Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Electronics and Electrical Drives 1: Exercise 1 (Chapter 5)
Power Electronics and Electrical Drives 1: Exercise 1 (Chapter 5)
Uploaded by
Bhushan NikumbhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Electronics and Electrical Drives 1: Exercise 1 (Chapter 5)
Power Electronics and Electrical Drives 1: Exercise 1 (Chapter 5)
Uploaded by
Bhushan NikumbhCopyright:
Available Formats
STE6217 Power Electronics and
Electrical Drives 1
Assignment: 6
Published:
04.05.2015
Return to:
Edited by:
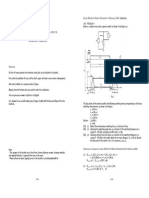
Exercise 1 (chapter 5)
Basic AC rectifier.
Consider the basic commutation circuit of Fig. 1 with Id =10A .
a) With vS=230 V at 50 Hz and LS=0, Calculate vd and average power Pd.
Figure 1. Diode rectifier
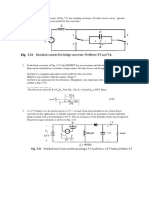
Exercise 2 (Chapter 5)
In the single phase rectifier circuit shown in Fig. 2 vS=230V at 50 Hz, LS= 0.5mH and id=5 A. Calculate
the commutation interval u, DC output voltage vd and output power Pd . What is the percentage voltage
drop in vd due to LS.?
Fig. 2
05/04/15
Fag STE6217
Side 1 av 2
Exercise 3 (chapter 5) Three phase AC rectifier.
Some of the questions need to use the Fourier analysis (chapter 3).
Based on Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Diode rectifier with a constant dc current.
a. Derive the solution shown in (1). This is the RMS current.
b.
1. What is the value for Is if Id=100 A?
2
= (1)
3
c. Derive the RMS value for the fundamental.
1. What is the value for Is1 if Id=100 A?
d. Derive the result in equation (2)
.
1. If the line to neutron voltage is 400 V. Find the DC voltage.
2. With a current Id=100 A, find the input power.
0 = 1.35 (2)
e. For the same problem, find the PF.
f.
If the fundamental current is 1% of the short circuit current.
1. Find the inductance.
2. Find the value of the voltage drop at the dc voltage output.
Remark: See Figures 5-32 and 5-33a in book [1].
[1]
2003.
N. Mohan, T. Undeland, W. Robins, Power electronics, Converters, applications and design, Third edition, Wiley,
05/04/15
Fag STE6217
Side 2 av 2
You might also like
- Diode ExercisesDocument5 pagesDiode ExercisesbruhNo ratings yet
- Ece 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Document2 pagesEce 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Deepanshu SehgalNo ratings yet
- GATE CLOUD Network Analysis by R K KanodiaDocument126 pagesGATE CLOUD Network Analysis by R K KanodiaAmit150462% (13)
- Power Electronics Questions AnswersDocument59 pagesPower Electronics Questions AnswersPascal UZABAKIRIHONo ratings yet
- Assignmenlk, MLT 7 Solution NewDocument3 pagesAssignmenlk, MLT 7 Solution NewAnkit BhoomiaNo ratings yet
- Ee 328 Final 2017 SolDocument4 pagesEe 328 Final 2017 SolFawzi Radwan100% (1)
- Ejercicios Diodos PerillaDocument9 pagesEjercicios Diodos PerillaArturo MontealegreNo ratings yet
- EE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 2: DC Power SupplyDocument5 pagesEE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 2: DC Power SupplySruthiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Modified)Document8 pagesExperiment 5 (Modified)Mark Sangalang100% (1)
- Lab 1 Circuit ElementsDocument8 pagesLab 1 Circuit ElementsDawood SulemanNo ratings yet
- Sheet - HWRDocument2 pagesSheet - HWRhebatarekgNo ratings yet
- PE Lab 08Document4 pagesPE Lab 08Haseeb BalochNo ratings yet
- ET4119 2007-12-07 Ten Met BundelDocument23 pagesET4119 2007-12-07 Ten Met BundelmeteNo ratings yet
- EE325 ExamDocument4 pagesEE325 ExamrobkhNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated Circuits Exercise 4: Common-Source and Differential AmplifiersDocument9 pagesAnalog Integrated Circuits Exercise 4: Common-Source and Differential Amplifiersubuntu 13.04No ratings yet
- TRANS SOLtransDocument9 pagesTRANS SOLtranskkd3No ratings yet
- Qatar University College of Engineering Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesQatar University College of Engineering Department of Electrical EngineeringShafiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Rahman Tutorial 2Document3 pagesRahman Tutorial 2John Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3William ZhuangNo ratings yet
- LAB LEDs and ZenerDocument12 pagesLAB LEDs and ZenerjosembosemNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Electronics PDFDocument34 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics PDFJatinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Arul AnandanNo ratings yet
- The Main of Objective of The First Assignment Is To Understand A Boost Converter Characteristic in The Circuit Fig.1 Using PSIMDocument2 pagesThe Main of Objective of The First Assignment Is To Understand A Boost Converter Characteristic in The Circuit Fig.1 Using PSIMnwk71No ratings yet
- ECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument20 pagesECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineeringsenpai_mendozaNo ratings yet
- EC212 Assignment 1 Analog Circuits TheoryDocument3 pagesEC212 Assignment 1 Analog Circuits Theorynjfdht24nmNo ratings yet
- DMC M3 AssignmentDocument14 pagesDMC M3 AssignmentHannanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics PDFDocument16 pagesDiode Characteristics PDFJOECELLE ABLEGINANo ratings yet
- Electronics I Suggested Exercises 2: Problem 1Document3 pagesElectronics I Suggested Exercises 2: Problem 1Ibrahim Al-HusariNo ratings yet
- C Non 10 100 Vac VDC DC RatioDocument4 pagesC Non 10 100 Vac VDC DC RatioMeso NoorNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report2 - Diode Characteristicsdonatello8480% (5)
- Experiment 2: Semiconductor Diodes and Diode Circuits A. BackgroundDocument12 pagesExperiment 2: Semiconductor Diodes and Diode Circuits A. BackgroundShivankur KapoorNo ratings yet
- Lab3 PowersupplyfinalDocument10 pagesLab3 PowersupplyfinalShiela Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Misbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Pasindu PramodNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocument6 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFDocument24 pagesGATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- EEE2045F Tutorial 2Document3 pagesEEE2045F Tutorial 2jaconlateNo ratings yet
- Solution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsDocument15 pagesSolution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsWajdi BELLILNo ratings yet
- Ehsan (3050) Lab 05Document7 pagesEhsan (3050) Lab 05Antenna /// Power ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Question BankDocument1 pageModule 1 Question BankAbcNo ratings yet
- Widlar Current MirrorDocument14 pagesWidlar Current MirrorAnonymous EeXuSRvlNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesZener Diode CharacteristicsPaulbert ThomasNo ratings yet
- TECC3791 Power Electronics Tutorial 8 (03 April 2023) DC-AC ConvertersDocument1 pageTECC3791 Power Electronics Tutorial 8 (03 April 2023) DC-AC ConvertersEfeninge MarthaNo ratings yet
- DC-DC ConvertersDocument30 pagesDC-DC ConvertersTema HassanNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Set 1Document6 pagesPractice Problems Set 1Angelo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 325 Lab 10 ReportDocument12 pages325 Lab 10 Reportapi-241454978No ratings yet
- Average Value, RMS Value, Fourier AnalysisDocument10 pagesAverage Value, RMS Value, Fourier AnalysisDuy Bùi Thế MinhNo ratings yet
- Ee141 hw6 sp10Document3 pagesEe141 hw6 sp10Brenda PalmerNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Name: Anees Chohan Roll NO.: 19013123-062 Section: B: Title: Study of Power DC Circuit Experiment # 06Document3 pagesName: Anees Chohan Roll NO.: 19013123-062 Section: B: Title: Study of Power DC Circuit Experiment # 06Muhammad Toseef ChohanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 FinalDocument11 pagesExperiment 7 Finalernie5000No ratings yet
- ELEC2530 Rectifier Tutorial-1Document2 pagesELEC2530 Rectifier Tutorial-1Khairul IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Expt. # CKTS 1 L-3 Power - Heat-Light: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExpt. # CKTS 1 L-3 Power - Heat-Light: ObjectivesCesar CalboniNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Smoke Detector CircuitDocument1 pageSmoke Detector CircuitBhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet
- Application For The Job of System EngineerDocument1 pageApplication For The Job of System EngineerBhushan Nikumbh100% (1)
- Letter of Recommendation: Prof. A. M. PatilDocument1 pageLetter of Recommendation: Prof. A. M. PatilBhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document1 pageAssignment 7Bhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet
- Ranking of PMUDocument17 pagesRanking of PMUBhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet
- Automation of Vehicles: KeywordsDocument7 pagesAutomation of Vehicles: KeywordsBhushan NikumbhNo ratings yet