Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diuretics
Diuretics
Uploaded by
lilipop_xtream91Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pcol Exp 9Document18 pagesPcol Exp 9windgazer07No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument6 pagesDiureticsJihad AnadNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument17 pagesWebinarapi-249760371No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticssumit kumariNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument16 pagesWebinarapi-249728281No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On: Renal SystemDocument75 pagesDrugs Acting On: Renal SystemCarlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic 2Document11 pagesDiuretic 2Loan KimNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Jan 14Document1 pageDiuretic Jan 14Gurpreet ⎝⎝⎲⎵⎲⎠⎠ SinghNo ratings yet
- Diuretic: Hazha S. Ameen MSCDocument17 pagesDiuretic: Hazha S. Ameen MSCAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument42 pagesDiureticsKumah WisdomNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument3 pagesDiureticsCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument42 pagesDiureticsKeziah TampusNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument2 pagesDiureticsArnel Leonard TungbabanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Document44 pagesDrugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Juliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Renal DiureticsDocument24 pagesPharmacology Renal Diureticskpsuan100% (1)
- Lecture15-Diuretics and AntidiureticsDocument36 pagesLecture15-Diuretics and Antidiureticsharis.18No ratings yet
- Medicnal AssignmentDocument12 pagesMedicnal Assignmentwaee0565No ratings yet
- Diuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatDocument17 pagesDiuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatAnalizaNo ratings yet
- Renal Note On DiureticsDocument12 pagesRenal Note On DiureticsLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic and Brand NamesDocument22 pagesDiuretics: Generic and Brand NamesKish GabrielNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Sindwa KanyimbaDocument43 pagesDiuretics: DR Sindwa Kanyimbaedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsDocument49 pagesAnti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument2 pagesDiureticsClophia LidresNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 171130131557Document31 pagesDiuretics 171130131557Lety AgistiniaNo ratings yet
- PDF DiureticsDocument20 pagesPDF DiureticsIhjas HabeebNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolytes and Diuretics 2020Document33 pagesFluid, Electrolytes and Diuretics 2020Tasya FakhiraNo ratings yet
- Diuretics How They Work Cautions and ContraindicationsDocument5 pagesDiuretics How They Work Cautions and ContraindicationsCatalina Paz DiazNo ratings yet
- Topic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Document28 pagesTopic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Arvi KhanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocument98 pagesDrugs Acting On Renal SystemIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologyDocument96 pagesDrugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drug: First Semester 2019-2020 College of Dentistry University of HailDocument5 pagesDiuretic Drug: First Semester 2019-2020 College of Dentistry University of HailMaha NoorNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of HemodialysisDocument5 pages1 Principles of HemodialysisZaid Alfaathih100% (2)
- Why Dialysis HappensDocument2 pagesWhy Dialysis HappensAfiqah OsmeraNo ratings yet
- Why Dialysis HappensDocument3 pagesWhy Dialysis HappensAfiqah OsmeraNo ratings yet
- Renal PCODocument17 pagesRenal PCOHonour JamesNo ratings yet
- Complete ExcretionDocument61 pagesComplete Excretionethankhoo2007No ratings yet
- What Is Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesWhat Is Kidney DiseaseEllie ELLNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument74 pagesDiureticsm1k0e100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument3 pagesDiureticsarshu98172No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsDocument16 pagesAssignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocument58 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal SystemDaniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Laxatives: By: ﺰﯾﺰﻋ ﺪﻤﺤﻣ ﮫط ﺎﻨﯿﻟ Stage: 3rd Stage Supervised by: Dr. Hakeem AlaniDocument11 pagesLaxatives: By: ﺰﯾﺰﻋ ﺪﻤﺤﻣ ﮫط ﺎﻨﯿﻟ Stage: 3rd Stage Supervised by: Dr. Hakeem AlaniTayf AlrawINo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument62 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesLacy Ds FruitNo ratings yet
- Phamaco TrenslatorDocument1 pagePhamaco TrenslatorDagahawakaNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-5Document27 pagesPHARMA-5yuson.joan001No ratings yet
- Diuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSDocument51 pagesDiuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurDocument33 pagesDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome + ArfDocument64 pagesNephrotic Syndrome + ArfkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Kidney Failure (Reference Summary) : AnatomyDocument3 pagesKidney Failure (Reference Summary) : AnatomyUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 - Laxative DrugsDocument27 pagesTopic 12 - Laxative Drugsthieuleminhchaut65No ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- Kidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Document4 pagesKidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Jacinto Adolph Agustin CagorolNo ratings yet
- Excretion in HumansDocument6 pagesExcretion in HumansMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Wcppe Guides - Thiazides and DiureticsDocument2 pagesWcppe Guides - Thiazides and Diureticsdaniela bosoagaNo ratings yet
- 19-DiureticsDocument14 pages19-Diureticsali khan100% (1)
- Acid BaseDocument74 pagesAcid BaseMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- 09 Diuretics UpdDocument42 pages09 Diuretics UpdYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutNo ratings yet
- PCL 302 Lecture DiureticsDocument7 pagesPCL 302 Lecture DiureticsZayyanu AminuNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
Diuretics
Diuretics
Uploaded by
lilipop_xtream91Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diuretics
Diuretics
Uploaded by
lilipop_xtream91Copyright:
Available Formats
DIURETICS
Explain briefly on the drug classification and group
Definition:
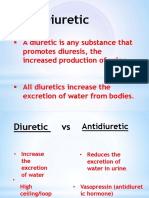
A diuretic is any drug that elevates the rate of urination and thus provides a means of
forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the
excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way
All diuretic drugs -- which are usually called, more simply, diuretics -- cause a person
to "lose water" but they do so by diverse means, including:
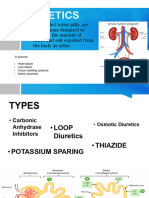
• Inhibiting the kidney's ability to reabsorb sodium, thus enhancing the loss of
sodium in the urine. And when sodium is lost in the urine, water goes with it.
(This type of diuretic is called a high-ceiling diuretic or a loop diuretic).
• Enhancing the excretion of both sodium and chloride in the urine so that water
is excreted with them. This is how the thiazide diuretics work.
• Blocking the exchange of sodium for potassium, resulting in excretion of
sodium and potassium but relatively little loss of potassium. These diuretics
are therefore termed potassium sparing diuretics.
Some diuretics work by still other mechanisms. And some diuretics have other effects
and uses such as in treating hypertension.
Explain the indication of the drug
Explain the action of the drug
Explain the side effect of the drug
Explain and describe the nursing responsibility while administer the drug)
Provide example for each type of the drugs
You might also like
- Pcol Exp 9Document18 pagesPcol Exp 9windgazer07No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument6 pagesDiureticsJihad AnadNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument17 pagesWebinarapi-249760371No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument28 pagesDiureticssumit kumariNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument16 pagesWebinarapi-249728281No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On: Renal SystemDocument75 pagesDrugs Acting On: Renal SystemCarlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic 2Document11 pagesDiuretic 2Loan KimNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Jan 14Document1 pageDiuretic Jan 14Gurpreet ⎝⎝⎲⎵⎲⎠⎠ SinghNo ratings yet
- Diuretic: Hazha S. Ameen MSCDocument17 pagesDiuretic: Hazha S. Ameen MSCAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument42 pagesDiureticsKumah WisdomNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument3 pagesDiureticsCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument42 pagesDiureticsKeziah TampusNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument2 pagesDiureticsArnel Leonard TungbabanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Document44 pagesDrugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Juliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Renal DiureticsDocument24 pagesPharmacology Renal Diureticskpsuan100% (1)
- Lecture15-Diuretics and AntidiureticsDocument36 pagesLecture15-Diuretics and Antidiureticsharis.18No ratings yet
- Medicnal AssignmentDocument12 pagesMedicnal Assignmentwaee0565No ratings yet
- Diuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatDocument17 pagesDiuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatAnalizaNo ratings yet
- Renal Note On DiureticsDocument12 pagesRenal Note On DiureticsLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic and Brand NamesDocument22 pagesDiuretics: Generic and Brand NamesKish GabrielNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Sindwa KanyimbaDocument43 pagesDiuretics: DR Sindwa Kanyimbaedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsDocument49 pagesAnti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument2 pagesDiureticsClophia LidresNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 171130131557Document31 pagesDiuretics 171130131557Lety AgistiniaNo ratings yet
- PDF DiureticsDocument20 pagesPDF DiureticsIhjas HabeebNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolytes and Diuretics 2020Document33 pagesFluid, Electrolytes and Diuretics 2020Tasya FakhiraNo ratings yet
- Diuretics How They Work Cautions and ContraindicationsDocument5 pagesDiuretics How They Work Cautions and ContraindicationsCatalina Paz DiazNo ratings yet
- Topic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Document28 pagesTopic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Arvi KhanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocument98 pagesDrugs Acting On Renal SystemIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologyDocument96 pagesDrugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drug: First Semester 2019-2020 College of Dentistry University of HailDocument5 pagesDiuretic Drug: First Semester 2019-2020 College of Dentistry University of HailMaha NoorNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of HemodialysisDocument5 pages1 Principles of HemodialysisZaid Alfaathih100% (2)
- Why Dialysis HappensDocument2 pagesWhy Dialysis HappensAfiqah OsmeraNo ratings yet
- Why Dialysis HappensDocument3 pagesWhy Dialysis HappensAfiqah OsmeraNo ratings yet
- Renal PCODocument17 pagesRenal PCOHonour JamesNo ratings yet
- Complete ExcretionDocument61 pagesComplete Excretionethankhoo2007No ratings yet
- What Is Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesWhat Is Kidney DiseaseEllie ELLNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument74 pagesDiureticsm1k0e100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument3 pagesDiureticsarshu98172No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsDocument16 pagesAssignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocument58 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal SystemDaniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Laxatives: By: ﺰﯾﺰﻋ ﺪﻤﺤﻣ ﮫط ﺎﻨﯿﻟ Stage: 3rd Stage Supervised by: Dr. Hakeem AlaniDocument11 pagesLaxatives: By: ﺰﯾﺰﻋ ﺪﻤﺤﻣ ﮫط ﺎﻨﯿﻟ Stage: 3rd Stage Supervised by: Dr. Hakeem AlaniTayf AlrawINo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument62 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesLacy Ds FruitNo ratings yet
- Phamaco TrenslatorDocument1 pagePhamaco TrenslatorDagahawakaNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-5Document27 pagesPHARMA-5yuson.joan001No ratings yet
- Diuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSDocument51 pagesDiuretics: PHRM 306: Drugs Affecting CVSEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurDocument33 pagesDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome + ArfDocument64 pagesNephrotic Syndrome + ArfkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Kidney Failure (Reference Summary) : AnatomyDocument3 pagesKidney Failure (Reference Summary) : AnatomyUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 - Laxative DrugsDocument27 pagesTopic 12 - Laxative Drugsthieuleminhchaut65No ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- Kidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Document4 pagesKidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Jacinto Adolph Agustin CagorolNo ratings yet
- Excretion in HumansDocument6 pagesExcretion in HumansMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Wcppe Guides - Thiazides and DiureticsDocument2 pagesWcppe Guides - Thiazides and Diureticsdaniela bosoagaNo ratings yet
- 19-DiureticsDocument14 pages19-Diureticsali khan100% (1)
- Acid BaseDocument74 pagesAcid BaseMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- 09 Diuretics UpdDocument42 pages09 Diuretics UpdYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutNo ratings yet
- PCL 302 Lecture DiureticsDocument7 pagesPCL 302 Lecture DiureticsZayyanu AminuNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet