Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bond Mill Throughput
Bond Mill Throughput
Uploaded by
Genaro MachacaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bond Mill Throughput
Bond Mill Throughput
Uploaded by
Genaro MachacaCopyright:
Available Formats
About the Bond_Mill Throughput Spreadsheet ...
Scope :
The Bond_Mill Throughput spreadsheet was designed to estimate the Grinding Capacity of a given mill of known
dimensions and operating conditions - Net Power Draw in particular - based on the traditional Bond's Law and the Hogg
& Fuersteneau Power Model (see Mill Power_Ball Mills spreadsheet for further details on such model).
Theoretical Framework :
Undoubtedly, the extensive work of Fred C. Bond ("The Third Theory of Comminution", AIME Trans.,Vol. 193, p. 484,
1952. Also in Mining Engineering, May 1952) has been widely recognized as a very significant contribution to a first
understanding of the operational response of conventional ball mills in various grinding circuits. His Third Theory or
"Law" of Comminution has become the most traditionally accepted framework for the evaluation of existing grinding
operations as well as the design of new installations :
E = 10 Wi (1/P801/2 1/F801/2)
where :
E
F80
P80
Wi
=
=
=
=
Specific Energy Consumption, kWh/ton ground.
80% passing size in the Fresh Ore Feed Stream, microns.
80% passing size in the Final Ground Product, microns.
Bond's Work Index, indicative of the hardness of the ore, kWh/ton.
The Bond's Law so allows, as a first approach, to estimate the energy demand (kWh) required to grind each ton of ore.
Such Specific Energy Consumption determines in turns the Capacity of the grinding section, by the expression :
M = P/E
where :
M
P
= Fresh Ore Throughput (not including Circulating Load), ton/hr.
= Net Mill Power Demand, kW.
Bond's Work Index may be estimated directly from operational data (whenever available) from back-calculation of the first
equation above. In such case is denoted as the Operational Work Index :
Wio = E / 10 (1/P801/2 1/F801/2)
Data Input :
All data required by the calculation routine must be defined in each corresponding unprotected white background cell of
the here attached Data File worksheet. Gray background cells contain the results of the corresponding formulas there
defined and are protected to avoid any accidental editing.
Moly-Cop Tools / 320926388.xls
06/12/2016 / 20:04:42
Moly-Cop Tools / 320926388.xls
06/12/2016 / 20:04:42
Moly-Cop Tools
TM
(Version 2.0)
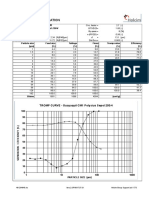
BOND'S LAW APPLICATION
Estimation of a Conventional Ball Mill Grinding Capacity
Remarks
Base Case Example
GRINDING TASK :
Ore Work Index, kWh/ton (metric)
Feed Size, F80, microns
Product Size, P80, microns
Total Plant Throughput, ton/hr
13.00
9795
150.0
835.30
Specific Energy, kWh/ton
Net Power Available, kW
Number of Mills for the Task
Net kW / Mill
Mill
Power, kW
3348
0
536
3885
10.0
4316
Balls
Overfilling
Slurry
Net Total
% Losses
Gross Total
Mill Charge Weight, tons
Ball
Slurry
Charge
Interstitial
above Balls
296.48
47.48
0.00
Apparent
Density
ton/m3
5.395
MILL DIMENSIONS AND OPERATING CONDITIONS :
Eff. Diameter
ft
18.50
Eff. Length
ft
22.00
L/D
1.189
% Solids in the Mill
Ore Density, ton/m3
Slurry Density, ton/m3
Balls Density, ton/m3
Moly-Cop Tools / 320926388.xls
Mill Speed
% Critical
72.00
rpm
12.82
72.00
2.80
1.86
7.75
Charge
Filling,%
38.00
Balls
Interstitial
Filling,%
Slurry Filling,%
38.00
100.00
Charge
Volume,
m3
63.76
9.30
7769
2
3885
Lift
Angle, ()
35.00
06/12/2016 / 20:04:42
You might also like
- Multistage Flowsheets SampleDocument1 pageMultistage Flowsheets SampleDanny joaquinNo ratings yet
- The Selection and Design of Mill LinersDocument11 pagesThe Selection and Design of Mill Linersluis martinezNo ratings yet
- LGDocument12 pagesLGFaisal Khan JaisiNo ratings yet
- Imposition Studio User GuideDocument45 pagesImposition Studio User Guidemrclprnt100% (1)
- Bond Mill ThroughputDocument5 pagesBond Mill ThroughputAnonymous TsKN7XZBNo ratings yet
- Bond Op. Work IndexDocument3 pagesBond Op. Work IndexDiego Galicia100% (1)
- Bond Mill SizingDocument3 pagesBond Mill SizingDidi Paul Huilca RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Teoria de BondDocument8 pagesTeoria de BondMarcelaChavezNo ratings yet
- Grinding Plants-Optimization and ModellingDocument12 pagesGrinding Plants-Optimization and ModellingaghilifNo ratings yet
- CERRO VERDE-HPGRSim - OpenDocument85 pagesCERRO VERDE-HPGRSim - OpenCezar JulNo ratings yet
- Hpgrsim OpenDocument83 pagesHpgrsim OpenCarlos DiazNo ratings yet
- Fuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Document5 pagesFuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Christofer EspinozaNo ratings yet
- SAGDesign Mill Throughput Calculation ToolDocument10 pagesSAGDesign Mill Throughput Calculation ToolLuis Daniel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Mill Power SAG MillsDocument5 pagesMill Power SAG MillsRolando QuispeNo ratings yet
- Media Charge - Linear Wear - Ball MillsDocument5 pagesMedia Charge - Linear Wear - Ball MillsLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Single Stage Sag-Ag Milling DesignDocument11 pagesSingle Stage Sag-Ag Milling DesignrobigedNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Grinding EfficiencyDocument27 pagesFactors Influencing The Grinding Efficiencygrameshkreddy2013No ratings yet
- A New Autogenous and Semi-Autogenous Mill Model For Scale-Up, Design and OptimisationDocument9 pagesA New Autogenous and Semi-Autogenous Mill Model For Scale-Up, Design and OptimisationJuanOlivaresNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of The Bond Method For Sizing Wet Tumbling Mills With A Size Mass Balance Simulation ModelDocument14 pagesA Comparison of The Bond Method For Sizing Wet Tumbling Mills With A Size Mass Balance Simulation ModelJavier Enrique Toro YentzenNo ratings yet
- Media Charge - Linear Wear - Ball MillsDocument5 pagesMedia Charge - Linear Wear - Ball MillsLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Power Drawn by Grinding MediaDocument5 pagesPower Drawn by Grinding MediaanruloNo ratings yet
- AG and SAG Mill Circuit Selection and Design by SimulationDocument22 pagesAG and SAG Mill Circuit Selection and Design by Simulationbob2341No ratings yet
- Some Observations Regarding SAG MillingDocument5 pagesSome Observations Regarding SAG MillingLevent ErgunNo ratings yet
- BallParam BatchDocument16 pagesBallParam BatchAnonymous TsKN7XZBNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Single Stage Autogenous and Semiautogenous Grinding MillsDocument12 pagesAn Overview of Single Stage Autogenous and Semiautogenous Grinding Millsjosesejo123No ratings yet
- Ball Mill Grinding Media Max Ball Size CalculationDocument2 pagesBall Mill Grinding Media Max Ball Size Calculationvvijaybhan100% (1)
- BallSim OpenDocument44 pagesBallSim OpenGonzalo LopezNo ratings yet
- Media Charge Dynamics Ball MillsDocument31 pagesMedia Charge Dynamics Ball Millsedwin javier valdivia guillenNo ratings yet
- Paper # 153 - The Appropriateness of The Transfer Size in Ag and Sag Mill Circuit DesignDocument13 pagesPaper # 153 - The Appropriateness of The Transfer Size in Ag and Sag Mill Circuit Designcuberbill1980No ratings yet
- Mill Calculation: Plant: Date: Mill: VisaDocument2 pagesMill Calculation: Plant: Date: Mill: VisaThaigroup CementNo ratings yet
- Guide Grind Plants 3rd Edition11 PDFDocument53 pagesGuide Grind Plants 3rd Edition11 PDFTOULASSI-ANANI Yves Lolo0% (1)
- Multi-Component AG-SAG Mill Model JK PDFDocument10 pagesMulti-Component AG-SAG Mill Model JK PDFNicolas PerezNo ratings yet
- Mediacharge TrajectoriesDocument8 pagesMediacharge TrajectoriesRolando QuispeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Grinding Media Wear-Rate by A Combined Grinding MethodDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Grinding Media Wear-Rate by A Combined Grinding MethodW ZuoNo ratings yet
- Procemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsDocument25 pagesProcemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsNereo SpenglerNo ratings yet
- Scope:: About The Ballparam - Dual Spreadsheet ..Document57 pagesScope:: About The Ballparam - Dual Spreadsheet ..lewis poma rojasNo ratings yet
- Mill Calculation: Plant: Date: Mill: VisaDocument2 pagesMill Calculation: Plant: Date: Mill: VisaIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Application of High Chrome Grinding Media at MMG Century Mine For Improved Grinding Media Consumption and Metallurgy PerformanceDocument15 pagesThe Application of High Chrome Grinding Media at MMG Century Mine For Improved Grinding Media Consumption and Metallurgy PerformanceYaser Mohamed Abas100% (1)
- Media Charge - Optimal Ball SizeDocument6 pagesMedia Charge - Optimal Ball SizeMetalurgia ProcesosNo ratings yet
- SDM Mill CalcsDocument6 pagesSDM Mill CalcsHoàng HùngNo ratings yet
- 02 Comminution TheoryDocument28 pages02 Comminution TheoryPham tony1604No ratings yet
- Ball Mill SimulatorDocument4 pagesBall Mill SimulatorIrshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Study of The Grinding Balls Distribution Inside The MillDocument2 pagesStudy of The Grinding Balls Distribution Inside The Millsempatik721100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Comminution and Energy Requirement For Size ReductionDocument18 pagesLecture 3 Comminution and Energy Requirement For Size ReductionKhana Rizki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Comminution Circuit DesignDocument17 pagesComminution Circuit DesignW ZuoNo ratings yet
- BM TrompcurveDocument1 pageBM Trompcurveniladri.jagatyNo ratings yet
- Power-Based Comminution Calculations Using AusgrindDocument12 pagesPower-Based Comminution Calculations Using AusgrindW ZuoNo ratings yet
- Design of The 40 Foot Diameter SAG Mill Installed at The Cadia Gold Copper Mine, R. DunneDocument8 pagesDesign of The 40 Foot Diameter SAG Mill Installed at The Cadia Gold Copper Mine, R. DunneNicolas MirandaNo ratings yet
- Ball MillDocument3 pagesBall MillTeeTee PenGen SetiyaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Comminution Testwork Results in SAG Mill DesignDocument16 pagesThe Use of Comminution Testwork Results in SAG Mill DesignLevent ErgunNo ratings yet
- Mill Ops AusIMM Kirsch and DanielDocument7 pagesMill Ops AusIMM Kirsch and DanielMicheael JohnNo ratings yet
- Power-Based Comminution Calculations Using AusgrindDocument13 pagesPower-Based Comminution Calculations Using AusgrindMarcos Bueno100% (1)
- Communition Theory Reference and FormulasDocument10 pagesCommunition Theory Reference and Formulasharishkumar.ravichandranNo ratings yet
- Scope:: About The Ballbal - Reverse Spreadsheet ..Document15 pagesScope:: About The Ballbal - Reverse Spreadsheet ..julio carpio Franco100% (1)
- Scope:: & Fuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Document2 pagesScope:: & Fuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Mauro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Document3 pagesFuersteneau Power Model (See Mill Power - Ball Mills Spreadsheet For Further Details On Such Model)Rolando QuispeNo ratings yet
- Mediacharge Dynamics BallMillsDocument30 pagesMediacharge Dynamics BallMillstanainaNo ratings yet
- #12. Doll-Simonian-Bond-s Work Index - What It Is and What It Isn-T-Thumbnail - ThumbnailDocument13 pages#12. Doll-Simonian-Bond-s Work Index - What It Is and What It Isn-T-Thumbnail - ThumbnailCristian CanazaNo ratings yet
- SAG2019 Doll Simonian-BondWiDocument13 pagesSAG2019 Doll Simonian-BondWiAbdulrahim SegirNo ratings yet
- Media Charge - Wear & Impact - SAG MillsDocument9 pagesMedia Charge - Wear & Impact - SAG MillsAldo PabloNo ratings yet
- Toscotec - Pratical Applications For Energy Consumption ReductionDocument7 pagesToscotec - Pratical Applications For Energy Consumption ReductionKoushik MadapatiNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument1 pageFormulaGenaro MachacaNo ratings yet
- Invent A RiosDocument9 pagesInvent A RiosGenaro MachacaNo ratings yet
- AÑO Semestre Escala PuntajeDocument39 pagesAÑO Semestre Escala PuntajeGenaro MachacaNo ratings yet
- DRBC Workshop Water System Audits and Water Loss Control Module 2 Session 2Document31 pagesDRBC Workshop Water System Audits and Water Loss Control Module 2 Session 2Genaro MachacaNo ratings yet
- Gamification in Teaching PPT Final N Talaga ItoDocument35 pagesGamification in Teaching PPT Final N Talaga ItoEmerson Delima MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Warfare Iranian and Russian Versions of "Little Green Men" and Contemporary ConflictDocument17 pagesHybrid Warfare Iranian and Russian Versions of "Little Green Men" and Contemporary ConflictVICENTE JOSUE AULAR RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- FortiManager DatasheetDocument13 pagesFortiManager DatasheetmagnusfischerNo ratings yet
- ProcessesValueStreams&Capabilities RosenDocument4 pagesProcessesValueStreams&Capabilities RosenAndré SousaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets and Performance AnalysisDocument37 pagesFlexible Budgets and Performance AnalysisSana IjazNo ratings yet
- CSS Syllabus 2023 PDF Download - FPSCDocument8 pagesCSS Syllabus 2023 PDF Download - FPSCshahid Ramzan0% (1)
- Orafol Wrapping Films: Product Summary SheetDocument4 pagesOrafol Wrapping Films: Product Summary SheetAgung SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade Boundaries - June 2019 Exams Oxfordaqa International GcseDocument3 pagesSubject Grade Boundaries - June 2019 Exams Oxfordaqa International GcseHala ShetaNo ratings yet
- Photocopiable Activities Teacher's NotesDocument29 pagesPhotocopiable Activities Teacher's NotesbrayanNo ratings yet
- The Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesThe Passive VoiceДинараNo ratings yet
- 6.334 Power Electronics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument4 pages6.334 Power Electronics: Mit OpencoursewareLocalized Prayer AppNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001 Module II-Lecture 2 Urea ProductionDocument12 pagesChemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001 Module II-Lecture 2 Urea ProductionU SANKAR TEJONo ratings yet
- Ttlga 1250Document2 pagesTtlga 1250anerak0412No ratings yet
- X-Plane Installer LogDocument3 pagesX-Plane Installer LogMarsala NistoNo ratings yet
- MKTG 5th Canadian EditionDocument418 pagesMKTG 5th Canadian EditionArturo VeranoNo ratings yet
- Methods of Matrix InversionDocument17 pagesMethods of Matrix InversionPaawanDubalNo ratings yet
- 1978 Handbook of Birds of India and Pakistan Vol 1 by Ali and Ripley S PDFDocument481 pages1978 Handbook of Birds of India and Pakistan Vol 1 by Ali and Ripley S PDFsreelathapNo ratings yet
- Born To WinDocument23 pagesBorn To WinSuvra PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Aditya Solanki Expriment No.2Document5 pagesAditya Solanki Expriment No.2Kertik SinghNo ratings yet
- For Health Week2Document23 pagesFor Health Week2Mary Grace CatubiganNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 2015 Quality Manual Template For Service IndustryDocument21 pagesISO 9001 2015 Quality Manual Template For Service IndustryJose Luis Zimic100% (1)
- Pile Cutting / Hacking (Sub-Structure Work)Document2 pagesPile Cutting / Hacking (Sub-Structure Work)Rahmat HariNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Engl 1010Document3 pages1.1 Engl 1010Joey ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study On The Billones Family 1Document63 pagesFamily Case Study On The Billones Family 1Ivy Mae DecenaNo ratings yet
- C1 UseDocument4 pagesC1 UseMichał JanickiNo ratings yet
- PDU-G1, 2: UHF Sensor For Partial Discharge Monitoring of GIS/GILDocument2 pagesPDU-G1, 2: UHF Sensor For Partial Discharge Monitoring of GIS/GILHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- BCA Notes FinalDocument150 pagesBCA Notes Finalsahil vermaNo ratings yet
- Tangerine DreamDocument6 pagesTangerine DreamPedro BricenoNo ratings yet