Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Virus Classification Assignment
Virus Classification Assignment
Uploaded by
CismaanAbdulahiFarahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Virus Classification Assignment
Virus Classification Assignment
Uploaded by
CismaanAbdulahiFarahCopyright:
Available Formats
Virus classification
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system.
Similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms, virus classification is the subject
of ongoing debate and proposals. This is mainly due to the pseudo-living nature of viruses,
which are not yet definitively classified as living or non-living. As such, they do not fit neatly
into the established biological classification system in place for cellular organisms.
Viruses are mainly classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid
type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. Currently there are
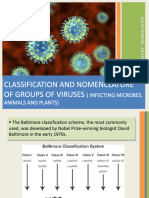
two main schemes used for the classification of viruses, The Baltimore classification system,
which places viruses into one of seven groups. Named after David Baltimore, a Nobel Prize-
winning biologist, these groups are designated by Roman numerals and discriminate viruses
depending on their mode of replication, and genome type. Accompanying this broad method of
classification are specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines set out by the
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses.
ETIOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY OF DISEASES
Diseases ETIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
FMD Aphthovirus genus and picornaviridae High morbidity rate and low mortality rate
family
RP Morbillivirus genus and paramyxoviridae High morbidity rate and high mortality rate
family
PPR Morbillivirus genus and paramyxoviridae High morbidity rate and high mortality rate
family
BT Orbivirus genus and reoviridae family High morbidity rate and high mortality rate
BVD Pestvirus genus and flaviviridae family High morbidity rate and high mortality rate
You might also like
- Virology, Parasitology and MycologyDocument87 pagesVirology, Parasitology and MycologyNur Nabilah100% (5)
- Virus Nomenclature and Viral Pathogenesis Reviewer_PDF(1)Document85 pagesVirus Nomenclature and Viral Pathogenesis Reviewer_PDF(1)alyneshdNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument19 pagesDocumentfaiqan93No ratings yet
- VirusDocument6 pagesVirusAmeena Beebi B Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Lect. 4 Plant Virus Nomenclature & ClassificationDocument34 pagesLect. 4 Plant Virus Nomenclature & Classificationامید سحرNo ratings yet
- What Is A Virus?: MaterialsDocument22 pagesWhat Is A Virus?: Materialswahyu kurniawanNo ratings yet
- BacteriophageDocument13 pagesBacteriophageDrSiva Prasad GuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 111Document31 pagesGeneral Biology 111Chioma AlexNo ratings yet
- Animal VirologyDocument94 pagesAnimal Virologyabrilama90No ratings yet
- Viruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Document21 pagesViruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-2020-Navaratnarajah-jbc - REV119.009961Document31 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-2020-Navaratnarajah-jbc - REV119.009961Ramya RallabandiNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification (L8) - 26 TH MayDocument42 pagesBiological Classification (L8) - 26 TH MayUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- May Be Defined As: VirusesDocument21 pagesMay Be Defined As: VirusesZeresenayNo ratings yet
- Virus Classification and Properties Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesVirus Classification and Properties Lecture NotesdoyinsolaolusanyaNo ratings yet
- Viruses Their ReplicationDocument39 pagesViruses Their ReplicationYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Course Code 6451 Assignment No. 1Document14 pagesCourse Code 6451 Assignment No. 1Tahirullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Classificaton of Viruses and BacteriophageDocument55 pagesClassificaton of Viruses and BacteriophageRomeo GasparNo ratings yet
- Viruses Definition PDFDocument10 pagesViruses Definition PDFAndreina ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mikafar 2 Eng PAK AKMALDocument12 pagesTugas Mikafar 2 Eng PAK AKMALRahmaAuliaNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To VirologyDocument19 pages1 Intro To Virologyhamza najmNo ratings yet
- 11 Viral Disease Plants & AnimalsDocument38 pages11 Viral Disease Plants & Animalshamza najmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Viruses and Their Parti - 2023 - Cann S Principles of Molecular ViroDocument28 pagesChapter 2 - Viruses and Their Parti - 2023 - Cann S Principles of Molecular Viroj.castanedalNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 5: World of VirusesDocument15 pagesMicrobiology 5: World of VirusesAya CendonNo ratings yet
- RNA 1 FlashDocument5 pagesRNA 1 FlashSamqureshiNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument21 pagesList of Contentsankur bharaliNo ratings yet
- Ebola Virus Outbreak, Updates On Current Therapeutic StrategiesDocument13 pagesEbola Virus Outbreak, Updates On Current Therapeutic StrategiesAde Hanna Natalia SitohangNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Classification of Viruses: GeneralDocument10 pagesTaxonomy and Classification of Viruses: GeneralSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Virology Is The Study of Viruses (Latin, Virus Means Poison)Document31 pagesVirology Is The Study of Viruses (Latin, Virus Means Poison)Jacob MasikaNo ratings yet
- DokumentDocument1 pageDokumentTADEUSZ WIELGONo ratings yet
- Viruses in Reptiles: Review Open AccessDocument12 pagesViruses in Reptiles: Review Open AccessLin KlaymanNo ratings yet
- Classifying of MicroorganismsDocument26 pagesClassifying of MicroorganismsDaman Huri WibowoNo ratings yet
- Z03950010220174014Session 7. Microbial Foodborne PathogensDocument26 pagesZ03950010220174014Session 7. Microbial Foodborne Pathogensjoenni hansNo ratings yet
- Virus LectureDocument23 pagesVirus LectureRafay JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Classification and NomenclatureDocument18 pagesLecture 2 Classification and Nomenclatureyusraanjum624No ratings yet
- Reo VirusesDocument17 pagesReo VirusesLaura Anghel-MocanuNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment 3rd RegularDocument21 pagesMicrobiology Assignment 3rd RegularMuzzamalNo ratings yet
- Acellular Microbes PPT Feb. 2024Document61 pagesAcellular Microbes PPT Feb. 202421-54405No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document54 pagesChapter 4jovendiestro822No ratings yet
- General Virology 3.doc - 0Document14 pagesGeneral Virology 3.doc - 0Isak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Medical VirologyDocument23 pagesMedical Virologyour lectureNo ratings yet
- Virus: Measuring The Size of VirusesDocument18 pagesVirus: Measuring The Size of VirusesVargheseNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project Viral DiseasesDocument20 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Viral DiseasesAchu Jaseem0% (2)
- Plant Viruses ThesisDocument7 pagesPlant Viruses ThesisHelpInWritingPaperCanada100% (2)
- RhabdoviridaeDocument3 pagesRhabdoviridaeSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Classification & Nomenclature of VirusesDocument27 pagesClassification & Nomenclature of Virusesgduttamba23No ratings yet
- Viruses in ReptilesDocument12 pagesViruses in ReptilesKhoirina Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Jvim 34 1690Document17 pagesJvim 34 1690margaridasousa1No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya 1Document13 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya 1shyamacharaniyaNo ratings yet
- Module3 PDFDocument28 pagesModule3 PDFAeron TamayoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Viruses Basis of ClassificationDocument6 pagesClassification of Viruses Basis of ClassificationRahul MoreNo ratings yet
- Virus - Group 5Document132 pagesVirus - Group 5Kent RebongNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis E Virus: A Review: P. Vasickova, I. Psikal, P. Kralik, F. Widen, Z. Hubalek, I. PavlikDocument20 pagesHepatitis E Virus: A Review: P. Vasickova, I. Psikal, P. Kralik, F. Widen, Z. Hubalek, I. Pavlikyo4nutzNo ratings yet
- Hunter, E. (2008) - Encyclopedia of Virology. Retroviruses General Features.Document9 pagesHunter, E. (2008) - Encyclopedia of Virology. Retroviruses General Features.afinaNo ratings yet
- The Quest For Extraterrestrial Life What About The VirusesDocument10 pagesThe Quest For Extraterrestrial Life What About The VirusesLal CardenasNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument37 pagesVirusSuprabuddha KunduNo ratings yet
- Plant Virus Replication and StructureDocument24 pagesPlant Virus Replication and StructureAdarsh AdiNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and VirusesDocument39 pagesBacteria and VirusesDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Virus MophologyDocument71 pagesVirus MophologySirwan SalmanNo ratings yet
- CH#04Document12 pagesCH#04Emran khanNo ratings yet