Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation
F3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation
Uploaded by
Susan SuanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation
F3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation
Uploaded by
Susan SuanCopyright:
Available Formats
Intensive
SCIENCE
SCIENCE
FOR
FOR
FORM
FORM 333
FOR FORM
WWW.SMKSP.COM
SCIENCE INTENSIVE PROGRAMME FOR FROM 3
CHAPTER 2 : BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
SMK SUNGAI PASIR , O8OOO SUNGAI PETANI , KEDAH DARULAMAN.
TEL : 04-421 1764 FAX : 422 0203 LAMAN WEB : WWW.SMKSP.COM
1 Human Blood Circulatory System is the transport
5 The function of the heart is to pump blood to all parts
of the body.
system which consists of heart, blood vessels and blood.
Human Blood Circulatory System
Heart
Blood Vessels
Blood
2 Functions of the human blood circulatory system :
Transport useful substances :
oxygen, nutrients, hormones and antibodies to
all part of the body.
Transport waste products :
carbon dioxide, urea, excess water/mineral salts.
3 Human blood circulatory system act as a system of
tubes with a pump (heart) and valves that ensure
one-way flow of blood.
4 Blood flow in the human blood circulatory system can
be divided into two paths :
Pulmonary Circulation :
6 The valves prevent backflow of blood therefore
ensures the blood flow in one direction.
7 Blood vessels are tubes in the body that channel blood.
There are 3 types of blood vessel :
- Transports deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
- Transports oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
Systemic Circulation
Characteristics
- Transports oxygenated blood and useful substances
from heart to all parts of the body (except lungs)
- Transports deoxygenated blood from all parts of the
body (except lungs) to heart
Artery
Vein
Capillary
Thickness of wall
Thick
Thin
Blood flow
Blood pressure
Fast
Slow
Very slow
High
Low
Very low
Cross section
Pulmonary Circulation
(From heart to lungs
very thin(one
-cell thick)
and back to heart)
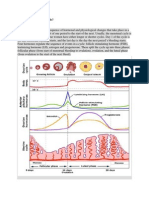
8 Constituents of blood and their functions :
Constituents of blood
Systemic Circulation
Blood
cells
(From heart to all parts
of the body except
Plasma
Transport
lungs and back to
heart)
Red
blood cells
White
blood cells
Platelets
Transport
Protect body
Helps blood
oxygen
clotting
medium
9 The ABO System group human blood grouped into
four groups called A, B, AB and O.
16 Functions of the stomata :
Allow water vapour to diffuse during transpiration.
Allow the exchange of gases during photosynthesis
and respiration.
10 During blood transfusion, the donor's blood must be
compatible with the recipient's blood to prevent blood
agglutinate (clump together) and cause fatal blockage
in the recipient's blood vessels.
Recipient's
blood group
O
A
B
AB
17 The size of the stoma is controlled by the guard cells.
Donor's blood group
A
X
B
X
X
AB
X
X
X
18 Roles of transpiration :
Helps in absorption and transportation of water
and minerals in plants.
Supplies water for photosynthesis
Loses excess water
Maintains freshness of plant cells.
Cools the plant by evaporation during hot weather.
X Incompatibles
Compatibles
Universal Donor
People with blood group O
is able to donate blood to all the blood groups
Universal Recipient
19 Factors that affect the rate of transpiration :
People with blood group AB
is able to receive from all the blood groups
Factors
Temperature
Increase
Air movement
Increase
Light intensity
Increase
Humidity
Increase
11 Blood donation needed for treatment of accident or surgery.
The donated blood (usually 450 ml /1 pint or less e.g.400 ml)
can save the live of others.
12 The donated blood can be used either as unfiltered
blood or separated into components :
Component
Plasma
Rate of transpiration
increase
increase
increase
decrease
20 The transport system in plants consists of xylem and
phloem which are found in the leaves, stems and roots
To show the transport of water through xylem
Main uses
Great loss of blood in surgery & chilbirth
Red Blood Cells Anaemia
Platelets
Bone marrow failure, Leukaemia
13 Donated blood is collected in sterile plastic bags that
contain an anticoagulant to prevent clotting as well as
preservatives to keep the red blood cells alive.
14 Screening tests are performed for evidence of donor
infection with hepatitis, AIDS and others sexual
transmitted diseases.
To show the transport of synthesised food through phloem
15 Transpiration is a process of losing water (water
vapour) from the plants.
Transpiration occurs through the stomata / stoma of the leaves
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Seminar Cover PageDocument1 pageSeminar Cover PageJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationDocument1 pageForm 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Seminar Abdominal InjuryDocument83 pagesSeminar Abdominal InjuryJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- 0610 s16 QP 41Document20 pages0610 s16 QP 41Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- 2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersDocument27 pages2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- 9780198390183Document14 pages9780198390183Jessica Stewart100% (1)
- 0f F FDDocument12 pages0f F FDEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- What Is The Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Menstrual CycleJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- English Paper 1Document5 pagesEnglish Paper 1Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Zako HematologyDocument35 pagesZako Hematologydoctormehmeteren8292No ratings yet
- Form 4 English: SMK Elopura Sandakan 2011 End of The Year Assessment Paper 1Document12 pagesForm 4 English: SMK Elopura Sandakan 2011 End of The Year Assessment Paper 1Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- LEC3Document26 pagesLEC3Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Anaemia by Dr. Hanan Said AliDocument37 pagesAnaemia by Dr. Hanan Said AliJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Calcium Parathyroid, Vitamin D & CalcitoninDocument29 pagesRegulation of Calcium Parathyroid, Vitamin D & CalcitoninJessica StewartNo ratings yet