Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam Review 2v2
Exam Review 2v2
Uploaded by
MrWestburyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam Review 2v2
Exam Review 2v2
Uploaded by
MrWestburyCopyright:
Available Formats
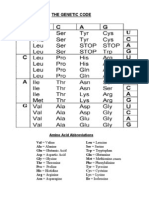
Molecular Genetics Study Guide
1. Know the structure of DNA, how the different subunits piece together, and
how the double helix is held together.
2. Be able to identify the major people and their contributions involved in
the discovery, importance, and structure of DNA (Watson/Crick;
Hershey/Chase, etc)
3. Outline the steps in DNA Replication using proper terms (leading/lagging
strand, DNA Helicase/Polymerase, RNA primers, ssbp’s, Okazaki
Fragments, etc).
4. Describe the link between DNA, RNA, and proteins.
5. Explain the steps (with enzymes) that lead from a piece of DNA becoming
a protein (Protein Synthesis) AND be able to take a strand of DNA and get
an amino acid sequence from it.
6. Know the “Central Dogma” and how an mRNA sequence is converted to
proteins.
7. Be able to explain how different mutations can alter the amino acid
sequence of a protein.
Evolution Study Guide
1. Be able to properly use the terms allele, locus, gene, heterozygous,
homozygous (dominant & recessive), genotype, phenotype, gene pool,
species, allele/gene frequency, genetic drift, ‘fixed’.
2. Explain the process of natural selection and how this could lead to the
formation of new species.
3. Compare and Contrast the theories of Gradualism and Punctuated
Equilibrium as they apply to the Theory of Evolution using examples.
4. List the factors that must be in place for a population to be in Hardy-
Weinberg Equilibrium.
5. Use the Hardy-Weinberg Principle to calculate allele frequencies given
data about a population (#dominant phenotype & #recessive
phenotypes).
6. Explain how genetic drift, mutations, gene flow and other factors can
result in the formation of new species.
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Microbiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 4th Edition Marjorie Kelly Cowan Heidi SmithDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Microbiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 4th Edition Marjorie Kelly Cowan Heidi SmithMichaelArchermtyg97% (38)
- Dwnload Full Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions Manual PDFbeliefknackq3zcb100% (11)
- Biol 308 - Study QuestionsDocument47 pagesBiol 308 - Study QuestionsDivya100% (1)
- BIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsDocument8 pagesBIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsTristan ScottNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 1 Course Outline PDFDocument5 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 1 Course Outline PDFanabi wench100% (1)
- GeneticssololandscapeDocument2 pagesGeneticssololandscapeapi-284323075No ratings yet
- Dna-Structure and Roles of Nucleic AcidDocument8 pagesDna-Structure and Roles of Nucleic AcidParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- Molecular PhylogeneticsDocument4 pagesMolecular PhylogeneticsAb WassayNo ratings yet
- VCE BIOLOGY UnitDocument24 pagesVCE BIOLOGY Unitjess_heathNo ratings yet
- Genetics QuestionsDocument3 pagesGenetics Questionsa spelluNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Student ObjectivesDocument1 pageTopic 2 Student Objectivesapi-102850034No ratings yet
- BioInf 5Document4 pagesBioInf 5Özlem GünayNo ratings yet
- Biology Final Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesBiology Final Exam Study Guideapi-236677776No ratings yet
- Remediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaDocument6 pagesRemediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaFlozieNo ratings yet
- Topic_6_Genes_and_Inheritance_Learning_Objectives (1)Document2 pagesTopic_6_Genes_and_Inheritance_Learning_Objectives (1)Nishad PatkarNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic AnalysisDocument6 pagesPhylogenetic AnalysisSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Yearly 10 Revision Biology AnswersDocument3 pagesYearly 10 Revision Biology AnswerspotpalNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1001 CH 13 Study GuideDocument1 pageBIOL 1001 CH 13 Study GuideNikola LeticNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Clinical EpigeneticsDocument270 pages2019 - Clinical EpigeneticsCharls100% (1)
- Cells and Heredity: Unit OneDocument4 pagesCells and Heredity: Unit Oneapi-287848315No ratings yet
- Yr10 Biology Revision GuideDocument9 pagesYr10 Biology Revision Guideanas.amr.abdullahNo ratings yet
- Exam Review - Jan 2012Document3 pagesExam Review - Jan 2012Ms Ratna Lestyana DewiNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document6 pagesBiology 1gabrielle.singerNo ratings yet
- Traffic Light Topic 4 GeneticsDocument2 pagesTraffic Light Topic 4 GeneticsAlison HillNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis Reveals Epigenomic Evolution Related To Species Traits and Genomic Imprinting in MammalsDocument67 pagesComparative Analysis Reveals Epigenomic Evolution Related To Species Traits and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals廖晨延No ratings yet
- Biology 211 Final Exam Study Guide 2016Document4 pagesBiology 211 Final Exam Study Guide 2016GregNo ratings yet
- Review B6 Inheritance, Variation and EvolutionDocument2 pagesReview B6 Inheritance, Variation and EvolutionCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (1) ..Document4 pagesUnit 3 (1) ..Valentina RamírezNo ratings yet
- Biology Topic Guide EpigeneticsDocument19 pagesBiology Topic Guide EpigeneticsGazar100% (2)
- 10.1007@s11427 020 1709 6Document4 pages10.1007@s11427 020 1709 6Nouri RaidNo ratings yet
- 2023 SG5 DNA Replication and MutationDocument4 pages2023 SG5 DNA Replication and Mutationmairashah2004No ratings yet
- Developmental Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesDevelopmental Biology QuestionsSurajit Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- Bio II Final Exam Review Without Standards (Answers)Document12 pagesBio II Final Exam Review Without Standards (Answers)Contessa PetriniNo ratings yet
- Molecular Evolution and PhylogeneticsDocument16 pagesMolecular Evolution and PhylogeneticsHarsh Vardhan Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Notes LatestDocument104 pagesForm 4 Biology Notes LatestElvis KemboiNo ratings yet
- Genetic: Fakultas Kedokteran Umsu 2016Document21 pagesGenetic: Fakultas Kedokteran Umsu 2016Khemal MubaraqNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Outline Lower 6Document13 pagesCape Biology Outline Lower 6Yohance NewtonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Study GuideDocument4 pagesChapter 26 Study GuideBen ReebsNo ratings yet
- Teacher(s) Sreekala.K.P Subject Group and Course Course Part and Topic SL & HL/Year 2 Dates 15Document9 pagesTeacher(s) Sreekala.K.P Subject Group and Course Course Part and Topic SL & HL/Year 2 Dates 15Nana Refaye100% (1)
- Brenner 2003Document13 pagesBrenner 2003savalia.goldcoralNo ratings yet
- Take Home Long QuizDocument3 pagesTake Home Long QuizJay SamNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Exam1Document3 pagesStudy Guide Exam1Lizzy HoustonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis: DR Rabar MantikDocument10 pagesMolecular Phylogenetic Analysis: DR Rabar MantikRabar Mohsin Abdulrahman MantikNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics Topic GuideDocument16 pagesEpigenetics Topic GuideRidwan AbrarNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection Unit PlanDocument8 pagesNatural Selection Unit Planapi-207974201No ratings yet
- Genetics IntroDocument30 pagesGenetics IntroVin BaniquedNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Genetics Questions (IB Topic 3) : For Mader 10 EditionDocument2 pagesIB Biology Genetics Questions (IB Topic 3) : For Mader 10 EditionmanrajNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Genetics QuestionDocument3 pagesAP Bio Genetics QuestionSam GoldenNo ratings yet
- Exam #4 Review: Biology 125 (Human Biology) : Chapter 20: Genetics and Human InheritanceDocument3 pagesExam #4 Review: Biology 125 (Human Biology) : Chapter 20: Genetics and Human Inheritancejolie malakNo ratings yet
- BIOC16 Midterm Review PDFDocument5 pagesBIOC16 Midterm Review PDFOwishi ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- TransposonsDocument20 pagesTransposonsprerna tripathyNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0092867418301065Document19 pagesPi Is 0092867418301065Khushi TalaviyaNo ratings yet
- SB 3Document8 pagesSB 3diyasanjeev13No ratings yet
- Genetics Unit Test ReviewDocument3 pagesGenetics Unit Test ReviewvexelleNo ratings yet
- Pocket Biology (Card-2, Topic-2) ASDocument1 pagePocket Biology (Card-2, Topic-2) ASZawad7No ratings yet
- Molecular and Genetic EpidemiologyDocument16 pagesMolecular and Genetic EpidemiologyFhadla Nisaa100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Clinical Laboratory Hematology 2nd Edition Mckenzie Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Clinical Laboratory Hematology 2nd Edition Mckenzie Solutions Manual PDFcharlesdrakejth100% (18)
- Unit 2 Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Study Guideandrewhern210No ratings yet
- Research Paper EpigeneticsDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Epigeneticsxcjfderif100% (1)
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 5E Model of TeachingDocument3 pages5E Model of TeachingMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Viral Genome ProjectDocument1 pageViral Genome ProjectMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument1 pageAnaerobic RespirationMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument1 pageGenetic CodeMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- RFLPDocument14 pagesRFLPMrWestbury100% (2)
- Seniors APRDocument1 pageSeniors APRMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Restriction EnzymesDocument1 pageRestriction EnzymesMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Juniors APRDocument1 pageJuniors APRMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- Bio ChemistryDocument2 pagesBio ChemistryMrWestbury100% (2)
- GeneticsDocument2 pagesGeneticsMrWestburyNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument2 pagesMETABOLISMMrWestburyNo ratings yet