Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buzzer
Buzzer
Uploaded by
NationalinstituteDsnr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
346 views2 pagesA buzzer is an audio signaling device that can be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Mechanical buzzers operate purely through motion like a bicycle bell, while electromechanical buzzers use an electromagnet activated by alternating or direct current to vibrate a plate or diaphragm and produce sound. Piezoelectric buzzers contain an electronic oscillator and inductor to generate high voltage pulses that drive a piezoelectric transducer and create a high pitched beeping tone.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA buzzer is an audio signaling device that can be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Mechanical buzzers operate purely through motion like a bicycle bell, while electromechanical buzzers use an electromagnet activated by alternating or direct current to vibrate a plate or diaphragm and produce sound. Piezoelectric buzzers contain an electronic oscillator and inductor to generate high voltage pulses that drive a piezoelectric transducer and create a high pitched beeping tone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
346 views2 pagesBuzzer
Buzzer
Uploaded by
NationalinstituteDsnrA buzzer is an audio signaling device that can be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Mechanical buzzers operate purely through motion like a bicycle bell, while electromechanical buzzers use an electromagnet activated by alternating or direct current to vibrate a plate or diaphragm and produce sound. Piezoelectric buzzers contain an electronic oscillator and inductor to generate high voltage pulses that drive a piezoelectric transducer and create a high pitched beeping tone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
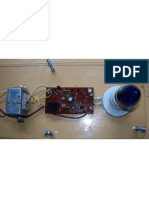
BUZZER
A buzzer is an audio signaling device, which may be mechanical,
electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Typical uses of buzzers include alarm
devices, timers and confirmation of user input such as a keystroke.
Mechanical:
Bicycle bell is an example of a purely mechanical buzzer.
Electromechanical
An electromagnet is the main part of all types of electromechanical
buzzers. These may be either AC operated or DC operated. In AC buzzers,
the AC Mains voltage is applied to an electromagnet coil. The alternating
voltage induced in the coil generates a varying magnetic field in
accordance to the applied voltage, which in turn vibrates an iron plate to
produce the required audible buzzing sound.
In DC buzzers as used in vehicles, when a DC battery voltage is applied to
its electromagnet, it pulls an iron diaphragm. Due to this the
electromagnet is switched OFF, the diaphragm is released to its original
position when again the DC supply is restored to repeat the cycle. This
cycle repeats at a very high speed to generate the typical loud honk from
it.
Piezoelectric
Electronic buzzers mostly used a piezo electric transducer. They operate
at very low currents and produce high pitched, sharp beeping sounds. The
heart of the circuit of piezo electric buzzers is an electronic oscillator. The
alternating voltage produced by the oscillator is dumped into an inductor
which effectively converts these signals into high voltage pulses to drive
the piezo electric transducer and produce an audible sound.
You might also like
- Mini Inverter Mini Project Report.Document34 pagesMini Inverter Mini Project Report.sravan75% (32)
- Automatic Speed Control For Fans and CoolersDocument54 pagesAutomatic Speed Control For Fans and CoolersPrudhvi Raj63% (8)
- Machine Lesson Final1Document94 pagesMachine Lesson Final1anon_156286001100% (8)
- Modeling of Arduino-Based Prepaid Energy Meter Using GSM TechnologyDocument3 pagesModeling of Arduino-Based Prepaid Energy Meter Using GSM TechnologyNationalinstituteDsnr0% (1)
- ReportDocument16 pagesReportMelinette QuilanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Introduction of Mini InverterDocument34 pagesChapter - I: Introduction of Mini InverterMayankNo ratings yet
- PUI ElectromechanicalTransducersDocument3 pagesPUI ElectromechanicalTransducersDragana JovanovićNo ratings yet
- Project Electrical Equipments Control Through SoundDocument44 pagesProject Electrical Equipments Control Through SoundMicron MegaNo ratings yet
- Summary of DC GeneratorDocument10 pagesSummary of DC GeneratorChristopher YsitNo ratings yet
- Mini Inverter Mini Project ReportDocument29 pagesMini Inverter Mini Project ReportSasanga HewagamaNo ratings yet
- Standard Electrical Symbols For Electrical Schematic DiagramsDocument8 pagesStandard Electrical Symbols For Electrical Schematic DiagramsDen Mark AlbayNo ratings yet
- Electronics AssDocument2 pagesElectronics AssajlouiseibanezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 2 Earthing, DBDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Part 2 Earthing, DBNaman JainNo ratings yet
- Wts 12 Physcs ElectrodynamicsDocument12 pagesWts 12 Physcs Electrodynamicsmngomezuluphiwokuhle2No ratings yet
- Alternator Part I Eac ReviewDocument15 pagesAlternator Part I Eac ReviewKevin MaramagNo ratings yet
- Ac/Dc Machines: Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument20 pagesAc/Dc Machines: Electromechanical Energy ConversionAshner NovillaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Lecture# 1Document4 pagesIndustrial Electronics Lecture# 1Hamza Tariq100% (1)
- Electrical SymbolsDocument9 pagesElectrical SymbolsNur Hafizah RazaliNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document-9Document1 pageUntitled Document-9xboxmallet5No ratings yet
- Presentation On DVR, JS Saroya, CS Singh, 03.12.11Document75 pagesPresentation On DVR, JS Saroya, CS Singh, 03.12.11Amit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Ass#1Document4 pagesAss#1Jay EyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - InverterDocument9 pagesTopic 4 - InverterAvinesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Inverter Based ProjectsDocument22 pagesInverter Based Projectssetsindia3735No ratings yet
- Selection of Various Types of Inverter - (Part-1) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument8 pagesSelection of Various Types of Inverter - (Part-1) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesRahul ItaliyaNo ratings yet
- CSY ReportDocument22 pagesCSY ReportKaushik BisenNo ratings yet
- How Is Ac Voltage Produced?Document4 pagesHow Is Ac Voltage Produced?Mariappan NaNo ratings yet
- Why An Electronic Choke Circuit Diagram Is ImportantDocument10 pagesWhy An Electronic Choke Circuit Diagram Is ImportantjackNo ratings yet
- An Active Circuit For Cancellation of Common-Mode Voltage Generated by A PWM InverterDocument8 pagesAn Active Circuit For Cancellation of Common-Mode Voltage Generated by A PWM InverterPratiksha ShindeNo ratings yet
- The Working Principles of AC Machines Can Be Explained Based On The Specific Type of AC MachineDocument2 pagesThe Working Principles of AC Machines Can Be Explained Based On The Specific Type of AC MachineSaurabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- WTS 12 ElectrodynamicsDocument28 pagesWTS 12 ElectrodynamicsTondani100% (1)
- Lec 2 - Fundamentals DC Machine - EEE 2205Document59 pagesLec 2 - Fundamentals DC Machine - EEE 2205Nasif TahmidNo ratings yet
- InverterDocument22 pagesInvertersetsindiaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical SystemDocument18 pagesAircraft Electrical SystemAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Physic Project Aksukit Ix ADocument7 pagesPhysic Project Aksukit Ix AAksukitz AungNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Origin and History of AC GeneratorsDocument58 pages1.0 Origin and History of AC GeneratorsAlfred AgihNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy Conversion: DC ACDocument26 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversion: DC ACNoel BactonNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocument10 pagesElectro Magnetic InductionBashoriie SAng MusafierNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 DC GeneratorDocument9 pagesLesson 2 DC GeneratormarpelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Experiment.Document5 pagesElectrical Technology Experiment.Joseph KavinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Instrument: Digital Multimeter DMMDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Instrument: Digital Multimeter DMMUzair AzziNo ratings yet
- DFDFDFDG SFDGDGFDocument5 pagesDFDFDFDG SFDGDGFmongiagoldyNo ratings yet
- ELECTRODYNAMOMETERDocument14 pagesELECTRODYNAMOMETERaisyahNo ratings yet
- AC To DC ParametersDocument4 pagesAC To DC ParametersJehnen BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Bells and AlarmsDocument17 pagesBells and Alarmsmedassan7100% (1)
- How Does A Power Inverter Work?: Inverters Can Also Be Used With Transformers To Change A Certain DC Input Voltage IntoDocument15 pagesHow Does A Power Inverter Work?: Inverters Can Also Be Used With Transformers To Change A Certain DC Input Voltage Intoshubham choudharyNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument5 pagesProject ProposalSarmast Bilawal Khuhro0% (1)
- Physcis Ac Generator ReportDocument15 pagesPhyscis Ac Generator ReportVishal Hirrtik100% (1)
- Mini Project DocumentationDocument57 pagesMini Project DocumentationSindhuja ThogaruNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Generation and Excitation SystemDocument20 pagesElectric Power Generation and Excitation SystemMansen NsubugaNo ratings yet
- AlternatorDocument23 pagesAlternatorpremameNo ratings yet
- 1 4 5 HornDocument2 pages1 4 5 HornShambhuNath VermaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines (31-141 Page)Document111 pagesElectrical Machines (31-141 Page)judieNo ratings yet
- Speaker & Amplifier: Ayush Saini-CH12B1005 Harmanpreet Singh-CS12B1017 Udhav Sethi-ES12B1022Document10 pagesSpeaker & Amplifier: Ayush Saini-CH12B1005 Harmanpreet Singh-CS12B1017 Udhav Sethi-ES12B1022qwertyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Level Iii Full NoticeDocument87 pagesElectrical Level Iii Full NoticeDaniel Madulu CharlesNo ratings yet
- Power InverterDocument10 pagesPower Inverterdakshina656087100% (1)
- FINAL ET NOTES-5 UnitsDocument121 pagesFINAL ET NOTES-5 Unitsbapiraju saripellaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic Induction TransformersDocument10 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic Induction Transformersapi-245497801No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- A Data Mining Based Model For Detection of Fraudulent Behaviour in Water ConsumptionDocument7 pagesA Data Mining Based Model For Detection of Fraudulent Behaviour in Water ConsumptionNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Pat AnjaDocument1 pagePat AnjaNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- IJTRD163Document5 pagesIJTRD163NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Heart Beat Monitoring and Intimate by GSM at Abnormal Condition1522869000Document2 pagesHeart Beat Monitoring and Intimate by GSM at Abnormal Condition1522869000NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Social Distancing Monitoring Robot For QueueDocument2 pagesSocial Distancing Monitoring Robot For QueueNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Voice Controlled Robotic Vehicle1534238864Document2 pagesVoice Controlled Robotic Vehicle1534238864NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Sensor Guided Robotics Using Ir Sensors and by Programming Micro Controller1550049190Document1 pageSensor Guided Robotics Using Ir Sensors and by Programming Micro Controller1550049190NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Letter Box Using Arduino and GSM1554330059Document2 pagesIntelligent Letter Box Using Arduino and GSM1554330059NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Opinion Minning On Feedback Management SystemDocument10 pagesOpinion Minning On Feedback Management SystemNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On: Consumer's Perception Towards Packaged Cold-Pressed Juices and Brand " PVT LTDDocument3 pagesA Synopsis On: Consumer's Perception Towards Packaged Cold-Pressed Juices and Brand " PVT LTDNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- ECE517 Project Fall2019 PDFDocument1 pageECE517 Project Fall2019 PDFNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Motorized Barrel LifterDocument1 pageFabrication of Motorized Barrel LifterNationalinstituteDsnr100% (1)
- Constructionprojectmanagemen PDFDocument1 pageConstructionprojectmanagemen PDFNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Mitigation Using 36-Pulse AC-DC Converter For Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor DrivesDocument10 pagesHarmonic Mitigation Using 36-Pulse AC-DC Converter For Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor DrivesNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Authentication by Encrypted Negative PasswordDocument3 pagesAuthentication by Encrypted Negative PasswordNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- Budgets and Budgetary Control of NFC (Nuclear Fuel Complex) 1583247683Document52 pagesBudgets and Budgetary Control of NFC (Nuclear Fuel Complex) 1583247683NationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet
- A Study On Budgetary Control at HDFC1567681191 PDFDocument28 pagesA Study On Budgetary Control at HDFC1567681191 PDFNationalinstituteDsnrNo ratings yet