Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry
Uploaded by
Akmar SN MYCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Practice Examples Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Petrucci 10th EdDocument7 pagesPractice Examples Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Petrucci 10th EdHaggai NidarNo ratings yet
- ChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Document23 pagesChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Jerick JasperNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistrysyazaNo ratings yet
- 100 Problem SetsDocument30 pages100 Problem Setsapi-380015371% (7)
- HW3 SolnDocument5 pagesHW3 SolnJeff Noah MendozaNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolnDocument5 pagesHW3 SolnNaury N OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework Assignment #1 CHM 152 Spring 2002: F D 2 F D 2 F D 2Document4 pagesSolutions To Homework Assignment #1 CHM 152 Spring 2002: F D 2 F D 2 F D 2josegpaNo ratings yet
- CHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-AnsDocument2 pagesCHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-Ansnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics Answer KeyDocument4 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics Answer Keylabacanacruzayesah5No ratings yet
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocument43 pages07 Petrucci10e CSMAlex100% (3)
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 17 (06.14.16)Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 17 (06.14.16)Tessa KodraNo ratings yet
- Enriquez Rovie C. ThermochemistryDocument9 pagesEnriquez Rovie C. ThermochemistryENRIQUEZ, ROVIE C.No ratings yet
- CH 7 Selected SolutionsDocument23 pagesCH 7 Selected SolutionsNimetKaraNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument3 pagesOriginalyigaf49105No ratings yet
- 2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Document4 pages2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Erika Mae Adoja Espejo100% (1)
- CHM13P Learning Task 3Document3 pagesCHM13P Learning Task 3Paolo Gochingco0% (1)
- Extra Practice Week 6Document2 pagesExtra Practice Week 6ShawnNo ratings yet
- Therm DynDocument13 pagesTherm DynSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MC Questions OnlyDocument31 pagesThermodynamics MC Questions OnlyMichael MansNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem AnswersDocument6 pagesSample Problem AnswersLabLeeNo ratings yet
- 11HThermoPracticeQsDocument5 pages11HThermoPracticeQsJust BetoNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 - Gibbs Free EnergyDocument3 pagesTugas 1 - Gibbs Free EnergyrichooNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJDocument12 pagesThermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJxyz7890No ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument24 pagesHess Lawactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentAfthirah AmiraNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Exam I Practice Problems Sp07Document6 pagesGen Chem II Exam I Practice Problems Sp07Camha NguyenNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of ReactionDocument22 pagesEnthalpy of ReactionPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- Previous Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Thermodynamics"Document8 pagesPrevious Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Thermodynamics"Muhammed SadiqNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Example Midterm KeyDocument7 pagesPractice Exam Example Midterm KeymebrahtomNo ratings yet
- Problems On Thermodynamics S.y.b.sc 2016Document4 pagesProblems On Thermodynamics S.y.b.sc 2016Kishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Review SolutionDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Review SolutionSFDLSFHIOANo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ExercisesDocument5 pagesEnthalpy ExercisesmpumelaqqNo ratings yet
- Exmn 3 TermoDocument7 pagesExmn 3 TermoJailene Gómez CollazoNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Module 1Document9 pagesThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranNo ratings yet
- 2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Document5 pages2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Minh ThungoNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyDocument2 pagesLesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyJan Yeasha MendezNo ratings yet
- Raffles Junior College H2 Chemistry 2010/2011 Tutorial 5b - Chemical Energetics IIDocument8 pagesRaffles Junior College H2 Chemistry 2010/2011 Tutorial 5b - Chemical Energetics IIDomNo ratings yet
- Practice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FDocument3 pagesPractice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FMaria GinzburgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Problems 1411 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Problems 1411 Answer KeyCreating the BestNo ratings yet
- A. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001Document6 pagesA. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001TanNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Problem Set #1: Angelica Avrielle C. Arevalo Bsce 1FDocument6 pagesThermochemistry Problem Set #1: Angelica Avrielle C. Arevalo Bsce 1FAngelica Avrielle C. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Change of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonateDocument12 pagesExperiment 1: Change of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonatenotmeNo ratings yet
- Chem XI (Thermo)Document5 pagesChem XI (Thermo)Lumyy PillenaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Multiple Choice-2011!11!17Document41 pagesThermodynamics Multiple Choice-2011!11!17sabdaliNo ratings yet
- 2011 Final AnswerDocument8 pages2011 Final Answerxuan1002No ratings yet
- Reactants Products Reactants Products 2 3 (S) (S) 2 (G)Document2 pagesReactants Products Reactants Products 2 3 (S) (S) 2 (G)kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- 1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersDocument12 pages1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersNor Afidah100% (1)
- LT2 ThermochemDocument3 pagesLT2 ThermochemRenzo AlvizNo ratings yet
- Hssive-Xi-Chem-6. Thermodynamics Q & ADocument9 pagesHssive-Xi-Chem-6. Thermodynamics Q & AArties MNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry
Uploaded by
Akmar SN MYOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry
Uploaded by
Akmar SN MYCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL THERMOCHEMISTRY
SKU1023
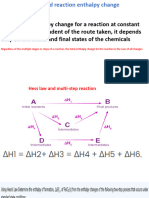
1) a. State Hess's Law
The enthalpy change for an overall process is equal to the sum of the enthalpy
changes of its individual steps.
(1m)
b. Use Hess's Law to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction
WO3(s) + 3H2(g) W(s) + 3H2O(g)
from the following data
2W(s) + 3O2(g) 2WO3(s) H = 1685.4 kJ (1)
2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g)
H = 477.84 kJ (2)
reaction (1) = reversed and times 1/2 ; H = 842.7kJ (1m)
reaction (2) = times 3/2 ; H = -716.76 kJ
(1m)
H for the reaction = 842.7kJ + (-716.76 kJ) = 125.9 kJ (1m)
2) 2.53 g of solid NaOH is dissolved in 100.00 g of water in a coffee cup calorimeter, all the
reagents initially being at 20.0C. Calculate the final temperature (in oC) of the solution
obtained, given the following information:
NaOH(s) NaOH(aq)
H = 43.0 kJ/mol
Heat capacity of NaOH solution = 4.18 J/(gK)
Mol NaOH = 2.53 / 40g/mol = 0.0633 mol
(1m)
q = -43.0 kJ/mol x 0.0633 mol = 2.72 kJ
(1m)
q = c x mass x T
2720 kJ = 4.18 J/g.K x 102.53 g x T
T = 6.34 K
(1m)
o
6.34 K = Tfinal - Tinitial = Tfinal - (20 C + 273.15) K
(1m)
Tfinal = 299.49 K - 273.15 = 26.3C
(1m)
3) The complete combustion of liquid benzene is represented by the equation:
C6H6(l) + 7 1 2 O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
Using the data below, calculate, for this reaction, at 25C.
a. H
b. S
c. G
Substance:
H f (kJ/mol):
S(J/mol.K):
C6H6(l)
49
173
O2(g)
0
205
CO2(g)
394
214
H2O(l)
286
70
a. H = Hoproduct - Horeaction = [3(-286) + 6(-394)] - [7 1/2 (0) +49) = -3271 kJ
(2m)
b. S=S
o
product
- S
reaction
= [3(70) + 6 (214)] - [7 1/2 (205) + 173] = -216.5 kJ
(2m)
c. G = Ho- TSo = -3271 - (273+25)(0.217) = -3206 kJ
(2m)
You might also like
- Practice Examples Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Petrucci 10th EdDocument7 pagesPractice Examples Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Petrucci 10th EdHaggai NidarNo ratings yet
- ChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Document23 pagesChemLec - Module 4.1 - 4.3Jerick JasperNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistrysyazaNo ratings yet
- 100 Problem SetsDocument30 pages100 Problem Setsapi-380015371% (7)
- HW3 SolnDocument5 pagesHW3 SolnJeff Noah MendozaNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolnDocument5 pagesHW3 SolnNaury N OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ThermoDocument1 pageTutorial 5 ThermoAkmar SN MYNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework Assignment #1 CHM 152 Spring 2002: F D 2 F D 2 F D 2Document4 pagesSolutions To Homework Assignment #1 CHM 152 Spring 2002: F D 2 F D 2 F D 2josegpaNo ratings yet
- CHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-AnsDocument2 pagesCHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-Ansnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics Answer KeyDocument4 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics Answer Keylabacanacruzayesah5No ratings yet
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocument43 pages07 Petrucci10e CSMAlex100% (3)
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 17 (06.14.16)Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 17 (06.14.16)Tessa KodraNo ratings yet
- Enriquez Rovie C. ThermochemistryDocument9 pagesEnriquez Rovie C. ThermochemistryENRIQUEZ, ROVIE C.No ratings yet
- CH 7 Selected SolutionsDocument23 pagesCH 7 Selected SolutionsNimetKaraNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument3 pagesOriginalyigaf49105No ratings yet
- 2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Document4 pages2010chem17 PracticeExercise1Erika Mae Adoja Espejo100% (1)
- CHM13P Learning Task 3Document3 pagesCHM13P Learning Task 3Paolo Gochingco0% (1)
- Extra Practice Week 6Document2 pagesExtra Practice Week 6ShawnNo ratings yet
- Therm DynDocument13 pagesTherm DynSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MC Questions OnlyDocument31 pagesThermodynamics MC Questions OnlyMichael MansNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem AnswersDocument6 pagesSample Problem AnswersLabLeeNo ratings yet
- 11HThermoPracticeQsDocument5 pages11HThermoPracticeQsJust BetoNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 - Gibbs Free EnergyDocument3 pagesTugas 1 - Gibbs Free EnergyrichooNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJDocument12 pagesThermochemistry Review - Answers: CH OH (L) + / O (G) Î Co (G) + 2 H O (L) H - 727 KJxyz7890No ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument24 pagesHess Lawactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentAfthirah AmiraNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Exam I Practice Problems Sp07Document6 pagesGen Chem II Exam I Practice Problems Sp07Camha NguyenNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of ReactionDocument22 pagesEnthalpy of ReactionPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- Previous Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Thermodynamics"Document8 pagesPrevious Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "Thermodynamics"Muhammed SadiqNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Example Midterm KeyDocument7 pagesPractice Exam Example Midterm KeymebrahtomNo ratings yet
- Problems On Thermodynamics S.y.b.sc 2016Document4 pagesProblems On Thermodynamics S.y.b.sc 2016Kishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Review SolutionDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Review SolutionSFDLSFHIOANo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ExercisesDocument5 pagesEnthalpy ExercisesmpumelaqqNo ratings yet
- Exmn 3 TermoDocument7 pagesExmn 3 TermoJailene Gómez CollazoNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Module 1Document9 pagesThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranNo ratings yet
- 2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Document5 pages2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Minh ThungoNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyDocument2 pagesLesson On Gibbs' Free EnergyJan Yeasha MendezNo ratings yet
- Raffles Junior College H2 Chemistry 2010/2011 Tutorial 5b - Chemical Energetics IIDocument8 pagesRaffles Junior College H2 Chemistry 2010/2011 Tutorial 5b - Chemical Energetics IIDomNo ratings yet
- Practice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FDocument3 pagesPractice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FMaria GinzburgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Problems 1411 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Problems 1411 Answer KeyCreating the BestNo ratings yet
- A. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001Document6 pagesA. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001TanNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Problem Set #1: Angelica Avrielle C. Arevalo Bsce 1FDocument6 pagesThermochemistry Problem Set #1: Angelica Avrielle C. Arevalo Bsce 1FAngelica Avrielle C. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Change of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonateDocument12 pagesExperiment 1: Change of Standard Gibbs Free Energy For The Decomposition of Sodium Hydrogen CarbonatenotmeNo ratings yet
- Chem XI (Thermo)Document5 pagesChem XI (Thermo)Lumyy PillenaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Multiple Choice-2011!11!17Document41 pagesThermodynamics Multiple Choice-2011!11!17sabdaliNo ratings yet
- 2011 Final AnswerDocument8 pages2011 Final Answerxuan1002No ratings yet
- Reactants Products Reactants Products 2 3 (S) (S) 2 (G)Document2 pagesReactants Products Reactants Products 2 3 (S) (S) 2 (G)kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- 1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersDocument12 pages1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersNor Afidah100% (1)
- LT2 ThermochemDocument3 pagesLT2 ThermochemRenzo AlvizNo ratings yet
- Hssive-Xi-Chem-6. Thermodynamics Q & ADocument9 pagesHssive-Xi-Chem-6. Thermodynamics Q & AArties MNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet