Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 viewsMain Features of Intel 8085
Main Features of Intel 8085
Uploaded by
Krish_666The Intel 8085 microprocessor was produced from 1975 to the 1990s. It has an 8-bit architecture, runs on a +5V power supply, and has a maximum clock rate of 3-6 MHz. It has 6,500 transistors, 40-pin DIP packaging, and succeeded the Intel 8080 as Intel's 8-bit CPU.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument16 pages8085 MicroprocessorVinay FelixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3زياد عبدالله عبدالحميدNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument9 pagesIntel 8085 Microprocessor Architectureapi-3740045100% (4)
- Microprocessor SystemDocument42 pagesMicroprocessor SystemHaseeb shaikhNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086Document4 pagesIntel 8086Shishir YalburgiNo ratings yet
- 8085 1Document17 pages8085 1Amar GhogaleNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BECE204L TH VL2023240505482 2024-03-26 Reference-Material-IDocument34 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BECE204L TH VL2023240505482 2024-03-26 Reference-Material-Iprathampalgandhi10No ratings yet
- Xpo KitDocument2 pagesXpo Kitgvkk123100% (1)
- Motorola 6800: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesMotorola 6800: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamarzukijalilNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument225 pagespdf24 MergedKanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- KL Intel D8086.jpgDocument12 pagesKL Intel D8086.jpgsapnarawa198799No ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 pagesMpi Unit 1sree ramyaNo ratings yet
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument1 page8051 MicrocontrollerMohamed AbubackerNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument79 pagesMicroprocessorvanshikalra142No ratings yet
- x-86 FamilyDocument14 pagesx-86 FamilyPrince VegetaNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers - 8051 Architecture: Advertisements Ad by ValueimpressionDocument2 pagesMicrocontrollers - 8051 Architecture: Advertisements Ad by ValueimpressionrajeshNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument31 pages8085 Architecturevellore gatewayNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 8085 MicroprocessorDocument14 pagesCase Study - 8085 MicroprocessorChat MateNo ratings yet
- 20 سؤال معماريةDocument23 pages20 سؤال معماريةمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor, Microcomputer and Assembly LanguageDocument48 pagesMicroprocessor, Microcomputer and Assembly LanguageKristine AbanadorNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - Mircroprocessor ConceptsDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor - Mircroprocessor ConceptsTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Intel CpusDocument37 pagesIntel Cpus我叫政揚UwUNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument37 pages8085 MicroprocessorTilottama Deore100% (1)
- Microprocessors & Its Applications CSM-3305 PDFDocument255 pagesMicroprocessors & Its Applications CSM-3305 PDFromesh1998No ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorAnonymous zaMNkL100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1lirina4508No ratings yet
- Notes For StudentsDocument29 pagesNotes For StudentsAnif Ilham IsmailNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Module 1 - 5Document260 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Module 1 - 5ncecentral0% (1)
- A Study On MicropocessorDocument12 pagesA Study On MicropocessormanaskollamNo ratings yet
- List of Intel Microprocessors: Participate in The World's Largest Photo Competition and Help Improve Wikipedia!Document52 pagesList of Intel Microprocessors: Participate in The World's Largest Photo Competition and Help Improve Wikipedia!Atul YadavNo ratings yet
- Organization of Intel 8085Document6 pagesOrganization of Intel 8085Athiesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CN 320: Microprocessor and Microcontroller SystemsDocument40 pagesCN 320: Microprocessor and Microcontroller SystemsAlango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Intel 4004Document2 pagesIntel 4004Johnedel RosalesNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument19 pagesMicroprocessorParasNo ratings yet
- Ece 8085 MicroprocessorDocument26 pagesEce 8085 Microprocessorgourav VermaNo ratings yet
- Reviewof Microprocessor PDFDocument23 pagesReviewof Microprocessor PDFSatyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Its Applications EssayDocument15 pagesMicroprocessors and Its Applications EssayAshish BirwalNo ratings yet
- 7) Describe The Pin Out of 8085 Microprocessor With Neat DescriptionDocument2 pages7) Describe The Pin Out of 8085 Microprocessor With Neat Descriptionnirmal_inboxNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Unit OneDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor Unit OneUtshab ChapagainNo ratings yet
- MICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaDocument27 pagesMICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaAlfred SharmaNo ratings yet
- 8051 Mic Rocontroller: Features of 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument3 pages8051 Mic Rocontroller: Features of 8051 MicrocontrollerchandrakanthNo ratings yet
- MicropDocument5 pagesMicropNaza RenkoNo ratings yet
- 8051 TutorialDocument8 pages8051 TutorialVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesHyma Prasad GelliNo ratings yet
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument31 pages8051 Microcontrollernasof62012No ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8080.Document7 pagesMicroprocessor 8080.ضحى الغزيNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument51 pages8085 ArchitectureVaibhav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086 Microprocessor FamilyDocument3 pagesIntel 8086 Microprocessor FamilyMusabbir Adnan TamimNo ratings yet
- Micrprocessor Notes 2023Document18 pagesMicrprocessor Notes 2023GautamNo ratings yet
- Microsad Q2Document66 pagesMicrosad Q2John Railey P. PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors & MicrocontrollersDocument11 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollersitsaartihere001No ratings yet
- U3 8086 MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesU3 8086 MicroprocessorNishant Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CO Notes Mod 4Document10 pagesCO Notes Mod 4Amal MonichanNo ratings yet
- Part 01Document29 pagesPart 01Md AabishNo ratings yet
- The Birth of 8086Document2 pagesThe Birth of 8086Freddie MendezNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Micro Controller TrainerDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor Micro Controller TrainerHOD ECE KNCETNo ratings yet
- Practical Application of 8085Document16 pagesPractical Application of 8085Raj Shah100% (1)
- FPGA BoardDocument12 pagesFPGA Boardkamarajme2006No ratings yet
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15From EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Earth's Satellites (Space)Document19 pagesEarth's Satellites (Space)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Mobile Networks Generations (Technology)Document3 pagesMobile Networks Generations (Technology)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Basics of Neurophysiology and EEG 2020Document46 pagesBasics of Neurophysiology and EEG 2020Krish_666No ratings yet
- Redwoods (Trees)Document4 pagesRedwoods (Trees)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Nikon D3400 ManualDocument136 pagesNikon D3400 ManualKrish_666100% (1)
- Introduction To MicroWavesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicroWavesKrish_666No ratings yet
Main Features of Intel 8085
Main Features of Intel 8085
Uploaded by
Krish_6660 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesThe Intel 8085 microprocessor was produced from 1975 to the 1990s. It has an 8-bit architecture, runs on a +5V power supply, and has a maximum clock rate of 3-6 MHz. It has 6,500 transistors, 40-pin DIP packaging, and succeeded the Intel 8080 as Intel's 8-bit CPU.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Intel 8085 microprocessor was produced from 1975 to the 1990s. It has an 8-bit architecture, runs on a +5V power supply, and has a maximum clock rate of 3-6 MHz. It has 6,500 transistors, 40-pin DIP packaging, and succeeded the Intel 8080 as Intel's 8-bit CPU.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesMain Features of Intel 8085
Main Features of Intel 8085
Uploaded by
Krish_666The Intel 8085 microprocessor was produced from 1975 to the 1990s. It has an 8-bit architecture, runs on a +5V power supply, and has a maximum clock rate of 3-6 MHz. It has 6,500 transistors, 40-pin DIP packaging, and succeeded the Intel 8080 as Intel's 8-bit CPU.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Main features of Intel 8085
Produced
From 1975 to 1990s
Common
manufacturer(s)
Intel and several
others
Max. CPU clock rate
Bit size
Power Supply
Min. feature size
Instruction set
Transistors
Predecessor
Successor
3, 5 and 6 MHz
8 bits
+5V
3 m
80
6,500
Intel 8080
Intel 8086
Package(s)
40-pin DIP
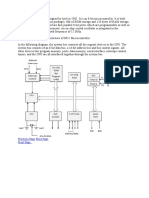
It is an 8 bit microprocessor (each character is represented by 8 bits or a
byte).
It is manufactured with N-MOS (n-type Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
technology implemented with 6200 transistors.
It has 16-bit address lines - A0-A15 (to point the memory locations) and
hence can point up to 2^16 = 65535 bytes (64KB) memory locations.
The first 8 lines of address bus and 8 lines of data bus are multiplexed AD0AD7. Data bus is a group of 8 lines D0-D7.
It provides 5 level interrupts and supports external interrupt request.
A 16 bit program counters (PC).
A 16 bit stack pointer (SP).
It provides 1 accumulator, 2 flag register, six 8-bit general purpose register
arranged in pairs: BC, DE, HL and 2 special purpose registers (PC, SP)
It consists of 74 instruction sets.
It performs arithmetic and logical operations.
It provides status for advanced control signals, On chip clock generator.
It requires a signal +5V power supply and operates at 3.2 MHZ single phase
clock with maximum clock frequency 6 MHz and minimum clock frequency
500 kHz.
Serial input/output port.
1.3 micro sec instruction cycles.
It is enclosed with 40 pins DIP (Dual in line package).
It can be used to implement (interface) 3 chip micro-computers (8085, 8155,
8255 and 8355: Peripheral IC's).
You might also like
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument16 pages8085 MicroprocessorVinay FelixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3زياد عبدالله عبدالحميدNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument9 pagesIntel 8085 Microprocessor Architectureapi-3740045100% (4)
- Microprocessor SystemDocument42 pagesMicroprocessor SystemHaseeb shaikhNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086Document4 pagesIntel 8086Shishir YalburgiNo ratings yet
- 8085 1Document17 pages8085 1Amar GhogaleNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BECE204L TH VL2023240505482 2024-03-26 Reference-Material-IDocument34 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BECE204L TH VL2023240505482 2024-03-26 Reference-Material-Iprathampalgandhi10No ratings yet
- Xpo KitDocument2 pagesXpo Kitgvkk123100% (1)
- Motorola 6800: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesMotorola 6800: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamarzukijalilNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument225 pagespdf24 MergedKanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- KL Intel D8086.jpgDocument12 pagesKL Intel D8086.jpgsapnarawa198799No ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 pagesMpi Unit 1sree ramyaNo ratings yet
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument1 page8051 MicrocontrollerMohamed AbubackerNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument79 pagesMicroprocessorvanshikalra142No ratings yet
- x-86 FamilyDocument14 pagesx-86 FamilyPrince VegetaNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers - 8051 Architecture: Advertisements Ad by ValueimpressionDocument2 pagesMicrocontrollers - 8051 Architecture: Advertisements Ad by ValueimpressionrajeshNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument31 pages8085 Architecturevellore gatewayNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 8085 MicroprocessorDocument14 pagesCase Study - 8085 MicroprocessorChat MateNo ratings yet
- 20 سؤال معماريةDocument23 pages20 سؤال معماريةمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor, Microcomputer and Assembly LanguageDocument48 pagesMicroprocessor, Microcomputer and Assembly LanguageKristine AbanadorNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - Mircroprocessor ConceptsDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor - Mircroprocessor ConceptsTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Intel CpusDocument37 pagesIntel Cpus我叫政揚UwUNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument37 pages8085 MicroprocessorTilottama Deore100% (1)
- Microprocessors & Its Applications CSM-3305 PDFDocument255 pagesMicroprocessors & Its Applications CSM-3305 PDFromesh1998No ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorAnonymous zaMNkL100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1lirina4508No ratings yet
- Notes For StudentsDocument29 pagesNotes For StudentsAnif Ilham IsmailNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Module 1 - 5Document260 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Module 1 - 5ncecentral0% (1)
- A Study On MicropocessorDocument12 pagesA Study On MicropocessormanaskollamNo ratings yet
- List of Intel Microprocessors: Participate in The World's Largest Photo Competition and Help Improve Wikipedia!Document52 pagesList of Intel Microprocessors: Participate in The World's Largest Photo Competition and Help Improve Wikipedia!Atul YadavNo ratings yet
- Organization of Intel 8085Document6 pagesOrganization of Intel 8085Athiesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CN 320: Microprocessor and Microcontroller SystemsDocument40 pagesCN 320: Microprocessor and Microcontroller SystemsAlango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Intel 4004Document2 pagesIntel 4004Johnedel RosalesNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument19 pagesMicroprocessorParasNo ratings yet
- Ece 8085 MicroprocessorDocument26 pagesEce 8085 Microprocessorgourav VermaNo ratings yet
- Reviewof Microprocessor PDFDocument23 pagesReviewof Microprocessor PDFSatyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Its Applications EssayDocument15 pagesMicroprocessors and Its Applications EssayAshish BirwalNo ratings yet
- 7) Describe The Pin Out of 8085 Microprocessor With Neat DescriptionDocument2 pages7) Describe The Pin Out of 8085 Microprocessor With Neat Descriptionnirmal_inboxNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Unit OneDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor Unit OneUtshab ChapagainNo ratings yet
- MICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaDocument27 pagesMICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaAlfred SharmaNo ratings yet
- 8051 Mic Rocontroller: Features of 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument3 pages8051 Mic Rocontroller: Features of 8051 MicrocontrollerchandrakanthNo ratings yet
- MicropDocument5 pagesMicropNaza RenkoNo ratings yet
- 8051 TutorialDocument8 pages8051 TutorialVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesHyma Prasad GelliNo ratings yet
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument31 pages8051 Microcontrollernasof62012No ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8080.Document7 pagesMicroprocessor 8080.ضحى الغزيNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument51 pages8085 ArchitectureVaibhav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086 Microprocessor FamilyDocument3 pagesIntel 8086 Microprocessor FamilyMusabbir Adnan TamimNo ratings yet
- Micrprocessor Notes 2023Document18 pagesMicrprocessor Notes 2023GautamNo ratings yet
- Microsad Q2Document66 pagesMicrosad Q2John Railey P. PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors & MicrocontrollersDocument11 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollersitsaartihere001No ratings yet
- U3 8086 MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesU3 8086 MicroprocessorNishant Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CO Notes Mod 4Document10 pagesCO Notes Mod 4Amal MonichanNo ratings yet
- Part 01Document29 pagesPart 01Md AabishNo ratings yet
- The Birth of 8086Document2 pagesThe Birth of 8086Freddie MendezNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Micro Controller TrainerDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor Micro Controller TrainerHOD ECE KNCETNo ratings yet
- Practical Application of 8085Document16 pagesPractical Application of 8085Raj Shah100% (1)
- FPGA BoardDocument12 pagesFPGA Boardkamarajme2006No ratings yet
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15From EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Earth's Satellites (Space)Document19 pagesEarth's Satellites (Space)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Mobile Networks Generations (Technology)Document3 pagesMobile Networks Generations (Technology)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Basics of Neurophysiology and EEG 2020Document46 pagesBasics of Neurophysiology and EEG 2020Krish_666No ratings yet
- Redwoods (Trees)Document4 pagesRedwoods (Trees)Krish_666No ratings yet
- Nikon D3400 ManualDocument136 pagesNikon D3400 ManualKrish_666100% (1)
- Introduction To MicroWavesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicroWavesKrish_666No ratings yet