Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Circuits
Electrical Circuits
Uploaded by
Darwin Lajato TipdasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Circuits
Electrical Circuits
Uploaded by
Darwin Lajato TipdasCopyright:
Available Formats
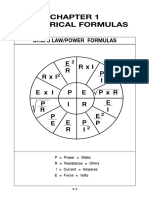
FORMULAS
in
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
OHMS LAW
where:
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
R = resistance, Ohms()
ELECTRICAL POWER
where:
P = power, Watts(W)
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
W = work, Joules(J)
t = time, seconds(s)
Q = charge, Coulombs(C)
JOULES LAW
where:
P = power, Watts(W)
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
R = resistance, Ohms()
SERIES CIRCUIT
where:
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
R = resistance, Ohms()
P = power, Watts(W)
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
where:
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
R = resistance, Ohms()
P = power, Watts(W)
VOLTAGE DIVIDER
where:
V = source voltage, Volts(V)
V1 = voltage at the component R1, Volts(V)
R1 & R2= resistance, Ohms()
CURRENT DIVIDER
where:
I = total current, Amperes(A)
I1 = branch current, Amperes(A)
R1 & R2 = resistances, Ohms()
PERIOD
where:
T = period, seconds(s)
f = frequency, Hertz(Hz)
WAVELENGTH
where:
= wavelength
INSTANTANEOUS VALUE
where:
= the angle of rotation, (rad)
= the angular velocity of a radius vector generating the waveform, (rad/sec)
t = time, seconds(s)
Vm = maximum voltage value
Im = maximum current value
PEAK VALUE
where:
Vm = maximum voltage value
Im = maximum current value
Vp = peak voltage
Ip = peak current
Vrms = effective voltage value
Irms = effective current value
PEAK TO PEAK VALUE
where:
Vp-p = peak to peak voltage
Ip-p = peak to peak current
Vp = peak voltage
Ip = peak current
Vrms = effective voltage value
Irms = effective current value
TOTAL IMPEDANCE
where:
Z = impedance ()
R = resistance ()
X = reactance ()
= angle
TOTAL CURRENT IN PARALLEL AC CIRCUIT
where:
TRUE POWER
where:
REACTIVE POWER
where:
APPARENT POWER
where:
POWER TRIANGLE
where:
POWER FACTOR
where:
REACTIVE FACTOR
where:
OHMS LAW
where:
V = voltage, Volts(V)
I = current, Amperes(A)
R = resistance, Ohms()
You might also like
- Electrical FormulaDocument5 pagesElectrical FormulaAmbi Tion100% (1)
- Matlab Music SynthesisDocument11 pagesMatlab Music SynthesisDarwin Lajato Tipdas0% (1)
- OHM'S LAW by ArchieGBDocument7 pagesOHM'S LAW by ArchieGBArchiemedez BatanganNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument9 pagesBasic ElectricityAnshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument25 pagesOhm's LawblanqbasilNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law PDFDocument44 pagesOhms Law PDFKeenjhar AyoobNo ratings yet
- NUmber of ZerosDocument24 pagesNUmber of ZerosGanesh SonwalkarNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms Lawceller101No ratings yet
- (Ohm's Law) Tutorial 2 For ElectricalsDocument5 pages(Ohm's Law) Tutorial 2 For ElectricalsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantity of ElectricityDocument79 pagesQuantity of Electricityjaiden.shaw25No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument12 pagesElectricityJERVIN JESALVANo ratings yet
- Electrical FormulaDocument2 pagesElectrical FormulaNehra GauravNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Perform Mensuration and Calculation: Information Sheet 1.1 - ElectronicsDocument12 pagesLesson 5 - Perform Mensuration and Calculation: Information Sheet 1.1 - ElectronicsEscanor Lions Sin of PrideNo ratings yet
- Lecture: Volts and CurrentDocument20 pagesLecture: Volts and CurrentRee-anne SabanalNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringDocument20 pagesIntro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringKrishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Theory Study Sheet (v3.1)Document1 pageBasic Electrical Theory Study Sheet (v3.1)Rick GouldNo ratings yet
- Ohm (Ω) 1Ω = 1V / 1A = 1J ⋅ 1s / 1C: ² Table of resistance values of OhmDocument3 pagesOhm (Ω) 1Ω = 1V / 1A = 1J ⋅ 1s / 1C: ² Table of resistance values of OhmTCS WorkNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument24 pagesOhms LawVon MendozaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electric ChargeDocument6 pagesElectricity and Electric ChargeVôDanhNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document7 pagesExperiment No 2Mohsin TariqNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument20 pagesOhms LawWilfredo Ijan, JrNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2Document5 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument1 pageBasic ElectronicsVoid ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law With CircuitsDocument11 pagesOhms Law With CircuitsJaliesa Ann ValdezNo ratings yet
- AlternatingCurrentCircuit ClassNotes - NG 1709124407198Document14 pagesAlternatingCurrentCircuit ClassNotes - NG 1709124407198dasiakennethNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8: Ms. Rose Ann A. BolanteDocument21 pagesIntegrated Science 8: Ms. Rose Ann A. BolanteRose Ann Bolante CruzNo ratings yet
- 17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsDocument12 pages17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Module2 Qbank 2023-24Document3 pagesModule2 Qbank 2023-24Aqsa MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and EquationsDocument4 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Formulas and EquationsJoseval SantosNo ratings yet
- Bonifacio - Lab 1.1 - Ohms LawDocument4 pagesBonifacio - Lab 1.1 - Ohms LawJun BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Cto. 13Document13 pagesCto. 13Gómez Sánchez Luis GustavoNo ratings yet
- 02 Ohms and Power LawsDocument10 pages02 Ohms and Power LawsJoven Andrei R. LagahitNo ratings yet
- EimDocument16 pagesEimJayson Deocareza Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- The Ohms Law Power Point 1Document16 pagesThe Ohms Law Power Point 1Kyle Valleza VilletaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltageDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltagechristiankenthusaNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: y Tenzin SingeyDocument11 pagesElectric Current: y Tenzin SingeyTenzin SingeyNo ratings yet
- Electrical FormulasDocument2 pagesElectrical FormulasvickymuruganNo ratings yet
- Electrical UnitsDocument4 pagesElectrical Unitsamilcar93No ratings yet
- Q1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityDocument48 pagesQ1 WEEK 7 Basic ElectricityAileen OcampoNo ratings yet
- 4 Electric Circuits Series Parallel Q1M6 7Document9 pages4 Electric Circuits Series Parallel Q1M6 7Erra ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Relationship: (V = I x R) V (volts) = I (amps) x R (Ω)Document8 pagesOhms Law Relationship: (V = I x R) V (volts) = I (amps) x R (Ω)Rasos Jhon BryanNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument119 pagesElectric CurrentSM_Ing.No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DC and AC CircuitsDocument13 pagesLecture 1 DC and AC CircuitsnoneNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument10 pagesOhms Lawblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- Rumus ConvertDocument14 pagesRumus ConvertIrlan MalikNo ratings yet
- LAB Manual (EEE)Document27 pagesLAB Manual (EEE)imtiaz hossainNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 02 Ele 290 - Power Ac Circuits - QuestionDocument5 pagesTutorial 02 Ele 290 - Power Ac Circuits - QuestionAmiruddinMohktarNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Power FormulaDocument17 pagesOhms Law Power FormulaRaymond SuriagaNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument45 pagesOhms LawMarc Oliver Pamintuan OtawaNo ratings yet
- 7750 - Alternating Current PDFDocument3 pages7750 - Alternating Current PDFWambe MbavaNo ratings yet
- Electricalcircuits 100212170304 Phpapp01Document30 pagesElectricalcircuits 100212170304 Phpapp01srgroups118No ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryDocument25 pagesAC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryAlex ZulNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formulas PDFDocument5 pagesOhms Law Formulas PDFAnonymous P1r2fMJ9No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Course Number Description Grade Teacher Year Semester Units Finalgp Gpweight FinunitsDocument7 pagesCourse Number Description Grade Teacher Year Semester Units Finalgp Gpweight FinunitsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Design Rules For MORBN20 Process PDFDocument5 pagesDesign Rules For MORBN20 Process PDFDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Advanced Router ConfigurationDocument3 pagesLab 2 - Advanced Router ConfigurationDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document4 pagesPart 1Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part I From Article 18 To Article 33Document63 pagesPart I From Article 18 To Article 33Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument13 pagesElectricity and MagnetismDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument1 pageFlow ChartDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Design Proposal For Establishing A Company NetworkDocument1 pageDesign Proposal For Establishing A Company NetworkDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part Ii. Awareness Level On The Use of Led Lamps Yes NoDocument2 pagesPart Ii. Awareness Level On The Use of Led Lamps Yes NoDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Tables IN Solid State DevicesDocument3 pagesTables IN Solid State DevicesDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Transmission FundamentalsDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 1 Transmission FundamentalsDarwin Lajato Tipdas0% (1)
- Electric CircuitsDocument6 pagesElectric CircuitsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Electrical ElementsDocument13 pagesElectrical ElementsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- DC and AC GeneratorsDocument3 pagesDC and AC GeneratorsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Electric FundamentalsDocument5 pagesElectric FundamentalsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- TelevisionDocument3 pagesTelevisionDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet