Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tarea #1 IQ205 Entregar Agosto 24 (Lunes), 2015
Tarea #1 IQ205 Entregar Agosto 24 (Lunes), 2015
Uploaded by
saraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tarea #1 IQ205 Entregar Agosto 24 (Lunes), 2015
Tarea #1 IQ205 Entregar Agosto 24 (Lunes), 2015
Uploaded by
saraCopyright:
Available Formats
TAREA #1
1.
IQ205
Entregar agosto 24 (lunes), 2015
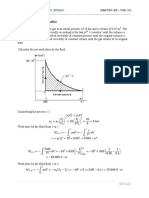
The following table lists temperatures and specific volumes of water vapor at two
pressures:
p = 0.1 MPa
p = 0.12 MPa
T (C)
v (m3/kg)
T (C)
v (m3/kg)
200
2.172
200
1.808
240
2.359
240
1.965
280
2.546
280
2.120
Using the data provided here, estimate:
a. The specific volume, in m3/kg, at T = 200C, p = 0.113 Mpa
b. The temperature, in C, at p = 0.12 Mpa, v = 1.85 m3/kg
c. The temperature, in K, at p = 0.11 Mpa, v = 2.20 m3/kg
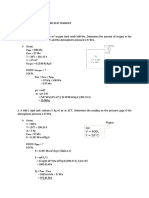
2. A manometer is attached to a tank of gas in which the pressure is greater than that of
3
the surroundings. The manometer liquid is mercury, with a density of 13.59 g/cm .
The difference in mercury levels in the manometer is 2 cm. The acceleration of
gravity is g = 9.81 m/s2. The atmospheric pressure is 93.0 kPa. Calculate in kPa:
a. The gage pressure of the gas.
b. The absolute pressure of the gas.
3. The
absolute pressure inside a tank is 0.2 bar, and the surroundings atmospheric
pressure is 101 kPa. What reading would a Bourdon gage mounted in the tank will
give, in kPa? Is this a gage or vacuum reading?
You might also like
- PPE Problem Set 1Document128 pagesPPE Problem Set 1Gracee87% (15)
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1ampalacios1991100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Problems 7th EditionDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Problems 7th Editionallswell0% (2)
- Thermo 5th Chap03P061Document22 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P061IENCSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 PDFAri Reza KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 PDFLily Antonette AgustinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Tut Midsem NewDocument167 pagesThermo Tut Midsem NewRaghav ChhaparwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3luminaNo ratings yet
- Borgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global EditionDocument67 pagesBorgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global Edition정윤서No ratings yet
- Worksheet AP Gas LawDocument12 pagesWorksheet AP Gas LawtaipantaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Tut 1Document31 pagesChapter 3 Tut 1Yash KrNo ratings yet
- Che 302 - Last Name, FirstDocument12 pagesChe 302 - Last Name, FirstJEFFRYNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionDocument10 pagesThermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionEarl Maxie Lagdamin ErederaNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Chapter 3 Problems 7th Edition PRDocument25 pagesToaz - Info Chapter 3 Problems 7th Edition PRFiras 01No ratings yet
- Sample Problems - Pure SubstanceDocument6 pagesSample Problems - Pure SubstanceRonalie DavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Tut-1 - Problems - AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Tut-1 - Problems - AnswersArchishman SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Document7 pagesAssignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Ali Hamza ManzoorNo ratings yet
- JuasDocument49 pagesJuasAndrés RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Set 3 AnsDocument12 pagesSet 3 AnsMuhammad Fathi Samsul AnuarNo ratings yet
- AsdqweqDocument2 pagesAsdqweqtrushalvoraNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Presentation ReportDocument8 pagesPresentation ReportJackson ChongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 2Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 4 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Engineers Si Edition 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesThermodynamics For Engineers Si Edition 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualBrianDaviswxfd100% (28)
- Problem SetDocument2 pagesProblem SetLORD BOY SILONGNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law Extra Practice CHALLENGE QUESTIONSDocument7 pagesIdeal Gas Law Extra Practice CHALLENGE QUESTIONSTanisha DamleNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesThermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualRhondaFisherjity100% (57)
- ME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionDocument3 pagesME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionallyhawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Tut 1Document16 pagesChapter 5 Tut 1Yash KrNo ratings yet
- Valdez, Shenny RoseDocument3 pagesValdez, Shenny Roseyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Tut 3Document23 pagesChapter 3 Tut 3Yash KrNo ratings yet
- H MethanolDocument8 pagesH MethanolfaroukNo ratings yet
- Kpa) (10,000 K) K) (673 /KG M Kpa (0.4615Document4 pagesKpa) (10,000 K) K) (673 /KG M Kpa (0.4615CatherineNo ratings yet
- Me 211 Examples SolutionsDocument30 pagesMe 211 Examples SolutionsBryan Dominic Gabriel PaduaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Solution 2012Document35 pagesSheet 3 Solution 2012jp2away68No ratings yet
- Solution of Assignment 2Document9 pagesSolution of Assignment 2Mahmoud AbdelghfarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Tut-2Document24 pagesChapter 8 - Tut-2Raghav ChhaparwalNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Chapter 2 Problems: V 0.002 M V 0.2 MDocument13 pagesSolutions To Chapter 2 Problems: V 0.002 M V 0.2 MJoanne DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PTT 108 Material and Energy Balance: ID = Inner diameter = 1-in. Volume flowrate = 3.00 gal/min A =πrDocument6 pagesTutorial PTT 108 Material and Energy Balance: ID = Inner diameter = 1-in. Volume flowrate = 3.00 gal/min A =πrMohd FaizNo ratings yet
- Problemas CompletosDocument16 pagesProblemas CompletosakksNo ratings yet
- ChemTeam - Assorted Gas Law Problems 1-10Document8 pagesChemTeam - Assorted Gas Law Problems 1-10Koh Jiun AnNo ratings yet
- Koretsky - SolucionárioDocument738 pagesKoretsky - Solucionárioetlrt100% (6)
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2rustam effendyNo ratings yet
- HW 04Document4 pagesHW 04SNo ratings yet
- 122 Chap 5Document36 pages122 Chap 5b166rNo ratings yet
- 101 GasesDocument6 pages101 GasesQaz Zaq100% (1)
- HX 103Document13 pagesHX 103Weng Keat ChongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MED205Document4 pagesTutorial MED205Anonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- Takehome ActivityDocument5 pagesTakehome ActivityEdmond Yurag LLusalaNo ratings yet
- Complete The Following Table For H O:: Chapter 3, Solution 26Document5 pagesComplete The Following Table For H O:: Chapter 3, Solution 26Uriel GuerraNo ratings yet
- COT ANGAN BrendaDocument3 pagesCOT ANGAN Brendayeng botzNo ratings yet
- GATE ThermodynamicsDocument84 pagesGATE ThermodynamicsRajesh Verma75% (4)
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)