Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Uploaded by
GeneBhooiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- LipidsDocument25 pagesLipidsJeaniee Zosa Ebias50% (10)
- Saponification of SoapDocument11 pagesSaponification of SoapMsfaeza Hanafi80% (5)
- Synthesis of SoapDocument34 pagesSynthesis of SoapAlex Atienza100% (1)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry ProjectHameed Ahmed Khas KheliNo ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument1 pageSaponificationscholar peterNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationHritik LalNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.Document16 pagesLab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.niniwani59No ratings yet
- Lab 6 (Soaps & Detergents)Document21 pagesLab 6 (Soaps & Detergents)AmeerRashidNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstract903l.arivazhagan1977No ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument4 pagesSaponificationtedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Syntheses of Soaps and DetergentsDocument2 pagesSyntheses of Soaps and DetergentsClare CariñoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5bDocument4 pagesExperiment 5bKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- Soap ReportDocument16 pagesSoap ReportAddison JuttieNo ratings yet
- SoapDocument15 pagesSoapindumathijayakaranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Soap DetergentDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Soap DetergentTiny100% (5)
- Lipid Solubility in Dilute Acid and Dilute AlkaliDocument11 pagesLipid Solubility in Dilute Acid and Dilute AlkaliCyrene Grace BrionesNo ratings yet
- Soap PDFDocument3 pagesSoap PDFanna marieNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of Organic CompoundsDocument96 pagesThe Synthesis of Organic CompoundsDoroteo Jose StationNo ratings yet
- That They Have Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic RegionsDocument4 pagesThat They Have Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic RegionsChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- PJONDocument3 pagesPJONhafizul188No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument26 pagesChemistry ProjectMaster PrateekNo ratings yet
- Practicals InvestagatoryDocument3 pagesPracticals InvestagatorysanyamskismnNo ratings yet
- EXP6 Soap and DetergentheheDocument19 pagesEXP6 Soap and DetergenthehesamengNo ratings yet
- Lipid Jurnal KevinDocument12 pagesLipid Jurnal KevinErik Pavel EredNo ratings yet
- L I P I D SDocument42 pagesL I P I D SCindy FelixNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument2 pagesLIPIDSIshen MaujiNo ratings yet
- Soap Making and Fats TestingDocument94 pagesSoap Making and Fats TestingEra MelaniaNo ratings yet
- 9 Lipids SaponificationDocument12 pages9 Lipids SaponificationAlyssa De Jesus AgustinNo ratings yet
- 12 - Analysis of LipidsDocument15 pages12 - Analysis of LipidsLIAN KEI HILADONo ratings yet
- Frothing Power of SoapDocument3 pagesFrothing Power of SoapT sidharthNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Soap and DetergentDocument16 pagesLab 6 - Soap and DetergentamiraaikharahNo ratings yet
- Brain Lipid WrittenDocument19 pagesBrain Lipid WrittenAldwin Ray Pamplona100% (2)
- Experiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesJobel De Pedro100% (4)
- SOAPS and DetergentsDocument66 pagesSOAPS and DetergentsMkhalilizul SiHamba CintaIlahi100% (1)
- Chem Lab (Soaps)Document19 pagesChem Lab (Soaps)Amiro Iqbal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Soap DetergentDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Soap DetergentHarvey Mher RarangNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Complete (Preparation of Soap)Document15 pagesLab 6 Complete (Preparation of Soap)mirdza94No ratings yet
- Esterification and SaponificationDocument24 pagesEsterification and SaponificationpasatiemporoseanneNo ratings yet
- Lipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AreDocument8 pagesLipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AregymnasrischerNo ratings yet
- Lipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AreDocument8 pagesLipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AregymnasrischerNo ratings yet
- Summary For Integrated Science Term 1Document6 pagesSummary For Integrated Science Term 1Tshawna RockNo ratings yet
- Saponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Document5 pagesSaponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Anonymous UoRu4sNo ratings yet
- Chemical For ConsumersDocument17 pagesChemical For ConsumersBjergsenNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of A Soap: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesPreparation and Properties of A Soap: ObjectiveBodhi Satwa MishraNo ratings yet
- Atikah Punya Jugak...Document26 pagesAtikah Punya Jugak...Ika BakarNo ratings yet
- Theory: Mechanism of SaponificationDocument4 pagesTheory: Mechanism of SaponificationA/P MARICHELVAN PRADEBANo ratings yet
- Preparation of Toilet SoapsDocument4 pagesPreparation of Toilet Soapspradyumansharmaj333No ratings yet
- Preparation of Quinoa SoapafgdvdfDocument5 pagesPreparation of Quinoa SoapafgdvdfScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersDocument12 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersOrkid Fazz89% (9)
- SoapDocument6 pagesSoapkaram13No ratings yet
- Syntheses of Soap and DetergentDocument4 pagesSyntheses of Soap and DetergentChin Castro Zabat100% (2)
- Soap PreparationDocument40 pagesSoap PreparationDesiana Anggraeni100% (1)
- Lab 6Document16 pagesLab 6Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of A SoapDocument12 pagesPreparation and Properties of A SoapTinusha ParamananthanNo ratings yet
- Name: Kie Andro B. Odtojan DATE: SEP 27, 2020 Group No.: Na Experiment 10 - Soap and Detergents Objective(s)Document6 pagesName: Kie Andro B. Odtojan DATE: SEP 27, 2020 Group No.: Na Experiment 10 - Soap and Detergents Objective(s)Kiean OdtojanNo ratings yet
- EXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryDocument35 pagesEXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryedriansamaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document12 pagesExperiment 6Keo De Leon100% (3)
- Soap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantFrom EverandSoap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Uploaded by
GeneBhooiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Act 5b For Cherry Ann
Uploaded by
GeneBhooiCopyright:
Available Formats
Principle of emulsification of fats
-The emulsion test is a test done to show the presence or absence of lipids in a substance. In
this test the substance is first dissolved in alcohol. This solution is then dissolved in water. If
lipids are present in the mixture then it will precipitate and the hydrophilic head will surround the
hydrophobic tails forming an emulsion.
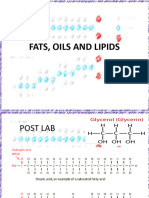
Sponification:
Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester under basic conditions to form an alcohol and
the salt of acarboxylic acid (carboxylates). Saponification is commonly used to refer to the
reaction of a metallic alkali (base) with a fat or oil to form soap. Saponifiable substances are
those that can be converted into soap.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a caustic base. If NaOH is used a hard soap is formed,
whereas whenpotassium hydroxide (KOH) is used, a soft soap is formed. Vegetable
oils and animal fats are fatty esters in the form of triglycerides. The alkali breaks the ester
bond and releases the fatty acid salt andglycerol. If necessary, soaps may
be precipitated by salting it out with saturated sodium chloride. Thesaponification value is
the amount of base required to saponify a fat sample.
In a classic laboratory procedure the triglyceride trimyristin is obtained by
extracting nutmeg withdiethyl ether.[1] Saponification to the sodium salt of myristic acid takes
place with NaOH in water. The acid itself can be obtained by adding dilute hydrochloric
acid.[2]
Chemical eq..
You might also like
- LipidsDocument25 pagesLipidsJeaniee Zosa Ebias50% (10)
- Saponification of SoapDocument11 pagesSaponification of SoapMsfaeza Hanafi80% (5)
- Synthesis of SoapDocument34 pagesSynthesis of SoapAlex Atienza100% (1)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry ProjectHameed Ahmed Khas KheliNo ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument1 pageSaponificationscholar peterNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationHritik LalNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.Document16 pagesLab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.niniwani59No ratings yet
- Lab 6 (Soaps & Detergents)Document21 pagesLab 6 (Soaps & Detergents)AmeerRashidNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstract903l.arivazhagan1977No ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument4 pagesSaponificationtedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Syntheses of Soaps and DetergentsDocument2 pagesSyntheses of Soaps and DetergentsClare CariñoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5bDocument4 pagesExperiment 5bKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- Soap ReportDocument16 pagesSoap ReportAddison JuttieNo ratings yet
- SoapDocument15 pagesSoapindumathijayakaranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Soap DetergentDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Soap DetergentTiny100% (5)
- Lipid Solubility in Dilute Acid and Dilute AlkaliDocument11 pagesLipid Solubility in Dilute Acid and Dilute AlkaliCyrene Grace BrionesNo ratings yet
- Soap PDFDocument3 pagesSoap PDFanna marieNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of Organic CompoundsDocument96 pagesThe Synthesis of Organic CompoundsDoroteo Jose StationNo ratings yet
- That They Have Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic RegionsDocument4 pagesThat They Have Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic RegionsChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- PJONDocument3 pagesPJONhafizul188No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument26 pagesChemistry ProjectMaster PrateekNo ratings yet
- Practicals InvestagatoryDocument3 pagesPracticals InvestagatorysanyamskismnNo ratings yet
- EXP6 Soap and DetergentheheDocument19 pagesEXP6 Soap and DetergenthehesamengNo ratings yet
- Lipid Jurnal KevinDocument12 pagesLipid Jurnal KevinErik Pavel EredNo ratings yet
- L I P I D SDocument42 pagesL I P I D SCindy FelixNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument2 pagesLIPIDSIshen MaujiNo ratings yet
- Soap Making and Fats TestingDocument94 pagesSoap Making and Fats TestingEra MelaniaNo ratings yet
- 9 Lipids SaponificationDocument12 pages9 Lipids SaponificationAlyssa De Jesus AgustinNo ratings yet
- 12 - Analysis of LipidsDocument15 pages12 - Analysis of LipidsLIAN KEI HILADONo ratings yet
- Frothing Power of SoapDocument3 pagesFrothing Power of SoapT sidharthNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Soap and DetergentDocument16 pagesLab 6 - Soap and DetergentamiraaikharahNo ratings yet
- Brain Lipid WrittenDocument19 pagesBrain Lipid WrittenAldwin Ray Pamplona100% (2)
- Experiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesJobel De Pedro100% (4)
- SOAPS and DetergentsDocument66 pagesSOAPS and DetergentsMkhalilizul SiHamba CintaIlahi100% (1)
- Chem Lab (Soaps)Document19 pagesChem Lab (Soaps)Amiro Iqbal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Soap DetergentDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Soap DetergentHarvey Mher RarangNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Complete (Preparation of Soap)Document15 pagesLab 6 Complete (Preparation of Soap)mirdza94No ratings yet
- Esterification and SaponificationDocument24 pagesEsterification and SaponificationpasatiemporoseanneNo ratings yet
- Lipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AreDocument8 pagesLipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AregymnasrischerNo ratings yet
- Lipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AreDocument8 pagesLipids Are A Large and Diverse Group of Natural Occurring Organic Compounds That AregymnasrischerNo ratings yet
- Summary For Integrated Science Term 1Document6 pagesSummary For Integrated Science Term 1Tshawna RockNo ratings yet
- Saponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Document5 pagesSaponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Anonymous UoRu4sNo ratings yet
- Chemical For ConsumersDocument17 pagesChemical For ConsumersBjergsenNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of A Soap: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesPreparation and Properties of A Soap: ObjectiveBodhi Satwa MishraNo ratings yet
- Atikah Punya Jugak...Document26 pagesAtikah Punya Jugak...Ika BakarNo ratings yet
- Theory: Mechanism of SaponificationDocument4 pagesTheory: Mechanism of SaponificationA/P MARICHELVAN PRADEBANo ratings yet
- Preparation of Toilet SoapsDocument4 pagesPreparation of Toilet Soapspradyumansharmaj333No ratings yet
- Preparation of Quinoa SoapafgdvdfDocument5 pagesPreparation of Quinoa SoapafgdvdfScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersDocument12 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersOrkid Fazz89% (9)
- SoapDocument6 pagesSoapkaram13No ratings yet
- Syntheses of Soap and DetergentDocument4 pagesSyntheses of Soap and DetergentChin Castro Zabat100% (2)
- Soap PreparationDocument40 pagesSoap PreparationDesiana Anggraeni100% (1)
- Lab 6Document16 pagesLab 6Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of A SoapDocument12 pagesPreparation and Properties of A SoapTinusha ParamananthanNo ratings yet
- Name: Kie Andro B. Odtojan DATE: SEP 27, 2020 Group No.: Na Experiment 10 - Soap and Detergents Objective(s)Document6 pagesName: Kie Andro B. Odtojan DATE: SEP 27, 2020 Group No.: Na Experiment 10 - Soap and Detergents Objective(s)Kiean OdtojanNo ratings yet
- EXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryDocument35 pagesEXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryedriansamaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document12 pagesExperiment 6Keo De Leon100% (3)
- Soap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantFrom EverandSoap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet