument8 pagesChitraJames SonNo ratings yet
- GeoGauge - Verifier Mass GuideDocument4 pagesGeoGauge - Verifier Mass GuideOmar CarlosNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorDocument2 pagesReasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorRobert AyalaNo ratings yet
- Performance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanDocument10 pagesPerformance: Task in Math 8 House Floor PlanJoshua Emmanuel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Ag Test Package FormatDocument25 pagesAg Test Package FormatoparoystNo ratings yet
- Sensor Nivel Murphy LS200Document3 pagesSensor Nivel Murphy LS200Sergio PluchinskyNo ratings yet