Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chlorination of Methane
Chlorination of Methane
Uploaded by
Carlo Joseph MoskitoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Free Radical Chlorination by Sulfuryl ChlorideDocument8 pagesFree Radical Chlorination by Sulfuryl Chloridevibhor_26janNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Free Radical SubstitutionDocument6 pagesMechanism of Free Radical SubstitutionleomNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of AlkanesDocument20 pagesThe Chemistry of AlkaneshussainNo ratings yet
- Free Radical SubstitutionDocument35 pagesFree Radical SubstitutionkitazzaedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Alkanes Alkenes PDFDocument56 pages2021 Alkanes Alkenes PDFEudora LauNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Document20 pagesAlkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of RadicalsDocument54 pagesCharacteristics of RadicalsdesyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Chemical Reactions of AlkanesDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Chemical Reactions of AlkanesDavidNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: F.N.D-B Form 6 Upper Unit 2 Module 1 Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesAlkanes: F.N.D-B Form 6 Upper Unit 2 Module 1 Chemistry NotesStudent1010No ratings yet
- Free Radical ChlorinationDocument1 pageFree Radical ChlorinationJohn Yves LubricoNo ratings yet
- Functional GR Analysis - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument9 pagesFunctional GR Analysis - Alkanes and AlkenesMakeedaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Document6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Jojo LeongNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 AliphaticDocument17 pagesTOPIC 1 AliphaticFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Free Radical SubstitutionDocument2 pagesFree Radical SubstitutionDaNo ratings yet
- Halogenacion de AlcanosDocument34 pagesHalogenacion de AlcanosAlejandra EcheverriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: 6 14 (L) 2 (L) 6 13 (L) (G)Document16 pagesAlkanes: 6 14 (L) 2 (L) 6 13 (L) (G)Lyana TaylorNo ratings yet
- P4 Radical ReactionsDocument51 pagesP4 Radical ReactionsShirl Angelee OcampoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 - SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz 5 - Solutionm3ghnaadNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CH 15Document22 pagesLec 1 CH 15Primandari UtamiNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Alkane TutorialDocument6 pagesTopic 10 Alkane TutorialTimNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument39 pagesUnit IGoopNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Explain Reactions of Methane/Ethane With Chlorine and Bromine Via Free Radical MechanismsDocument4 pages10.2 Explain Reactions of Methane/Ethane With Chlorine and Bromine Via Free Radical MechanismsYazan HammoudehNo ratings yet
- Carbocations & CarbanionDocument41 pagesCarbocations & CarbanionMuttu M100% (1)
- CHAPTER: Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers: LT Bipc Revision Prog Practice Assignment Subject: ChemistryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER: Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers: LT Bipc Revision Prog Practice Assignment Subject: ChemistryAssishNo ratings yet
- Notes Alkanes +alkenesDocument44 pagesNotes Alkanes +alkenesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 2Document14 pagesAlkanes 2Hasen umerNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent ProblemsDocument6 pagesLimiting Reagent ProblemsFarisDonNo ratings yet
- Chlorine: This Powerpoint Was Brought To You by The The Atomic Symbol CLDocument17 pagesChlorine: This Powerpoint Was Brought To You by The The Atomic Symbol CLruchita-tandon-9182No ratings yet
- Alkanes KODocument1 pageAlkanes KOabhishektheoneNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CH 15Document22 pagesLec 1 CH 15billNo ratings yet
- 16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandDocument29 pages16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandHayden Chappelear-RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Free Radicals: OO ONO Molecular Oxygen Nitrogen Dioxide NO Nitrogen MonoxideDocument11 pagesFree Radicals: OO ONO Molecular Oxygen Nitrogen Dioxide NO Nitrogen MonoxideAbdullahi abdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties Properties of AlkanesDocument23 pagesChemical Properties Properties of AlkanesLinatri Purwati Latifah SupriatnaNo ratings yet
- Radical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product FormationDocument2 pagesRadical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product Formationmegamon asabeNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDocument30 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanNo ratings yet
- Radical SederhanaDocument9 pagesRadical SederhanaNurillahi Febria LeswanaNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis and HalogenationDocument2 pagesPyrolysis and Halogenationarpitavashist11No ratings yet
- 16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandDocument29 pages16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine Demandahmedmagdi2009No ratings yet
- Bailey Alkanes PowerpointDocument31 pagesBailey Alkanes PowerpointBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FGs and AlkanesDocument28 pagesIntroduction To FGs and AlkanesAbdullah AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument6 pagesChapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesJERVINLIM100% (1)
- CHLOR ALKALI PROCESSES PresentationDocument20 pagesCHLOR ALKALI PROCESSES PresentationNAMRATA BHALERAO50% (2)
- Organic Chemistry,: Radical ReactionsDocument54 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Radical ReactionsNurul RamadanahNo ratings yet
- 208 Chlorine: Thermochemical PropertiesDocument5 pages208 Chlorine: Thermochemical PropertiesAHMEDNo ratings yet
- 204 Chlorine and ChloratesDocument2 pages204 Chlorine and ChloratesM DiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 ADocument16 pagesWeek 2 AsehunNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsDocument12 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsAgung Ratana Jayo Silim IPH StudentNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13Document23 pages11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13Deevanshi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument187 pagesHydrocarbon Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7Document61 pagesAlkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (4)
- Draw Out Some Suitable Structures Which Fit The Molecular Formula C HDocument4 pagesDraw Out Some Suitable Structures Which Fit The Molecular Formula C HSean s ChipangaNo ratings yet
- Free Radical PolymerizationDocument11 pagesFree Radical PolymerizationNaveed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Residual Chlorine Lab ManualDocument23 pagesResidual Chlorine Lab Manualali100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT SolutionsDocument32 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT Solutionschithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument54 pagesAlkyl HalideNelvianaNo ratings yet
- Cell Exam QuestionsDocument52 pagesCell Exam QuestionsNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Dwells God AquinoDocument16 pagesDwells God AquinoCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Grade 9 Science K-12Document161 pagesGrade 9 Science K-12Carlo Joseph Moskito93% (114)
- Amen Dumlao (AN2)Document2 pagesAmen Dumlao (AN2)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Anima Christi ArboledaDocument8 pagesAnima Christi ArboledaCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Come To The TableDocument7 pagesCome To The TableCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Hangad PrimerDocument2 pagesHangad PrimerCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Exer8 Handout (CJMM)Document6 pagesExer8 Handout (CJMM)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Amare Et Servire: Fr. Manoling Francisco, SJDocument3 pagesAmare Et Servire: Fr. Manoling Francisco, SJCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- BeatitudesDocument13 pagesBeatitudesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Chem 44.1 Special SynthesisDocument86 pagesChem 44.1 Special SynthesisCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (2)
- Youth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerDocument12 pagesYouth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Circles 2Document3 pagesCircles 2Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Solutions (Chemistry)Document11 pagesSolutions (Chemistry)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Youth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerDocument12 pagesYouth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Hydrocarbons - SummaryDocument15 pagesReactions of Hydrocarbons - SummaryCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Prayer For The Year of The YouthDocument14 pagesPrayer For The Year of The YouthCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (3)
- Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesColligative PropertiesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument12 pagesCirclesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument3 pagesWriting and Naming Chemical FormulasCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument10 pagesQualitative AnalysisCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Arithmetic of SolutionsDocument2 pagesChemical Arithmetic of SolutionsCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of The Acidity of Soft DrinksDocument64 pagesQuantitative Determination of The Acidity of Soft DrinksCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Certificate For Fun RunDocument7 pagesCertificate For Fun RunCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Batteries For DummiesDocument116 pagesBatteries For Dummiesjoseph katongoNo ratings yet
- MMPNov2017 170 1773 PDFDocument9 pagesMMPNov2017 170 1773 PDFMuh.naufal shidqiNo ratings yet
- 2025 Specimen Paper 2Document16 pages2025 Specimen Paper 2Ngô PhongNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry PPT-2Document29 pagesGeneral Chemistry PPT-2Temesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- Polyvinyl Alcohol Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites 1St Edition Visakh P M All ChapterDocument62 pagesPolyvinyl Alcohol Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites 1St Edition Visakh P M All Chaptermark.clark755100% (10)
- Nickel ElectroplatingDocument28 pagesNickel ElectroplatingRahul Pandey100% (2)
- Hypochlorous AcidDocument25 pagesHypochlorous AcidDirector Research100% (2)
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument13 pagesInorganic Chemistrybhargavthegreat123No ratings yet
- Water Quality Engineering and Wastewater TreatmentDocument320 pagesWater Quality Engineering and Wastewater TreatmentNayelli Vargas AntúnezNo ratings yet
- Florrea MaxTungsten Solution Success Case 240115Document4 pagesFlorrea MaxTungsten Solution Success Case 240115minhthienbkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2019Kristina FilipovićNo ratings yet
- Silicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Document7 pagesSilicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Deiby AraujoNo ratings yet
- Descripción General Del Material para Bombas Sumergibles EléctricasDocument13 pagesDescripción General Del Material para Bombas Sumergibles EléctricasCeleste ZapataNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Battery Material CharacterizationDocument2 pagesDatasheet Battery Material CharacterizationerNo ratings yet
- 6 Chemical EquilibriumDocument22 pages6 Chemical EquilibriumJoseph KfouryNo ratings yet
- Usp-Nf - 661.1 - Materiales Plásticos de Construcción PDFDocument32 pagesUsp-Nf - 661.1 - Materiales Plásticos de Construcción PDFEliza LosadaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument11 pagesFunctional GroupsAvinejNo ratings yet
- TitationDocument2 pagesTitationapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument13 pagesChapter 10 - Intermolecular ForcesCyrie sheene bilocuraNo ratings yet
- 3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsDocument4 pages3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsbackseeNo ratings yet
- Gengard Gn8020 Pfs SuezDocument2 pagesGengard Gn8020 Pfs SuezMuhammad Abdurrokhim ANo ratings yet
- IUPACDocument2 pagesIUPACAnubrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Aleksandrov - 2010 - Skarn-Greisen Deposits of The Lost River and Mount Ear Ore Field, Seward Peninsula, Alaska, UnitedDocument17 pagesAleksandrov - 2010 - Skarn-Greisen Deposits of The Lost River and Mount Ear Ore Field, Seward Peninsula, Alaska, UnitedDinarte JrNo ratings yet
- 11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsDocument44 pages11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsmohammedNo ratings yet
- ANSULITE® ARC 3% or 6% AR-AFFF PDFDocument2 pagesANSULITE® ARC 3% or 6% AR-AFFF PDFRuliNo ratings yet
- fcc10 IndexDocument27 pagesfcc10 IndexNaisadh PatelNo ratings yet
- BYK-300 BYK-301 BYK-302 BYK-331 BYK-332 BYK-335: Silicone Surface Additives With Medium Reduction of Surface TensionDocument4 pagesBYK-300 BYK-301 BYK-302 BYK-331 BYK-332 BYK-335: Silicone Surface Additives With Medium Reduction of Surface TensionSelim AkarNo ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue & MembraneDocument24 pagesCell, Tissue & MembranehumaNo ratings yet
- Pex 10 01Document5 pagesPex 10 01Gonzalo RojasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Results and Discussion Report: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator MethodDocument3 pagesExperiment 7 Results and Discussion Report: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator MethodNathalie DagmangNo ratings yet
Chlorination of Methane
Chlorination of Methane
Uploaded by
Carlo Joseph MoskitoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chlorination of Methane
Chlorination of Methane
Uploaded by
Carlo Joseph MoskitoCopyright:
Available Formats
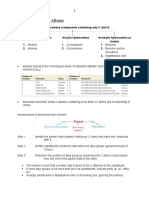
CHLORINATION OF METHANE
Pertinent Reactions:
CH 4 +Cl 2 ⃗Δ CH3 Cl +HCl⃗
Cl2 and Δ CH 2Cl 2+ HCl⃗
Cl 2 and Δ CHCl 3 +HCl⃗
Cl 2 and Δ CCl 4 +HCl
The Free Radical Chain Reaction:
1. The initiating step produces reactive intermediates.
2. The propagating steps, where the reactive intermediate + stable molecule ® another
reactive intermediate.
3. The terminating steps, where the reactive intermediates are destroyed and the reaction
stops.
A chlorine molecule (Cl2) is split by light energy into 2 chlorine radicals.
+
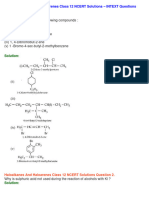
The propagation steps that produce all the products formed in the chlorination of methane.
Propagation steps produce radicals.
+ The •CH3 radical is formed.
+ The •CH2Cl radical is formed.
+ The chlorine radical can react with just
about any stable molecule.
+ The •CHCl2 radical is formed.
+ Another chlorine radical is formed.
+ The •CCl3 radical is formed.
+
The fully chlorinated product CCl4 is finally
produced as another chlorine radical is
formed.
Termination steps in the chlorination of methane.
The free radicals are consumed while no new
free radicals are produced.
You might also like
- Free Radical Chlorination by Sulfuryl ChlorideDocument8 pagesFree Radical Chlorination by Sulfuryl Chloridevibhor_26janNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Free Radical SubstitutionDocument6 pagesMechanism of Free Radical SubstitutionleomNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of AlkanesDocument20 pagesThe Chemistry of AlkaneshussainNo ratings yet
- Free Radical SubstitutionDocument35 pagesFree Radical SubstitutionkitazzaedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Alkanes Alkenes PDFDocument56 pages2021 Alkanes Alkenes PDFEudora LauNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Document20 pagesAlkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of RadicalsDocument54 pagesCharacteristics of RadicalsdesyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Chemical Reactions of AlkanesDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Chemical Reactions of AlkanesDavidNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: F.N.D-B Form 6 Upper Unit 2 Module 1 Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesAlkanes: F.N.D-B Form 6 Upper Unit 2 Module 1 Chemistry NotesStudent1010No ratings yet
- Free Radical ChlorinationDocument1 pageFree Radical ChlorinationJohn Yves LubricoNo ratings yet
- Functional GR Analysis - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument9 pagesFunctional GR Analysis - Alkanes and AlkenesMakeedaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Document6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Jojo LeongNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 AliphaticDocument17 pagesTOPIC 1 AliphaticFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Free Radical SubstitutionDocument2 pagesFree Radical SubstitutionDaNo ratings yet
- Halogenacion de AlcanosDocument34 pagesHalogenacion de AlcanosAlejandra EcheverriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: 6 14 (L) 2 (L) 6 13 (L) (G)Document16 pagesAlkanes: 6 14 (L) 2 (L) 6 13 (L) (G)Lyana TaylorNo ratings yet
- P4 Radical ReactionsDocument51 pagesP4 Radical ReactionsShirl Angelee OcampoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 - SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz 5 - Solutionm3ghnaadNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CH 15Document22 pagesLec 1 CH 15Primandari UtamiNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Alkane TutorialDocument6 pagesTopic 10 Alkane TutorialTimNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument39 pagesUnit IGoopNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Explain Reactions of Methane/Ethane With Chlorine and Bromine Via Free Radical MechanismsDocument4 pages10.2 Explain Reactions of Methane/Ethane With Chlorine and Bromine Via Free Radical MechanismsYazan HammoudehNo ratings yet
- Carbocations & CarbanionDocument41 pagesCarbocations & CarbanionMuttu M100% (1)
- CHAPTER: Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers: LT Bipc Revision Prog Practice Assignment Subject: ChemistryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER: Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers: LT Bipc Revision Prog Practice Assignment Subject: ChemistryAssishNo ratings yet
- Notes Alkanes +alkenesDocument44 pagesNotes Alkanes +alkenesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 2Document14 pagesAlkanes 2Hasen umerNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent ProblemsDocument6 pagesLimiting Reagent ProblemsFarisDonNo ratings yet
- Chlorine: This Powerpoint Was Brought To You by The The Atomic Symbol CLDocument17 pagesChlorine: This Powerpoint Was Brought To You by The The Atomic Symbol CLruchita-tandon-9182No ratings yet
- Alkanes KODocument1 pageAlkanes KOabhishektheoneNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CH 15Document22 pagesLec 1 CH 15billNo ratings yet
- 16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandDocument29 pages16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandHayden Chappelear-RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Free Radicals: OO ONO Molecular Oxygen Nitrogen Dioxide NO Nitrogen MonoxideDocument11 pagesFree Radicals: OO ONO Molecular Oxygen Nitrogen Dioxide NO Nitrogen MonoxideAbdullahi abdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties Properties of AlkanesDocument23 pagesChemical Properties Properties of AlkanesLinatri Purwati Latifah SupriatnaNo ratings yet
- Radical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product FormationDocument2 pagesRadical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product Formationmegamon asabeNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDocument30 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanNo ratings yet
- Radical SederhanaDocument9 pagesRadical SederhanaNurillahi Febria LeswanaNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis and HalogenationDocument2 pagesPyrolysis and Halogenationarpitavashist11No ratings yet
- 16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine DemandDocument29 pages16 - Residual Chlorine and Chlorine Demandahmedmagdi2009No ratings yet
- Bailey Alkanes PowerpointDocument31 pagesBailey Alkanes PowerpointBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FGs and AlkanesDocument28 pagesIntroduction To FGs and AlkanesAbdullah AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesDocument6 pagesChapter 22 - Alkanes and AlkenesJERVINLIM100% (1)
- CHLOR ALKALI PROCESSES PresentationDocument20 pagesCHLOR ALKALI PROCESSES PresentationNAMRATA BHALERAO50% (2)
- Organic Chemistry,: Radical ReactionsDocument54 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Radical ReactionsNurul RamadanahNo ratings yet
- 208 Chlorine: Thermochemical PropertiesDocument5 pages208 Chlorine: Thermochemical PropertiesAHMEDNo ratings yet
- 204 Chlorine and ChloratesDocument2 pages204 Chlorine and ChloratesM DiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 ADocument16 pagesWeek 2 AsehunNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsDocument12 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsAgung Ratana Jayo Silim IPH StudentNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13Document23 pages11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13Deevanshi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument187 pagesHydrocarbon Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7Document61 pagesAlkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (4)
- Draw Out Some Suitable Structures Which Fit The Molecular Formula C HDocument4 pagesDraw Out Some Suitable Structures Which Fit The Molecular Formula C HSean s ChipangaNo ratings yet
- Free Radical PolymerizationDocument11 pagesFree Radical PolymerizationNaveed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Residual Chlorine Lab ManualDocument23 pagesResidual Chlorine Lab Manualali100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT SolutionsDocument32 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT Solutionschithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument54 pagesAlkyl HalideNelvianaNo ratings yet
- Cell Exam QuestionsDocument52 pagesCell Exam QuestionsNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Dwells God AquinoDocument16 pagesDwells God AquinoCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Grade 9 Science K-12Document161 pagesGrade 9 Science K-12Carlo Joseph Moskito93% (114)
- Amen Dumlao (AN2)Document2 pagesAmen Dumlao (AN2)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Anima Christi ArboledaDocument8 pagesAnima Christi ArboledaCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Come To The TableDocument7 pagesCome To The TableCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Hangad PrimerDocument2 pagesHangad PrimerCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Exer8 Handout (CJMM)Document6 pagesExer8 Handout (CJMM)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Amare Et Servire: Fr. Manoling Francisco, SJDocument3 pagesAmare Et Servire: Fr. Manoling Francisco, SJCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- BeatitudesDocument13 pagesBeatitudesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Chem 44.1 Special SynthesisDocument86 pagesChem 44.1 Special SynthesisCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (2)
- Youth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerDocument12 pagesYouth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Circles 2Document3 pagesCircles 2Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Solutions (Chemistry)Document11 pagesSolutions (Chemistry)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Youth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerDocument12 pagesYouth Ministry Awareness Week PrayerCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Hydrocarbons - SummaryDocument15 pagesReactions of Hydrocarbons - SummaryCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Prayer For The Year of The YouthDocument14 pagesPrayer For The Year of The YouthCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (3)
- Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesColligative PropertiesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument12 pagesCirclesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument3 pagesWriting and Naming Chemical FormulasCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument10 pagesQualitative AnalysisCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Arithmetic of SolutionsDocument2 pagesChemical Arithmetic of SolutionsCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of The Acidity of Soft DrinksDocument64 pagesQuantitative Determination of The Acidity of Soft DrinksCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Certificate For Fun RunDocument7 pagesCertificate For Fun RunCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Batteries For DummiesDocument116 pagesBatteries For Dummiesjoseph katongoNo ratings yet
- MMPNov2017 170 1773 PDFDocument9 pagesMMPNov2017 170 1773 PDFMuh.naufal shidqiNo ratings yet
- 2025 Specimen Paper 2Document16 pages2025 Specimen Paper 2Ngô PhongNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry PPT-2Document29 pagesGeneral Chemistry PPT-2Temesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- Polyvinyl Alcohol Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites 1St Edition Visakh P M All ChapterDocument62 pagesPolyvinyl Alcohol Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites 1St Edition Visakh P M All Chaptermark.clark755100% (10)
- Nickel ElectroplatingDocument28 pagesNickel ElectroplatingRahul Pandey100% (2)
- Hypochlorous AcidDocument25 pagesHypochlorous AcidDirector Research100% (2)
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument13 pagesInorganic Chemistrybhargavthegreat123No ratings yet
- Water Quality Engineering and Wastewater TreatmentDocument320 pagesWater Quality Engineering and Wastewater TreatmentNayelli Vargas AntúnezNo ratings yet
- Florrea MaxTungsten Solution Success Case 240115Document4 pagesFlorrea MaxTungsten Solution Success Case 240115minhthienbkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2019Kristina FilipovićNo ratings yet
- Silicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Document7 pagesSilicone Resin Binders: Silsan® WR1750 WR1800 HSB Hsb-Gs WRF MSR 6575Deiby AraujoNo ratings yet
- Descripción General Del Material para Bombas Sumergibles EléctricasDocument13 pagesDescripción General Del Material para Bombas Sumergibles EléctricasCeleste ZapataNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Battery Material CharacterizationDocument2 pagesDatasheet Battery Material CharacterizationerNo ratings yet
- 6 Chemical EquilibriumDocument22 pages6 Chemical EquilibriumJoseph KfouryNo ratings yet
- Usp-Nf - 661.1 - Materiales Plásticos de Construcción PDFDocument32 pagesUsp-Nf - 661.1 - Materiales Plásticos de Construcción PDFEliza LosadaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument11 pagesFunctional GroupsAvinejNo ratings yet
- TitationDocument2 pagesTitationapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument13 pagesChapter 10 - Intermolecular ForcesCyrie sheene bilocuraNo ratings yet
- 3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsDocument4 pages3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsbackseeNo ratings yet
- Gengard Gn8020 Pfs SuezDocument2 pagesGengard Gn8020 Pfs SuezMuhammad Abdurrokhim ANo ratings yet
- IUPACDocument2 pagesIUPACAnubrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Aleksandrov - 2010 - Skarn-Greisen Deposits of The Lost River and Mount Ear Ore Field, Seward Peninsula, Alaska, UnitedDocument17 pagesAleksandrov - 2010 - Skarn-Greisen Deposits of The Lost River and Mount Ear Ore Field, Seward Peninsula, Alaska, UnitedDinarte JrNo ratings yet
- 11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsDocument44 pages11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsmohammedNo ratings yet
- ANSULITE® ARC 3% or 6% AR-AFFF PDFDocument2 pagesANSULITE® ARC 3% or 6% AR-AFFF PDFRuliNo ratings yet
- fcc10 IndexDocument27 pagesfcc10 IndexNaisadh PatelNo ratings yet
- BYK-300 BYK-301 BYK-302 BYK-331 BYK-332 BYK-335: Silicone Surface Additives With Medium Reduction of Surface TensionDocument4 pagesBYK-300 BYK-301 BYK-302 BYK-331 BYK-332 BYK-335: Silicone Surface Additives With Medium Reduction of Surface TensionSelim AkarNo ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue & MembraneDocument24 pagesCell, Tissue & MembranehumaNo ratings yet
- Pex 10 01Document5 pagesPex 10 01Gonzalo RojasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Results and Discussion Report: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator MethodDocument3 pagesExperiment 7 Results and Discussion Report: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator MethodNathalie DagmangNo ratings yet