Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gas Chromatography Thermal Energy Ionize Analyte Method Nitrogen Phosphorus Sensitivity Carbon Hydrogen Rubidium Cesium Nozzle Cold Plasma Excitation Anode Cathode Work Function
Gas Chromatography Thermal Energy Ionize Analyte Method Nitrogen Phosphorus Sensitivity Carbon Hydrogen Rubidium Cesium Nozzle Cold Plasma Excitation Anode Cathode Work Function
Uploaded by
supriatnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Chromatography Thermal Energy Ionize Analyte Method Nitrogen Phosphorus Sensitivity Carbon Hydrogen Rubidium Cesium Nozzle Cold Plasma Excitation Anode Cathode Work Function
Gas Chromatography Thermal Energy Ionize Analyte Method Nitrogen Phosphorus Sensitivity Carbon Hydrogen Rubidium Cesium Nozzle Cold Plasma Excitation Anode Cathode Work Function
Uploaded by
supriatnaCopyright:
Available Formats
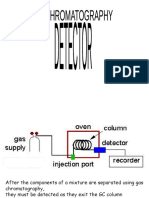
The nitrogenphosphorus detector (NPD) or thermionic specific detector (TSD) is a type of
detector commonly used with gas chromatography, in which thermal energy is used
toionize an analyte. It is a type of flame thermionic detector (FTD), the other being the alkali flameionization detector (AFID). With this method, nitrogen and phosphorus can be selectively detected
with a sensitivity that is 104 times greater than that for carbon. NP-Mode: A concentration
of hydrogen gas is used such that it is just below the minimum required for ignition.
A rubidium or cesium bead, which is mounted over the nozzle, ignites the hydrogen (by acting
catalytically), and forms a cold plasma. Excitation of the alkali metal results in ejection of electrons,
which in turn are detected as a current flow between an anode and cathode in the chamber. As
nitrogen or phosphorus analytes exit the column, they cause a reduction in the work function of the
metal bead, resulting in an increase in current. Since the alkali metal bead is consumed over time, it
must be replaced regularly .
http://www.thairohs.org/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_view&gid=52
You might also like
- Nitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryDocument3 pagesNitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryVarun Kumar100% (1)
- Quantitative Chemical Analysis Quantitative Chemical Analysis Failure Analysis Quantitative Chemical Analysis Material AnalysisDocument3 pagesQuantitative Chemical Analysis Quantitative Chemical Analysis Failure Analysis Quantitative Chemical Analysis Material AnalysisAnonymous rYZyQQot55No ratings yet
- Flame Ionization Detectors Unit 5Document5 pagesFlame Ionization Detectors Unit 5Abhishek SainiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical FieldDocument9 pagesQuantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Fieldcyper zoonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1Document9 pagesQuantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1cyper zoonNo ratings yet
- The Flame Emision Photometry RiswandiDocument4 pagesThe Flame Emision Photometry RiswandiAdi Surya AbdiNo ratings yet
- Referencia 74Document5 pagesReferencia 74XDEWSZAQNo ratings yet
- One Step Synthesis of Sodium TrimetaphosphateDocument5 pagesOne Step Synthesis of Sodium TrimetaphosphateNuttapong JongjitsatitmunNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen General TheoryDocument5 pagesDissolved Oxygen General TheoryJAY PARIKHNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrDocument29 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrNana BiotayudaNo ratings yet
- IR DetectorsDocument5 pagesIR DetectorsAnime GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Color-Control of Long-Lasting Phosphorescence (LLP) Through Rare Earth Ion-Doped Cadmium Metasilicate PhosphorsDocument7 pagesColor-Control of Long-Lasting Phosphorescence (LLP) Through Rare Earth Ion-Doped Cadmium Metasilicate PhosphorsIlse Guadalupe EncinasNo ratings yet
- Atomic AbsorptionDocument27 pagesAtomic Absorptionindustrial technoNo ratings yet
- Atomic AbsorptionDocument27 pagesAtomic Absorptionindustrial technoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) - AimanDocument27 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) - AimanNitiyanandanathan KamalanathanNo ratings yet
- Recoverd PDFDocument24 pagesRecoverd PDFkartikeyanreddyNo ratings yet
- Of The Reduction Behavior of W/Ti02 Catalysts XPS Using Curve Fitting, Deconvolution and Factor AnalysisDocument9 pagesOf The Reduction Behavior of W/Ti02 Catalysts XPS Using Curve Fitting, Deconvolution and Factor AnalysisinanoguruNo ratings yet
- Listicle GCDetectorsDocument6 pagesListicle GCDetectorsRoberto RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Phosphorus DetectorDocument5 pagesNitrogen Phosphorus DetectorVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Answer To The Question No. 1 (A)Document5 pagesAnswer To The Question No. 1 (A)Mohona JesicaNo ratings yet
- For The Determination of Precious Metals in Autocatalyst SamplesDocument6 pagesFor The Determination of Precious Metals in Autocatalyst SamplesScumpika ElenaNo ratings yet
- G C DetectorsDocument7 pagesG C DetectorsrajimarriNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD) : Not As Sensitive Non-Specific Non-DestructiveDocument11 pagesThermal Conductivity Detector (TCD) : Not As Sensitive Non-Specific Non-DestructiveKajal Dhawde100% (1)
- CP Na5p3o10Document6 pagesCP Na5p3o10agnarindra01_8550147No ratings yet
- Lectura Taller de Semana 6Document2 pagesLectura Taller de Semana 6Paulo RojasNo ratings yet
- Prezentacja CHEMIADocument5 pagesPrezentacja CHEMIAMabbumNo ratings yet
- Icp AppendixDocument55 pagesIcp AppendixKarthikeyan JagannathanNo ratings yet
- AAS FlamelessDocument42 pagesAAS FlamelessThomas IndraNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography DetectorsDocument24 pagesGas Chromatography Detectorsmarx aloisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Theory Project: Submitted byDocument42 pagesChemistry Theory Project: Submitted byVaibhav GulatiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Presented By: Amita Rai M. Pharm 1 Yr Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocument23 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Presented By: Amita Rai M. Pharm 1 Yr Pharmaceutical AnalysisAln AlbinNo ratings yet
- Ed.5.PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS PDFDocument28 pagesEd.5.PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS PDFShubham Sabale PatilNo ratings yet
- GC DetectorDocument34 pagesGC Detectorhanif fNo ratings yet
- Heated Quartz Cell Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Coupled With in Situ Butylation/Vaporization For The Determination of Iron and TinDocument3 pagesHeated Quartz Cell Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Coupled With in Situ Butylation/Vaporization For The Determination of Iron and Tincukuran jenggotNo ratings yet
- ENVE 450 - Lecture 5 - AAS PDFDocument6 pagesENVE 450 - Lecture 5 - AAS PDFclaudiutp100% (1)
- Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Supported Copper Oxide CatalystDocument16 pagesYttria-Stabilized Zirconia Supported Copper Oxide CatalystAndres FragosoNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography (GC) : Principle Partition of Molecules Between Gas (Mobile Phase) and Liquid (Stationary Phase)Document42 pagesGas Chromatography (GC) : Principle Partition of Molecules Between Gas (Mobile Phase) and Liquid (Stationary Phase)Pishta BmcNo ratings yet
- VSI Week9 Lecture9 InstAnal 4th Stage Theory 2022Document34 pagesVSI Week9 Lecture9 InstAnal 4th Stage Theory 2022Sozdar ArgoshiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Speectroscopy..Document3 pagesAtomic Absorption Speectroscopy..Deni Muhamad IkbalNo ratings yet
- SOLID STATE COLD FUSION AND CATALYTIC ENERGY SCIENCE, With Russ GeorgeDocument57 pagesSOLID STATE COLD FUSION AND CATALYTIC ENERGY SCIENCE, With Russ GeorgeTedd St Rain100% (1)
- Sylvania Engineering Bulletin - Fluorescent Lamps 1985Document26 pagesSylvania Engineering Bulletin - Fluorescent Lamps 1985Alan Masters100% (1)
- Wallace Chapter in Oxford HandbookDocument14 pagesWallace Chapter in Oxford HandbookSilver TouchstoneNo ratings yet
- AuTiO2preparedphotodeposition Weng 2009Document9 pagesAuTiO2preparedphotodeposition Weng 2009leonardoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy NotesDocument30 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy NotesUjjal Didar Singh100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument4 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosAye Ei MonNo ratings yet
- SL - PAP - F.Muller O.Kleppa - 1972 - Thermodynamics of Formation of Chromite SpinelsDocument6 pagesSL - PAP - F.Muller O.Kleppa - 1972 - Thermodynamics of Formation of Chromite SpinelsEduardo CandelaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument14 pages3 - Atomic Absorption SpectrosAnil ThomasNo ratings yet
- 15 Spektro 01 Aas and AesDocument81 pages15 Spektro 01 Aas and AesmaudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document18 pagesChapter 10Nini KhanNo ratings yet
- Katharometer and Thermal Conductivity DeviceDocument8 pagesKatharometer and Thermal Conductivity DeviceVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Flame Ionization DetectorDocument5 pagesFlame Ionization DetectorMat troi xanhNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - SeminarDocument8 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy - Seminarbolaji4411No ratings yet
- Optical Atomic SpectrosDocument61 pagesOptical Atomic SpectrosAristia MonequeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical of Organosphorus Compound With P-O, P-N and P-C Bonds From White Phosphorus by Yu. M. KarginDocument13 pagesElectrochemical of Organosphorus Compound With P-O, P-N and P-C Bonds From White Phosphorus by Yu. M. KarginSamuel ManaluNo ratings yet
- Hassan 1Document3 pagesHassan 1Hasan HashemiNo ratings yet
- Atomska Spektroskopija-1Document35 pagesAtomska Spektroskopija-1Andrés PacompíaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsNo ratings yet