Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
885 viewsGastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Gastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Uploaded by
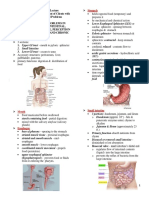
Katie JusayPredisposing factors for gastroenteritis include an infant's immune system not being exposed to pathogens to produce antibodies and immunocompromised patients from past illnesses. Precipitating factors include lack of clean water, crowding, poor hygiene, poor sanitation, and nutritional deficiency. Gastroenteritis is caused by inflammation of the stomach and small intestine lining from pathogens like rotavirus, salmonella, giardia, and shigella entering through the mouth and infecting epithelial cells. This damages cells and causes inflammation, increased gastric acid secretion, reflux, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation LetterBalusupati Praveen Babu72% (25)
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDocument19 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Case Studykirstenpapera100% (54)
- NCM 116 - Git (Module 5)Document15 pagesNCM 116 - Git (Module 5)Meryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Sic 2Document4 pagesSic 2Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Oral Fecal Route Diseases Oral Fecal Route Diseases: Afroz Lakhani RN, BSCNDocument74 pagesOral Fecal Route Diseases Oral Fecal Route Diseases: Afroz Lakhani RN, BSCNafrozlakhaniNo ratings yet
- DIARHEA IN CHILDRENDocument33 pagesDIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument9 pagesA Case Study of AmoebiasishsiriaNo ratings yet
- 4 Digestive Disorders of DogsDocument72 pages4 Digestive Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms Gi CompiledDocument6 pagesGlossary of Terms Gi CompiledANA DelafuenteNo ratings yet
- Acute Diarrhoea and VomitingDocument43 pagesAcute Diarrhoea and VomitingAdriana AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroentertisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroentertisHassan Bj MarabongNo ratings yet
- Problem 5 Git Aldi FDocument158 pagesProblem 5 Git Aldi Faldi firdausNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract Infections: General ConsiderationsDocument17 pagesGastrointestinal Tract Infections: General ConsiderationsDarpan GelalNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea NCP Pedia WardDocument4 pagesDiarrhea NCP Pedia WardKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in Children - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument10 pagesDiarrhea in Children - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional Editionimadeandi saputraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEYum CNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Document1 pagePathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Carl John ManaloNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument53 pagesAnimal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionAfifaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- (GI) A Child With DiarrheaDocument59 pages(GI) A Child With DiarrheaJo casNo ratings yet
- G Lamblia: (Open Table in A New Window)Document6 pagesG Lamblia: (Open Table in A New Window)Ahmed Ben BellaNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocument1 pagePathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Dirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningDocument17 pagesDirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningAbcdefg HijklNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Prepared By: Joycemay G. AndayaDocument14 pagesTyphoid Fever: Prepared By: Joycemay G. AndayaEmma AndayaNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument16 pagesAMOEBIASISAngeline TaghapNo ratings yet
- System Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseDocument6 pagesSystem Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseFharida AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document26 pagesModule 6xtnreyesNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectDocument11 pages3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectThaiz P.SNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Digestive System HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Digestive System HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Bowel and Urine EliminationDocument25 pagesBowel and Urine Elimination3amabelle arevalo100% (1)
- Pathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Document3 pagesPathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Fuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- THE Disgestive System: by Second GroupDocument17 pagesTHE Disgestive System: by Second GroupAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- PERITONITISDocument4 pagesPERITONITISAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- 08 Infectious DiarrheaDocument5 pages08 Infectious DiarrheaVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of GastroenteritisNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDrugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- CD TransDocument85 pagesCD TransDhang Cerilo AparenteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumDocument5 pagesPathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Notes - Digestive SystemDocument68 pagesUnit 9 Notes - Digestive Systemshrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- Digestive System GlossaryDocument3 pagesDigestive System GlossaryHASSAM KHANNo ratings yet
- Waterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenDocument6 pagesWaterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenMichael SamwelNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Prelim Week 1Document15 pagesNCM116 Prelim Week 1Loungayvan BatuyogNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesVisibleBody Digestive SystemcascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Digestion and The Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestion and The Digestive SystemIzelwyn DaguioNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Alimentary TractDocument25 pagesDisorders of The Alimentary Tract수안현100% (1)
- MIDTERMSDocument24 pagesMIDTERMSCherish Marie HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaDocument1 pagePeritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaInstituto Mexicano Seguro SocialNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition - 2023 2024Document49 pagesAnimal Nutrition - 2023 2024TohmNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea 130402200935 Phpapp02Document23 pagesDiarrhea 130402200935 Phpapp02jihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 16 - Digestive SystemmargaretNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and Nutritional StatusDocument4 pagesDigestive System and Nutritional StatusarsyzahraNo ratings yet
- Plenary 3 Group 13Document122 pagesPlenary 3 Group 13Obet Agung 天No ratings yet
- Digestive System Lecture NotesdocxDocument11 pagesDigestive System Lecture NotesdocxAdaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client BasedrtyytyttyDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client Basedrtyytyttyangeliejoy_1109No ratings yet
- Larceña Sic Rot 7Document11 pagesLarceña Sic Rot 7noemilauNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption For Depaul Plus1Document1 pageDigestion and Absorption For Depaul Plus1V̶a̶i̶s̶h̶n̶a̶v̶No ratings yet
- Outline and Learning Outcomes: 22.1 The Gastrointestinal Tract and Its DefensesDocument47 pagesOutline and Learning Outcomes: 22.1 The Gastrointestinal Tract and Its DefenseslilaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Digestive SystemDocument46 pagesUnit 3. Digestive SystemNURIA VAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2Document20 pagesNursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2wyneNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- Technique of Preserving A Dead BodyDocument4 pagesTechnique of Preserving A Dead BodyKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumDocument10 pagesThe Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- Badminton I: A New Game, But Unfortunately No Copy Has SurvivedDocument13 pagesBadminton I: A New Game, But Unfortunately No Copy Has SurvivedKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- Frog Ncert Based QuestionsDocument7 pagesFrog Ncert Based Questionssrivaishna123100% (1)
- DLL - Mapeh-Health 6 - Q3 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - Mapeh-Health 6 - Q3 - W2Eihcra SubacNo ratings yet
- BiofarDocument14 pagesBiofarAl Pharux Ox-CygenNo ratings yet
- Heal Your Gut ChallengeDocument17 pagesHeal Your Gut ChallengeJeesuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3 - Digestive Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Paralytic Ileus Complication of Acute Appendicitis Dudley, M.DDocument6 pagesParalytic Ileus Complication of Acute Appendicitis Dudley, M.Dandre nicholasNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument3 pagesHistologyUsama KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Git Physiology SikomaDocument214 pagesGit Physiology SikomaChikonde mwapeNo ratings yet
- Alternative Healing DictionaryDocument50 pagesAlternative Healing DictionaryDr. Jarrel100% (2)
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Food BioscienceDocument39 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Food BiosciencerenNo ratings yet
- Giardia LambliaDocument19 pagesGiardia LambliaAjishasughiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Chakra ChartDocument1 pageDetailed Chakra ChartJerricaBentonNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument13 pagesDLPjonnlin baldonado100% (2)
- Gastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemDocument7 pagesGastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Instussusception Group4Document18 pagesCase 3 Instussusception Group4younggirldavidNo ratings yet
- Systems of The Body (Digestive)Document3 pagesSystems of The Body (Digestive)KryztalGhail LlanoraNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarDocument5 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarJane MinNo ratings yet
- Ferruzzi 2007Document12 pagesFerruzzi 2007Oli PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Final Examination With Answers and RationalesDocument114 pagesFinal Examination With Answers and RationalesMonicaNo ratings yet
- ILEOSTOMYDocument11 pagesILEOSTOMYShine Khay100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesDigestive SystemDainalissa SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Female RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFDocument129 pagesFemale RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFsusdoctor100% (1)
- Nutrition SyllabusDocument14 pagesNutrition Syllabuscrissy29No ratings yet
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocument18 pages72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Promising TherapiesDocument30 pagesHHS Public Access: Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Promising TherapiesalexNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsDocument4 pagesFrog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsAlma LibangNo ratings yet
- Biol 1322 Exam 3Document19 pagesBiol 1322 Exam 3Tonya OliverNo ratings yet
Gastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Gastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Uploaded by
Katie Jusay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
885 views1 pagePredisposing factors for gastroenteritis include an infant's immune system not being exposed to pathogens to produce antibodies and immunocompromised patients from past illnesses. Precipitating factors include lack of clean water, crowding, poor hygiene, poor sanitation, and nutritional deficiency. Gastroenteritis is caused by inflammation of the stomach and small intestine lining from pathogens like rotavirus, salmonella, giardia, and shigella entering through the mouth and infecting epithelial cells. This damages cells and causes inflammation, increased gastric acid secretion, reflux, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPredisposing factors for gastroenteritis include an infant's immune system not being exposed to pathogens to produce antibodies and immunocompromised patients from past illnesses. Precipitating factors include lack of clean water, crowding, poor hygiene, poor sanitation, and nutritional deficiency. Gastroenteritis is caused by inflammation of the stomach and small intestine lining from pathogens like rotavirus, salmonella, giardia, and shigella entering through the mouth and infecting epithelial cells. This damages cells and causes inflammation, increased gastric acid secretion, reflux, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
885 views1 pageGastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Gastroenteritis - Pathology & Physiology
Uploaded by
Katie JusayPredisposing factors for gastroenteritis include an infant's immune system not being exposed to pathogens to produce antibodies and immunocompromised patients from past illnesses. Precipitating factors include lack of clean water, crowding, poor hygiene, poor sanitation, and nutritional deficiency. Gastroenteritis is caused by inflammation of the stomach and small intestine lining from pathogens like rotavirus, salmonella, giardia, and shigella entering through the mouth and infecting epithelial cells. This damages cells and causes inflammation, increased gastric acid secretion, reflux, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
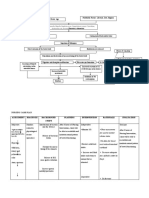
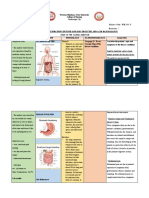
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Predisposing Precipitating
factors factors
Immune system of infants • Lack of clean water
Pathogens causing
not exposed to many
gastroenteritis
pathogens to produce • Crowning
(viruses, bacteria,
antibodies.
parasites) • Poor hygiene/poor
Immunocompromised
patient sanitation
• Rotavirus (viral) 3-24
(Cough and cold, and • Nutritional deficiency
mos.
fever) Past illnesses
• Salmonella(toddlers)
• Giardia shigella
GASTROENTERITIS
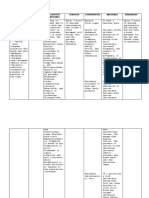
• Inflammation of mucosa lining of the stomach and
the small intestine
• Caused by abdominal intestinal water and
Pathogens enters the
digestive system through
the mouth
Larynx Nasophary Pass through the
nx oropharynx and
laryngopharynx
Trachea
Esophagu
s
Pathogen penetrates the mucus, stomach cell
Bronchi
Stoma are damaged, inflammation occurs due to
ch inflammatory cells
Lung Small (First line defense of the
inflammation Intestine stomach)
Secretion of gastric acid
Cough and cold Pathogen infects and destroys increases to eliminate
the epithelial cell by inflaming
the intestinal mucosal lining of Reflux
S.I
Food from the stomach with gastric
acid goes back passing the
Intestinal mucosal lining to
esophagus
secrete large amounts of
fluid
Causes esophagus to initiate
Therefore increases the anti-peristaltic movement
peristaltic movement of
food reducing the time that is
available for absorbing water Results to
of the large intestine VOMITING
specifically the colon to make
a more or less solid stool
Rectum
( where waste products are
stored for bowel
movement)
Generally empty, but when Dehydration and
feces are force into by its mass electrolyte
movement
imbalance
Diarrh
ea
You might also like
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation LetterBalusupati Praveen Babu72% (25)
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDocument19 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Case Studykirstenpapera100% (54)
- NCM 116 - Git (Module 5)Document15 pagesNCM 116 - Git (Module 5)Meryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Sic 2Document4 pagesSic 2Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Oral Fecal Route Diseases Oral Fecal Route Diseases: Afroz Lakhani RN, BSCNDocument74 pagesOral Fecal Route Diseases Oral Fecal Route Diseases: Afroz Lakhani RN, BSCNafrozlakhaniNo ratings yet
- DIARHEA IN CHILDRENDocument33 pagesDIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument9 pagesA Case Study of AmoebiasishsiriaNo ratings yet
- 4 Digestive Disorders of DogsDocument72 pages4 Digestive Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms Gi CompiledDocument6 pagesGlossary of Terms Gi CompiledANA DelafuenteNo ratings yet
- Acute Diarrhoea and VomitingDocument43 pagesAcute Diarrhoea and VomitingAdriana AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroentertisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroentertisHassan Bj MarabongNo ratings yet
- Problem 5 Git Aldi FDocument158 pagesProblem 5 Git Aldi Faldi firdausNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract Infections: General ConsiderationsDocument17 pagesGastrointestinal Tract Infections: General ConsiderationsDarpan GelalNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea NCP Pedia WardDocument4 pagesDiarrhea NCP Pedia WardKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in Children - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument10 pagesDiarrhea in Children - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional Editionimadeandi saputraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEYum CNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Document1 pagePathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Carl John ManaloNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument53 pagesAnimal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionAfifaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- (GI) A Child With DiarrheaDocument59 pages(GI) A Child With DiarrheaJo casNo ratings yet
- G Lamblia: (Open Table in A New Window)Document6 pagesG Lamblia: (Open Table in A New Window)Ahmed Ben BellaNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocument1 pagePathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Dirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningDocument17 pagesDirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningAbcdefg HijklNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Prepared By: Joycemay G. AndayaDocument14 pagesTyphoid Fever: Prepared By: Joycemay G. AndayaEmma AndayaNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument16 pagesAMOEBIASISAngeline TaghapNo ratings yet
- System Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseDocument6 pagesSystem Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseFharida AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document26 pagesModule 6xtnreyesNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectDocument11 pages3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectThaiz P.SNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Digestive System HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Digestive System HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Bowel and Urine EliminationDocument25 pagesBowel and Urine Elimination3amabelle arevalo100% (1)
- Pathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Document3 pagesPathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Fuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- THE Disgestive System: by Second GroupDocument17 pagesTHE Disgestive System: by Second GroupAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- PERITONITISDocument4 pagesPERITONITISAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- 08 Infectious DiarrheaDocument5 pages08 Infectious DiarrheaVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of GastroenteritisNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDrugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- CD TransDocument85 pagesCD TransDhang Cerilo AparenteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumDocument5 pagesPathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Notes - Digestive SystemDocument68 pagesUnit 9 Notes - Digestive Systemshrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- Digestive System GlossaryDocument3 pagesDigestive System GlossaryHASSAM KHANNo ratings yet
- Waterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenDocument6 pagesWaterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenMichael SamwelNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Prelim Week 1Document15 pagesNCM116 Prelim Week 1Loungayvan BatuyogNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesVisibleBody Digestive SystemcascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Digestion and The Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestion and The Digestive SystemIzelwyn DaguioNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Alimentary TractDocument25 pagesDisorders of The Alimentary Tract수안현100% (1)
- MIDTERMSDocument24 pagesMIDTERMSCherish Marie HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaDocument1 pagePeritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaInstituto Mexicano Seguro SocialNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition - 2023 2024Document49 pagesAnimal Nutrition - 2023 2024TohmNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea 130402200935 Phpapp02Document23 pagesDiarrhea 130402200935 Phpapp02jihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 16 - Digestive SystemmargaretNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and Nutritional StatusDocument4 pagesDigestive System and Nutritional StatusarsyzahraNo ratings yet
- Plenary 3 Group 13Document122 pagesPlenary 3 Group 13Obet Agung 天No ratings yet
- Digestive System Lecture NotesdocxDocument11 pagesDigestive System Lecture NotesdocxAdaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client BasedrtyytyttyDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client Basedrtyytyttyangeliejoy_1109No ratings yet
- Larceña Sic Rot 7Document11 pagesLarceña Sic Rot 7noemilauNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption For Depaul Plus1Document1 pageDigestion and Absorption For Depaul Plus1V̶a̶i̶s̶h̶n̶a̶v̶No ratings yet
- Outline and Learning Outcomes: 22.1 The Gastrointestinal Tract and Its DefensesDocument47 pagesOutline and Learning Outcomes: 22.1 The Gastrointestinal Tract and Its DefenseslilaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Digestive SystemDocument46 pagesUnit 3. Digestive SystemNURIA VAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2Document20 pagesNursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2wyneNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- Technique of Preserving A Dead BodyDocument4 pagesTechnique of Preserving A Dead BodyKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumDocument10 pagesThe Greatest Medical Discoveries of The MillenniumKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- Badminton I: A New Game, But Unfortunately No Copy Has SurvivedDocument13 pagesBadminton I: A New Game, But Unfortunately No Copy Has SurvivedKatie JusayNo ratings yet
- Frog Ncert Based QuestionsDocument7 pagesFrog Ncert Based Questionssrivaishna123100% (1)
- DLL - Mapeh-Health 6 - Q3 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - Mapeh-Health 6 - Q3 - W2Eihcra SubacNo ratings yet
- BiofarDocument14 pagesBiofarAl Pharux Ox-CygenNo ratings yet
- Heal Your Gut ChallengeDocument17 pagesHeal Your Gut ChallengeJeesuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3 - Digestive Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Paralytic Ileus Complication of Acute Appendicitis Dudley, M.DDocument6 pagesParalytic Ileus Complication of Acute Appendicitis Dudley, M.Dandre nicholasNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument3 pagesHistologyUsama KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Git Physiology SikomaDocument214 pagesGit Physiology SikomaChikonde mwapeNo ratings yet
- Alternative Healing DictionaryDocument50 pagesAlternative Healing DictionaryDr. Jarrel100% (2)
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Food BioscienceDocument39 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Food BiosciencerenNo ratings yet
- Giardia LambliaDocument19 pagesGiardia LambliaAjishasughiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Chakra ChartDocument1 pageDetailed Chakra ChartJerricaBentonNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument13 pagesDLPjonnlin baldonado100% (2)
- Gastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemDocument7 pagesGastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Instussusception Group4Document18 pagesCase 3 Instussusception Group4younggirldavidNo ratings yet
- Systems of The Body (Digestive)Document3 pagesSystems of The Body (Digestive)KryztalGhail LlanoraNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarDocument5 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarJane MinNo ratings yet
- Ferruzzi 2007Document12 pagesFerruzzi 2007Oli PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Final Examination With Answers and RationalesDocument114 pagesFinal Examination With Answers and RationalesMonicaNo ratings yet
- ILEOSTOMYDocument11 pagesILEOSTOMYShine Khay100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesDigestive SystemDainalissa SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Female RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFDocument129 pagesFemale RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFsusdoctor100% (1)
- Nutrition SyllabusDocument14 pagesNutrition Syllabuscrissy29No ratings yet
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocument18 pages72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Promising TherapiesDocument30 pagesHHS Public Access: Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Promising TherapiesalexNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsDocument4 pagesFrog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsAlma LibangNo ratings yet
- Biol 1322 Exam 3Document19 pagesBiol 1322 Exam 3Tonya OliverNo ratings yet