Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Physics
Uploaded by
Jamie Wallace0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageMotion represents the continuous change in an object's position over time, which is studied in kinematics. There are two types of motion - uniform motion where an object moves at a constant speed in a straight line, and non-uniform motion where speed or direction changes. Scalar quantities like distance, time, speed and mass only have magnitude and no direction, and are specified by a number and units.
Original Description:
PHYSICS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMotion represents the continuous change in an object's position over time, which is studied in kinematics. There are two types of motion - uniform motion where an object moves at a constant speed in a straight line, and non-uniform motion where speed or direction changes. Scalar quantities like distance, time, speed and mass only have magnitude and no direction, and are specified by a number and units.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pagePhysics
Physics
Uploaded by
Jamie WallaceMotion represents the continuous change in an object's position over time, which is studied in kinematics. There are two types of motion - uniform motion where an object moves at a constant speed in a straight line, and non-uniform motion where speed or direction changes. Scalar quantities like distance, time, speed and mass only have magnitude and no direction, and are specified by a number and units.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Unit 1: Motion
From everyday experience, we recognize that motion represents the
continuous changein the position of an object. Scientists call the study of
motion
kinematics
.
Uniform motion:
movement of an object at a constant speed in a straight line
Non-uniform motion:
movement of an object that involves change in speed or direction or both
Uniform motion examples:
a particle moving in one dimension or walking in a straightline
Non-uniform examples:
a car making a turn as it is in motion or a roller coaster
A
scalar quantity
has only magnitude and no direction. A scalar is a quantity that
iscompletely specified by a number with appropriate units.
Eg. Distance (m), time (s), speed (m/s), # of apples, and mass (kg)As
seen from the specific examples, each scalar quantity consists of units.
These units tell us specific information of an object being studied but lack
direction.
You might also like
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 9: Physics Revision Notes CH 8 (Motion)Document5 pagesClass 9: Physics Revision Notes CH 8 (Motion)Rajdeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 1Document1 pageFormative Assessment 1bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- Motion and VelocityDocument14 pagesMotion and Velocityatiqurrehman0074No ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics ReviewerEliza MaeNo ratings yet
- Phy Exam PrepDocument17 pagesPhy Exam PrepImoduNo ratings yet
- kinematics 5Document9 pageskinematics 5chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Motion NotesDocument5 pagesClass 9 Motion Notesyamamachi2009No ratings yet
- Reference Point: The Point From Which Position Is Measured Usually The Origin or Starting PointDocument2 pagesReference Point: The Point From Which Position Is Measured Usually The Origin or Starting PointJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To KinematicsilyaenoahNo ratings yet
- Sample Physics PPT - Chapter 2 - Motion in One DimensionDocument19 pagesSample Physics PPT - Chapter 2 - Motion in One DimensionSmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Types of MotionDocument4 pagesTypes of MotionCeasar Epsilonian MundalaNo ratings yet
- Motion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsDocument5 pagesMotion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsSandhya RoshanNo ratings yet
- Inquiry ReportDocument10 pagesInquiry ReportScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1Document49 pagesKinematics 1obiekwehenry00No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies (Group 1 Presentation)Document18 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies (Group 1 Presentation)RJ RodzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Dynamics of Rigid BodiesADOBONo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeDocument83 pagesMotion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeTanujNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet For STD 9Document8 pagesPhysics Worksheet For STD 9Amit GulatiNo ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THDocument11 pagesClass-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THBhav GrewalNo ratings yet
- Physics - Introduction and MechanicsDocument65 pagesPhysics - Introduction and Mechanicsstudy2478No ratings yet
- Movement WorkDocument12 pagesMovement WorkScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 9phy CH# 2. Self Assessment and Structured QuestionsDocument8 pages9phy CH# 2. Self Assessment and Structured QuestionsMehmud PashaNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Document8 pagesMotion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Sanaur Talukdar100% (1)
- 7287046397ba2fe8d39c8ea2223d6842Document7 pages7287046397ba2fe8d39c8ea2223d6842rheaNo ratings yet
- Scalar QuantitiesDocument18 pagesScalar QuantitiesPrincess ResterioNo ratings yet
- ENSC 22 Lecture 1 2Document10 pagesENSC 22 Lecture 1 2Cristine Joy CaporadoNo ratings yet
- Motion - Notes - Class 9Document5 pagesMotion - Notes - Class 9demoatlsasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Object Motion Distance Displacement Speed Velocity and Acceleration 202402080229366h6FDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Object Motion Distance Displacement Speed Velocity and Acceleration 202402080229366h6FEmily BautistaNo ratings yet
- Physgen Cu2Document27 pagesPhysgen Cu2emji miraNo ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument2 pagesLinear Motionzhungjian586No ratings yet
- JozeeettDocument4 pagesJozeeettMarifel Amor Dusal PerameNo ratings yet
- KuizDocument4 pagesKuizFarize HashimNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Mechanics: 2.1 Motion in One DimensionDocument8 pagesUnit - Ii Mechanics: 2.1 Motion in One DimensionJit AggNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - NotesDocument1 pageDynamics - NotesRoel SebastianNo ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument88 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineRonald Abrasaldo SatoNo ratings yet
- P Week II Kinematics IxDocument17 pagesP Week II Kinematics IxSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- High School Physics Notes (Kinematics)Document72 pagesHigh School Physics Notes (Kinematics)Zach David100% (2)
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDocument2 pagesChapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDivayam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics-Motion NotesDocument7 pagesPhysics-Motion Notesashwinnayar12No ratings yet
- Motion - Short NotesDocument2 pagesMotion - Short Notesalok.coding123No ratings yet
- kinematics 3Document4 pageskinematics 3chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- 03 Motion in A Straight LineDocument25 pages03 Motion in A Straight Linekarjuna815No ratings yet
- MotionDocument34 pagesMotionAbdullah MamunNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4 Pt. 1Document23 pagesWeek 3 and 4 Pt. 1Bradley HausNo ratings yet
- MOTION_L1_SCIENCE_CLASS_9_CBSE_BY_ASHU_SIRDocument17 pagesMOTION_L1_SCIENCE_CLASS_9_CBSE_BY_ASHU_SIRgapna001No ratings yet
- MotionDocument25 pagesMotionJuhi MahendraNo ratings yet
- 3 KinematicsDocument101 pages3 Kinematicsmustafa100% (1)
- Motion NcertDocument16 pagesMotion NcertRanjith RajNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument14 pagesKinematicsKhawaja EshaNo ratings yet
- Aees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 MotionDocument5 pagesAees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 Motionseenu nadarajanNo ratings yet
- Seven Fundamental Quantities of Measurement: SI Solid AngleDocument3 pagesSeven Fundamental Quantities of Measurement: SI Solid AngleTrixy Cueto CamotaNo ratings yet
- 4ch1 2cr Que 20230614Document24 pages4ch1 2cr Que 20230614Abdullah HeshamNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Systems Engineering 4th Messenger Solution ManualDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic Systems Engineering 4th Messenger Solution ManualJesus Carter100% (41)
- 2020 Ignite K3 Set Up GuideDocument30 pages2020 Ignite K3 Set Up GuidedjeisnerNo ratings yet
- Brochurre Abbemat 300, 350,500Document7 pagesBrochurre Abbemat 300, 350,500moriz52No ratings yet
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 83Document1 pageSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 83mydearteacherNo ratings yet
- Re50212 2007-04Document8 pagesRe50212 2007-04ministryofrapNo ratings yet
- What Are Pushes and Pulls?: Consolidation WorksheetDocument9 pagesWhat Are Pushes and Pulls?: Consolidation WorksheetOsvaldo Ola YaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Topics: Patterns and Numbers in Nature of The WorldDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Topics: Patterns and Numbers in Nature of The WorldPamela AmitNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument429 pagesService ManualChris CoulsonNo ratings yet
- RFI Radiographic Film Interpretation 30 - October - 2020Document7 pagesRFI Radiographic Film Interpretation 30 - October - 2020SUNIL BABURAO GAVADENo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument97 pagesFluid MechanicsABDFERNo ratings yet
- Improving Customer Service Operations atDocument24 pagesImproving Customer Service Operations atssanchet1981No ratings yet
- Ingarden Literary Work of ArtDocument4 pagesIngarden Literary Work of ArtDiana M.0% (1)
- Tower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularDocument2 pagesTower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularResti OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Percentile: ClassesDocument18 pagesPercentile: ClassesVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- 28-7-2019 Thesis@Jahidul IslamDocument52 pages28-7-2019 Thesis@Jahidul IslamMd. Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Review Questionsdee eeNo ratings yet
- MS Paint ComputerDocument11 pagesMS Paint ComputerLiza JeonNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring Through Non Destructive TechniqueDocument27 pagesCondition Monitoring Through Non Destructive Techniquepraveenkumar_bs2005No ratings yet
- Checkpoint KB Usefull LinksDocument11 pagesCheckpoint KB Usefull Linkspepekovalp1No ratings yet
- Pury P168tlmu A Bs 208 230v ProductdatasheetDocument2 pagesPury P168tlmu A Bs 208 230v ProductdatasheetLee ChorneyNo ratings yet
- Dzexams 1am Anglais 2161233Document2 pagesDzexams 1am Anglais 2161233أبو إياد بوزيدNo ratings yet
- Electric Guitar GuideDocument26 pagesElectric Guitar GuideGerardo Delgado100% (1)
- The Data.: Question 1: Create A Table Insert Records and ManipulateDocument32 pagesThe Data.: Question 1: Create A Table Insert Records and ManipulateSSC CHSL100% (1)
- BIDM RegDocument2 pagesBIDM RegSagar DamaniNo ratings yet
- PowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release NotesDocument23 pagesPowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release Noteskasimmsn0% (1)
- AMA46 3sum TarlBerry GeometricdesignoffruitpackaginginRSA PublishedDocument10 pagesAMA46 3sum TarlBerry GeometricdesignoffruitpackaginginRSA PublishedKosin HachaweeNo ratings yet
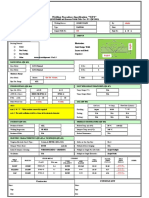
- WPS For A333 ADocument1 pageWPS For A333 ARamzi BEN AHMED100% (1)
- Transaksi Ngfeb15Document76 pagesTransaksi Ngfeb15hasta primaNo ratings yet
- 2008 Bookmatter FluidMechanics PDFDocument60 pages2008 Bookmatter FluidMechanics PDFDaniela Forero RamírezNo ratings yet